Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P4458 - Two for One: A Rare Case of Squamous Cell Lung Cancer With Synchronous Pancreatic and Hepatic Metastases
Tuesday, October 28, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- KM
Kathleen S. Moore
Creighton University School of Medicine
Phoenix, Arizona
Presenting Author(s)
Kathleen S. Moore, Vishnu Yanamaladoddi, MD, Ariana R. Tagliaferri, MD, Mary Fietz, MD, Dalbir Sandhu, MD
Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) can metastasize to the bone, brain, adrenal glands and liver. The incidence of pancreatic metastasis is less than 1%, and is most commonly large cell carcinoma. Though squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) has a 3-9% risk of metastasis within 1-2 years following diagnosis, it is very rare to develop in the pancreas and liver independently and, only one other case highlights synchronous pancreatic and hepatic metastasis from primary SqCC of the lung. Herein we present a 58-year-old-man with nausea and jaundice, found to have primary SqCC of the lung with concomitant pancreatic and hepatic metastasis.
Case Description/
Methods: A 58-year-old man with an extensive medical history, presented to the ER with acute intractable nausea and vomiting. On arrival, he was afebrile and hemodynamically stable with an exam remarkable for jaundice and generalized abdominal pain without peritonitis. Initial labs revealed normocytic anemia (Hgb 11 g/dL), hyperbilirubinemia (Tbili 5.5 mg/dL /Dbili 5 mg/dL), and elevated liver enzymes (ALP 718/ALT 213/AST 122). An abdominal US revealed CBD dilation (11.8 mm), intrahepatic duct dilation and gallbladder sludge. An abdominal MRI demonstrated diffuse liver metastases, pancreatic head mass and peripancreatic lymphadenopathy. Poorly differentiated SqCC was diagnosed via liver biopsy. EUS revealed a hypoechoic pancreatic head mass, which was biopsied and returned positive for SqCC. The pancreatic duct and ampulla were unremarkable. The patient underwent biliary sphincterotomy