Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P4588 - Comparing Safety and Efficacy of Different Bowel Preparation Regimens in Constipated Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials

Khadija Mohib, MD (she/her/hers)
Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at the University of Nevada Las Vegas
Las Vegas, NV
Presenting Author(s)
1University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 2King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 3Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Quetta Institute of Medical Sciences, Quetta, Balochistan, Pakistan; 5Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at the University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV; 6Punjab Medical College, Faisalabad, Punjab, Pakistan; 7Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction:
Insufficient bowel preparation (IBP) reduces colonoscopy effectiveness, with constipation as a key risk factor. This study conducts a network meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of different bowel preparation regimens for constipated patients.
Methods:
Databases including PubMed, Cochrane Central, and ScienceDirect were explored from their inception up to May 2025 for Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) examining various bowel preparation regimens in constipated patients undergoing colonoscopy. A frequentist network meta-analysis was executed using R version 4.2.1 with the “netmeta” package, applying a random effects model. Treatment rankings were established using p-scores, while the risk of bias was evaluated with the ROB 2.0 tool. Publication bias was assessed visually via funnel plots and statistically through Egger’s Regression test.
Results:
Fifteen RCTs were included in this network meta-analysis. Compared to 4L PEG (polyethylene glycol), 3L PEG + 3d-Lin (3 days-Linaclotide) (RR=1.29 ; 95%CI:[1.12,1.47], p=0.0002), 4L PEG + 1d-Lin (RR=1.25 ; 95%CI:[1.04,1.51], p=0.02), NaP (sodium phosphate) + bisacodyl (RR=1.52 ; 95%CI:[1.09,2.10], p=0.01) and Probiotic 14d + NaP (RR= 3.59 ; 95%CI:[1.83,7.04], p=0.0002) arms