Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P2451 - Impact of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Comorbidities on Immune-Mediated Diarrhea and Colitis Severity and Outcomes
- CN
Cristina Natha, MD
McGovern Medical School at UTHealth
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
1McGovern Medical School at UTHealth, Houston, TX; 2University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 3MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 4University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5University of Texas Health Sciences Center in Houston, Houston, TX; 6University of Texas at Houston, Houston, TX; 7Baylor College of Medicine / MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 8Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX; 9McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, Houston, TX; 10University of Texas Health, McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX
Introduction: Chronic low-grade inflammation, insulin resistance, and atherosclerosis are known to alter gut microbiome composition by disrupting the intestinal barrier, impairing glucose metabolism, and reducing gut perfusion. Additionally, long-term use of medications for coronary artery disease (CAD), type 2 diabetes mellitus, heart failure (HF), and hypertension may also influence gut microbial balance. Given the established association between dysbiosis and immune-mediated diarrhea and colitis (IMDC) in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors, this study investigates the impact of pre-existing cardiovascular and metabolic conditions on the clinical presentation and severity of IMDC.
Methods:
This retrospective, single-center study included patients diagnosed with IMDC between 2015 to 2025. Statistical analyses were performed using chi-square and binary logistic regression models with SPSS 24.
Results: Among 1,128 patients, 58.6% were male and 89.8% white. Serum lipid profile, average plasma glucose, and blood pressure were not significantly associated with IMDC outcomes. However, diagnosis of HF (9.5% vs 5.7%, p=0.025) and CAD (20.6% vs 14.9%, p=0.017) were more common in patients with colitis CTCAE grade < 2. Patients with CAD were less frequently treated with corticosteroids (66.8% vs 74.4%, p=0.027) or selective immunosuppressive therapy (SIT) (37.1% vs 44.6%, p=0.050). No significant associations were observed between cardiovascular risk factors and diarrhea severity. Univariate analysis revealed that HF (OR: 0.6, CI: 0.3–0.9, p=0.026) and CAD (OR: 0.6, CI: 0.5–0.9, p=0.017) were associated with milder colitis. Despite this, all-cause mortality was significantly higher in patients with HF (72.5% vs 52.2%, p< 0.0001) and CAD (60% vs 52.4%, p=0.049).
Discussion:
