Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4592 - Development and Internal Validation of a Simplified Clinical Prediction Model for Completion Colectomy in Patients With T1N0M0 Colorectal Cancer
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Hassam Ali, MD
East Carolina Gastroenterology
Greenville, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Hassam Ali, MD1, Sarah Jahangir, MD2, Jinye Liu, DO2, Abdul Aziz Swaiti, MD3, Rami Basmaci, MD2, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Umar Hayat, MD5, Douglas G. Adler, MD, FACG6
1East Carolina Gastroenterology, Greenville, NC; 2East Carolina University Medical Center, Greenville, NC; 3East Carolina University, Greenville, NC; 4University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 5Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 6Center for Advanced Therapeutic (CATE), Centura Health, Porter Adventist Hospital, Peak Gastroenterology, Denver, CO
Introduction: Completion colectomy is variably pursued following local excision for T1 colorectal cancer (CRC), often guided by histopathologic features. We aimed to develop a simplified model using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database to predict the likelihood of completion colectomy in patients with T1N0M0 CRC on endoscopy.
Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of SEER data from 2004–2015. Adults with histologically confirmed T1N0M0 CRC and known surgical treatment status were included. The primary outcome was receipt of completion colectomy following local excision. A multivariable logistic regression model was developed using Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) to identify predictive variables, followed by construction of a simplified logistic regression model. Final predictors included primary tumor site, race, sex, and tumor grade. Model discrimination was assessed using 10-fold cross-validation and bootstrap resampling. Calibration was evaluated using the GiViTI calibration belt. A manual scoring formula was derived using coefficient values from the final model.
Results: Among 3,289 patients (55% male; 80% White), 1,399 (42.5%) underwent completion colectomy. The final model demonstrated excellent performance with a cross-validated AUC of 0.84 (95% CI: 0.81–0.85), bootstrapped AUC of 0.83 (95% CI: 0.81–0.84), and standard ROC AUC of 0.84 (95% CI: 0.82–0.85). Calibration was strong (GiViTI p = 0.85), indicating no significant deviation from ideal prediction. Using a threshold probability ≥0.60, the model achieved 73.9% sensitivity, 83.9% specificity, 77.3% positive predictive value, 81.6% negative predictive value, and 78.6% overall accuracy. The full manual scoring equation was:
logit(p) = 1.6807 0.5543 × Appendix 0.2014 × Ascending colon 0.0929 × Hepatic flexure − 0.9138 × Transverse colon − 0.9886 × Splenic flexure − 0.6383 × Descending colon − 2.8347 × Sigmoid colon − 0.3868 × Overlapping lesion − 1.8755 × Colon, NOS − 3.8004 × Rectosigmoid junction − 3.0419 × Rectum − 0.5823 × Asian or Pacific Islander − 0.1340 × Black − 1.1498 × Unknown race − 0.3480 × White − 0.1091 × Male 0.1875 × Poorly differentiated 0.3356 × Undifferentiated − 0.2220 × Unknown grade 0.0883 × Well differentiated
Discussion: We developed a simplified model that accurately predicts completion colectomy after local excision for T1N0M0 CRC. A web-based calculator is available at https://tinyurl.com/Colectomy-Calculator. External validation is needed.
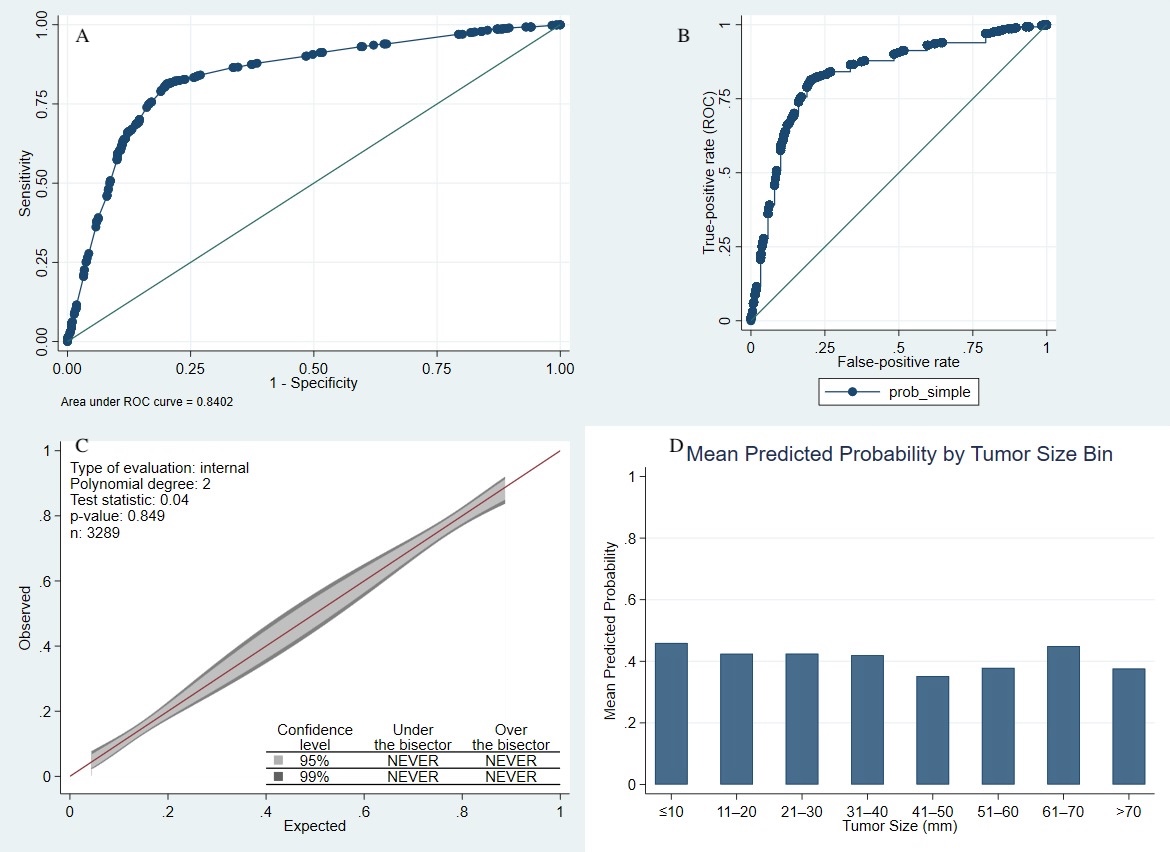
Figure: Figure 1. Discrimination (A–B), calibration (C), and predicted probabilities by tumor size (D) for the simplified model predicting completion colectomy in T1N0M0 colorectal cancer.