significantly increased the adequate bowel preparation with Probiotic 14d + NaP group ranked highest and Senna + MgSO4 (Magnesium sulphate) ranked lowest regarding this outcome. The risk of all other adverse effects, including nausea, vomiting, and bloating, was comparable between different regimens, except abdominal pain, which was significantly reduced in the 3L PEG + 3d-Lin arm (RR=0.18 ;95%CI:[0.04,0.88], p=0.03) compared to 4L PEG.
Discussion:
In constipated patients, Probiotic 14d + NaP showed the highest efficacy for adequate bowel preparation, while Senna + MgSO4 was least effective. Additionally, 3L PEG + 3d-Lin reduced abdominal pain compared to 4L PEG, with comparable rates of other adverse effects across bowel preparation regimens.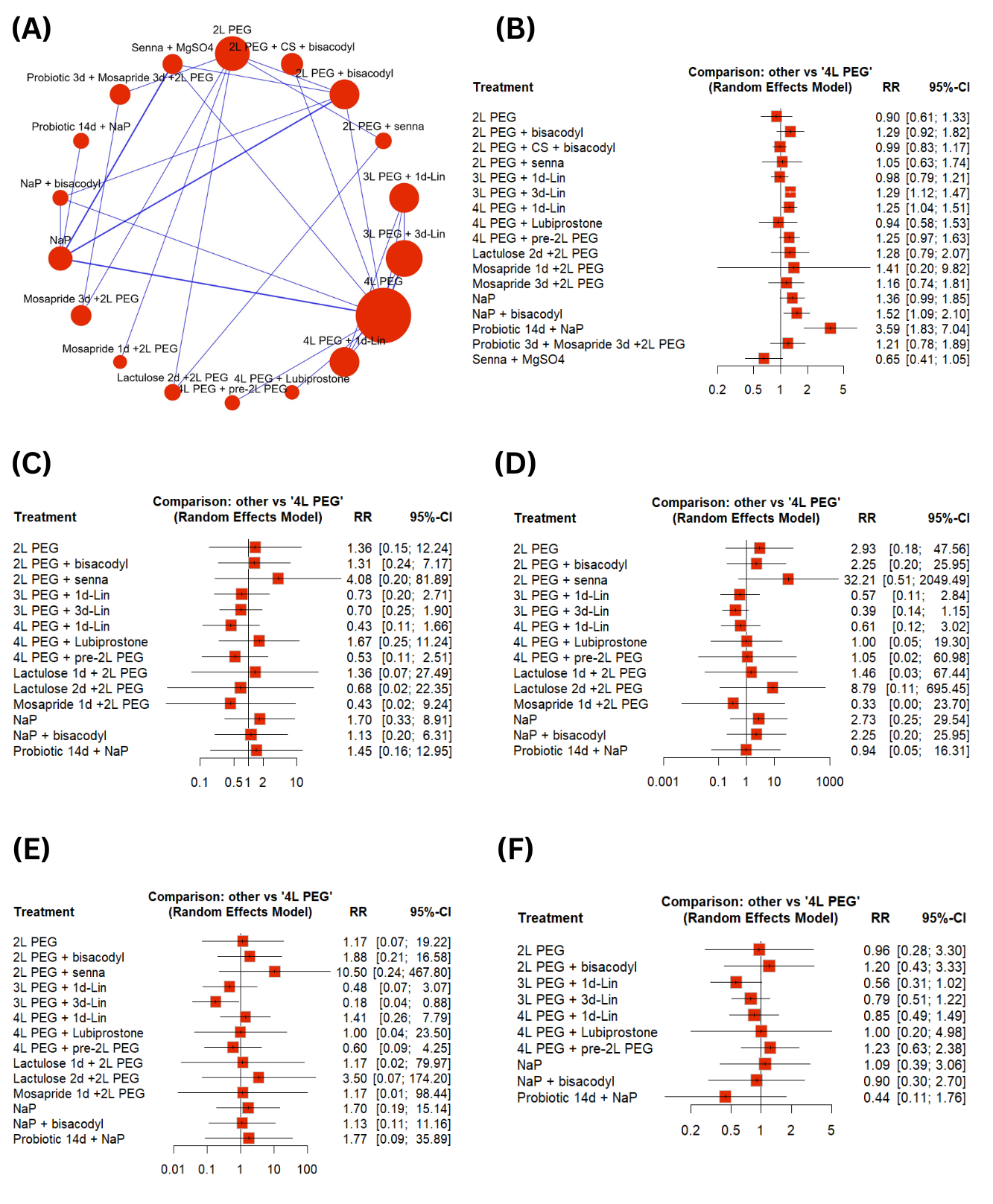
Figure: (A) Adequate Bowel Preparation Network Graph (B) Adequate Bowel Preparation Forest Plot (C) Nausea Forest Pot (D) Vomiting Forest Plot (E) Abdominal Pain Forest Plot
(F) Bloating Forest Plot 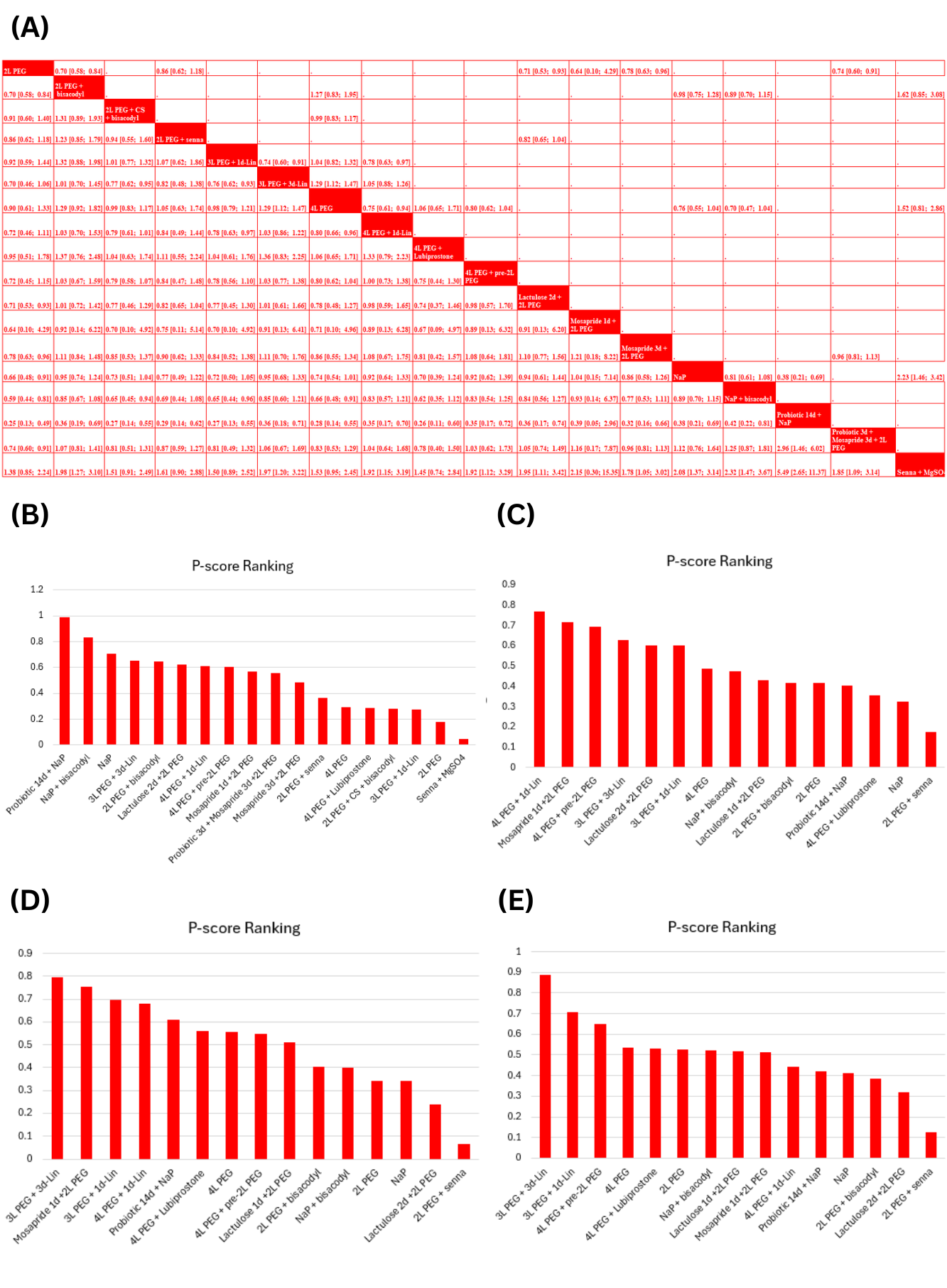
Figure: (A) Adequate Bowel Preparation League Plot (B) Adequate Bowel Preparation P-Score Ranking (C) Nausea P-Score Ranking (D) Vomiting P-Score Ranking (E) Abdominal Pain P-Score Ranking
Disclosures:
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zain Ul Abideen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hassan Waseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Aimen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abu-Bakr Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khadija Mohib indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mian Uman Anwer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prasun Jalal: AbbVie – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant.
Noor Ul Huda Ramzan, MD1, Zain Ul Abideen, MBBS2, Muhammad Hassan Waseem, MBBS3, Sania Aimen, MBBS4, Abu-Bakr Ahmed, BA5, Khadija Mohib, MD5, Mian Uman Anwer, MBBS6, Prasun K.. Jalal, MD7. P4588 - Comparing Safety and Efficacy of Different Bowel Preparation Regimens in Constipated Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