This is the first study to evaluate the influence of cardiovascular and metabolic conditions on IMDC severity and outcomes. While HF and CAD were associated with milder colitis, these patients had higher all-cause mortality. Findings suggest chronic disease or its treatment may modulate immune-related toxicity, potentially through gut microbiome or systemic pathways. Lower use of corticosteroids/SIT may reflect therapeutic caution due to cardiovascular risk. Despite less severe gastrointestinal disease, this population remains clinically vulnerable. Further studies are needed to validate these associations and to elucidate the mechanisms by which chronic comorbidities and their management may influence IMDC outcomes.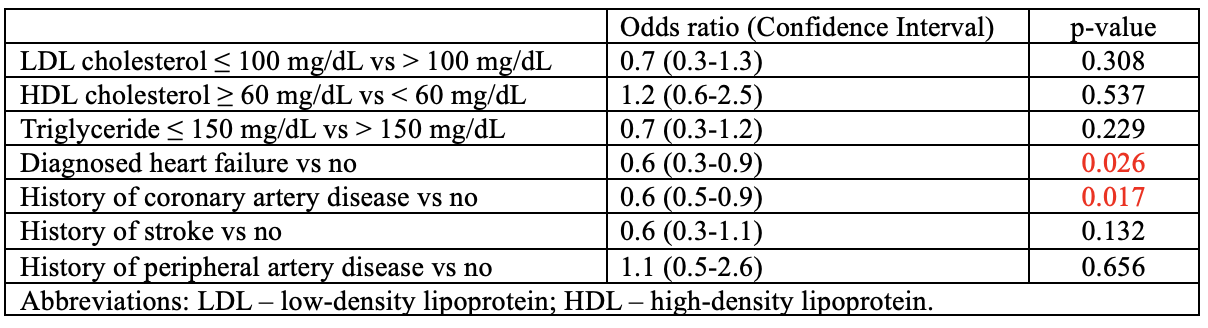
Figure: Association Between Cardiovascular and Lipid Parameters and Colitis Severity (n=1128)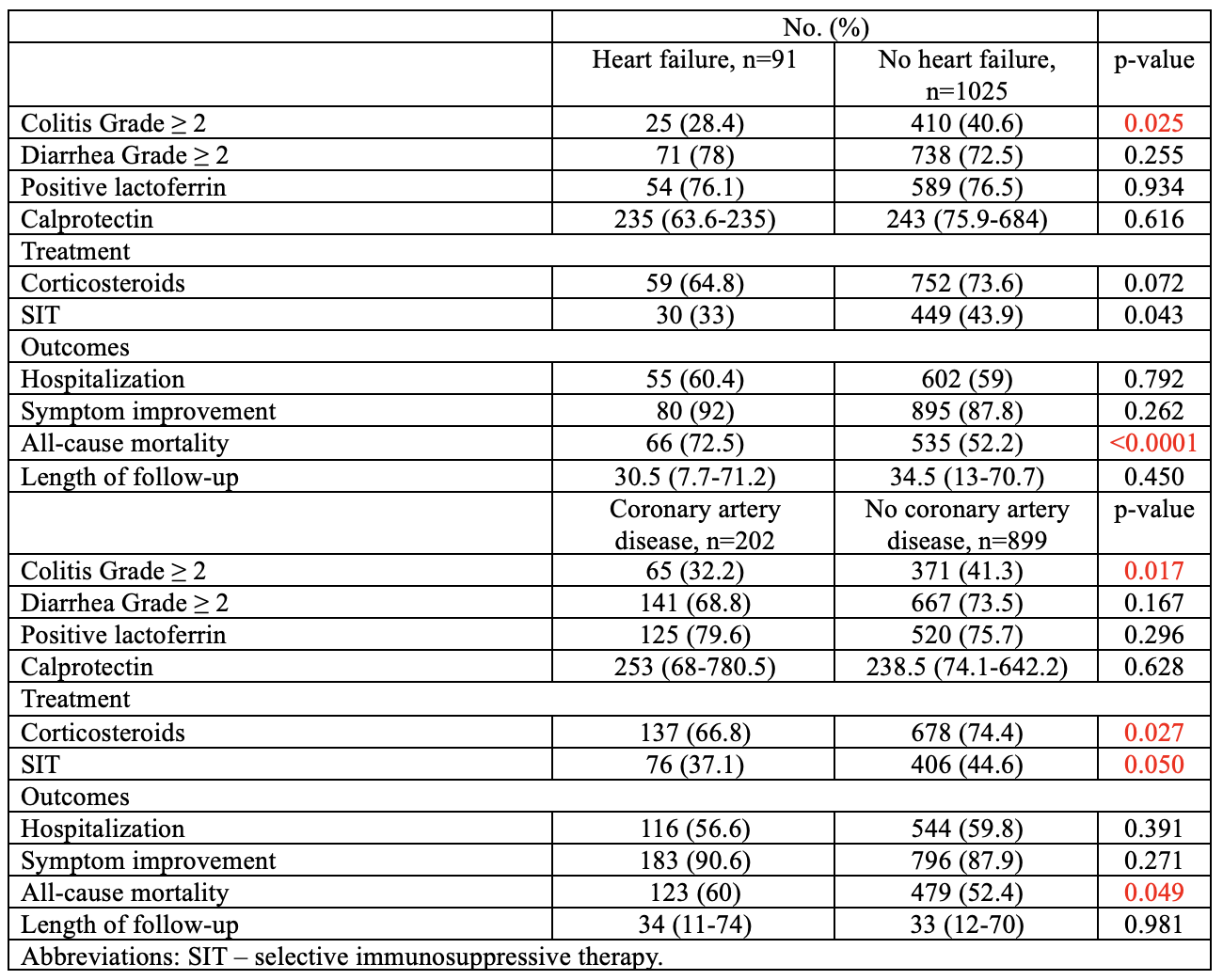
Figure: Comparison of Clinical Features, Treatment, and Outcomes in Patients With and Without Heart Failure or Coronary Artery Disease (n=1128)
Disclosures:
Cristina Natha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carolina Cruz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anirudha Chatterjee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Varun Vemulapalli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nina Quirk indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Mortan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Humberto Nieves-Jiménez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Ahuja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Irene Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacob Reitnauer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sean Ngo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jarrett Rong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tanvi Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Reema Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sharada Wali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria Julia Santos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnavathana Varatharajalu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jessemel Estrada indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yinghong Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cristina Natha, MD1, Carolina Cruz, MD2, Rohan Patel, 3, Anirudha Chatterjee, MD4, Varun Vemulapalli, MD1, Nina Quirk, MD, MS5, Rachel Mortan, MD6, Humberto R.. Nieves-Jiménez, MD7, Rohan Ahuja, MD6, Irene Lee, 8, Jacob Reitnauer, 6, Sean Ngo, BS1, Jarrett Rong, MD9, Tanvi Gupta, MD10, Reema Patel, MD4, Sharada Wali, MBBS, MPH2, Maria Julia M. N.. Santos, MD3, Krishnavathana Varatharajalu, MD3, Jessemel Estrada, MD4, Yinghong Wang, MD, PhD, MS2. P2451 - Impact of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Comorbidities on Immune-Mediated Diarrhea and Colitis Severity and Outcomes, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