Disclosures:
Hassam Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarah Jahangir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jinye Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Aziz Swaiti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rami Basmaci indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Douglas Adler: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Hassam Ali, MD1, Sarah Jahangir, MD2, Jinye Liu, DO2, Abdul Aziz Swaiti, MD3, Rami Basmaci, MD2, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Umar Hayat, MD5, Douglas G. Adler, MD, FACG6. P4592 - Development and Internal Validation of a Simplified Clinical Prediction Model for Completion Colectomy in Patients With T1N0M0 Colorectal Cancer, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1East Carolina Gastroenterology, Greenville, NC; 2East Carolina University Medical Center, Greenville, NC; 3East Carolina University, Greenville, NC; 4University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 5Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 6Center for Advanced Therapeutic (CATE), Centura Health, Porter Adventist Hospital, Peak Gastroenterology, Denver, CO
Introduction: Completion colectomy is variably pursued following local excision for T1 colorectal cancer (CRC), often guided by histopathologic features. We aimed to develop a simplified model using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database to predict the likelihood of completion colectomy in patients with T1N0M0 CRC on endoscopy.
Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of SEER data from 2004–2015. Adults with histologically confirmed T1N0M0 CRC and known surgical treatment status were included. The primary outcome was receipt of completion colectomy following local excision. A multivariable logistic regression model was developed using Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) to identify predictive variables, followed by construction of a simplified logistic regression model. Final predictors included primary tumor site, race, sex, and tumor grade. Model discrimination was assessed using 10-fold cross-validation and bootstrap resampling. Calibration was evaluated using the GiViTI calibration belt. A manual scoring formula was derived using coefficient values from the final model.
Results: Among 3,289 patients (55% male; 80% White), 1,399 (42.5%) underwent completion colectomy. The final model demonstrated excellent performance with a cross-validated AUC of 0.84 (95% CI: 0.81–0.85), bootstrapped AUC of 0.83 (95% CI: 0.81–0.84), and standard ROC AUC of 0.84 (95% CI: 0.82–0.85). Calibration was strong (GiViTI p = 0.85), indicating no significant deviation from ideal prediction. Using a threshold probability ≥0.60, the model achieved 73.9% sensitivity, 83.9% specificity, 77.3% positive predictive value, 81.6% negative predictive value, and 78.6% overall accuracy. The full manual scoring equation was:
logit(p) = 1.6807 0.5543 × Appendix 0.2014 × Ascending colon 0.0929 × Hepatic flexure − 0.9138 × Transverse colon − 0.9886 × Splenic flexure − 0.6383 × Descending colon − 2.8347 × Sigmoid colon − 0.3868 × Overlapping lesion − 1.8755 × Colon, NOS − 3.8004 × Rectosigmoid junction − 3.0419 × Rectum − 0.5823 × Asian or Pacific Islander − 0.1340 × Black − 1.1498 × Unknown race − 0.3480 × White − 0.1091 × Male 0.1875 × Poorly differentiated 0.3356 × Undifferentiated − 0.2220 × Unknown grade 0.0883 × Well differentiated
Discussion: We developed a simplified model that accurately predicts completion colectomy after local excision for T1N0M0 CRC. A web-based calculator is available at https://tinyurl.com/Colectomy-Calculator. External validation is needed.

Figure: Figure 1. Discrimination (A–B), calibration (C), and predicted probabilities by tumor size (D) for the simplified model predicting completion colectomy in T1N0M0 colorectal cancer.
Disclosures:
Hassam Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarah Jahangir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jinye Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Aziz Swaiti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rami Basmaci indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Douglas Adler: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Hassam Ali, MD1, Sarah Jahangir, MD2, Jinye Liu, DO2, Abdul Aziz Swaiti, MD3, Rami Basmaci, MD2, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Umar Hayat, MD5, Douglas G. Adler, MD, FACG6. P4592 - Development and Internal Validation of a Simplified Clinical Prediction Model for Completion Colectomy in Patients With T1N0M0 Colorectal Cancer, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