and balloon dilation, and a 10mm x 60mm metallic stent was deployed in the CBD. At this time, a CT of the chest revealed a left lower lobe multinodular mass with central necrosis, which was biopsied and again positive for poorly differentiated SqCC. This was determined to be the primary based on pathology, and the patient was treated with carboplatin, paclitaxel and pembrolizumab for palliative therapy.
Discussion: Primary squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) of the pancreas is an exceedingly rare entity, with an estimated incidence of 0.5–0.7%. When it does occur, it is believed to arise within the pancreatic ducts, often in the setting of chronic inflammation and squamous metaplasia. Pancreatic metastasis commonly infiltrates the pancreatic head and body, consistent with our patient. Though there are other infrequent reports of primary pulmonary SqCC metastasizing to the pancreas, this is the second case highlighting concomitant metastatic disease to both the liver and pancreas.
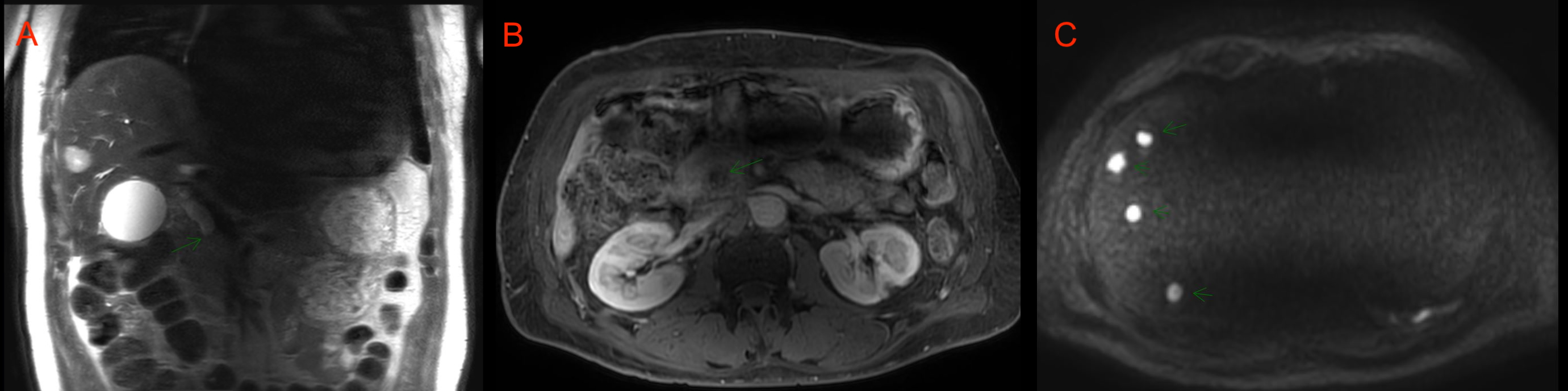
Figure: A. Coronal MRI showing Ill-defined hypoenhancing lesion in the head of the pancreas
B. Axial MRI showing Ill-defined hypoenhancing lesion in the head of the pancreas
C. Axial MRI showing liver metastases
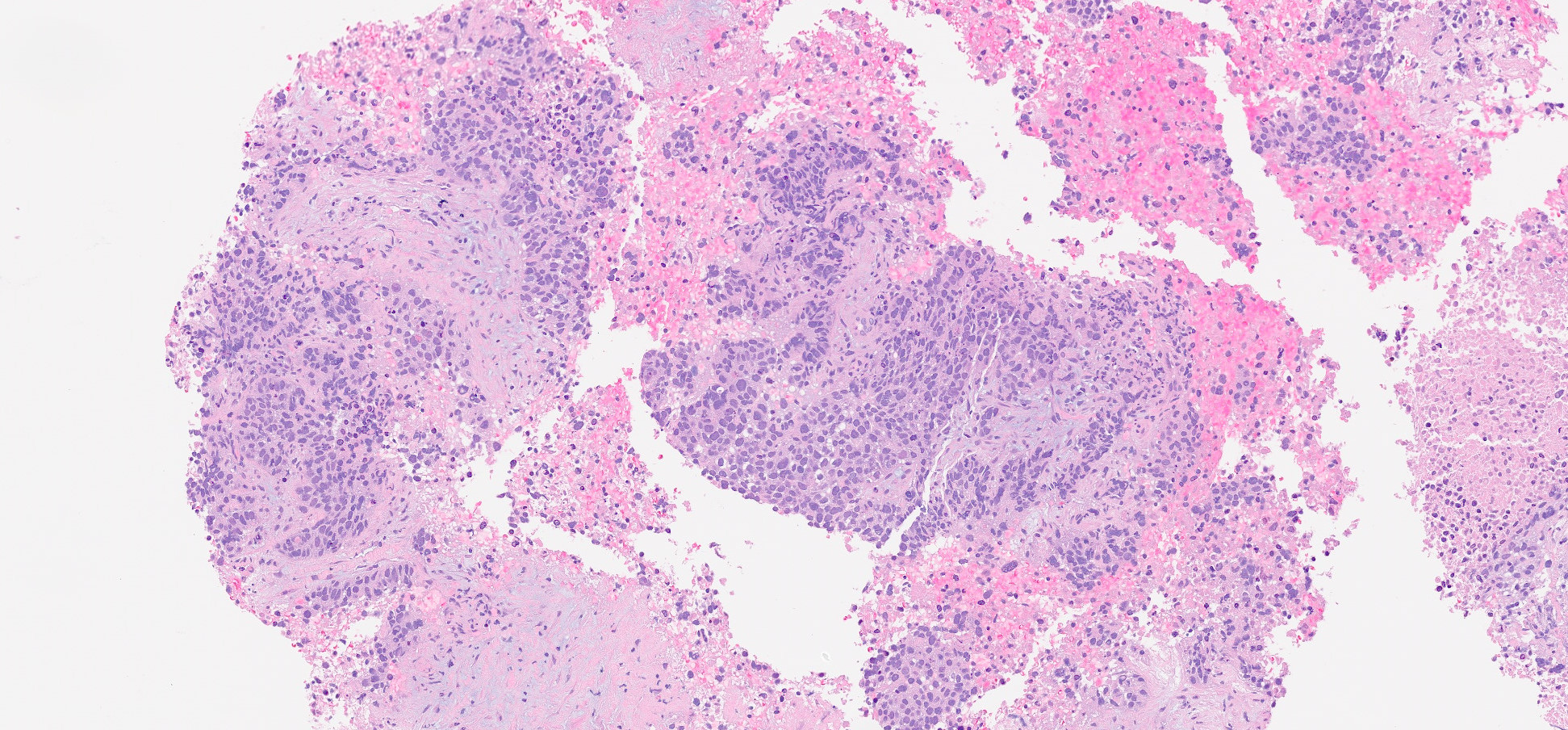
Figure: Pancreatic lesion biopsy showing metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
Disclosures:
Kathleen Moore indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishnu Yanamaladoddi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ariana Tagliaferri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Fietz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalbir Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kathleen S. Moore, Vishnu Yanamaladoddi, MD, Ariana R. Tagliaferri, MD, Mary Fietz, MD, Dalbir Sandhu, MD. P4458 - Two for One: A Rare Case of Squamous Cell Lung Cancer With Synchronous Pancreatic and Hepatic Metastases, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) can metastasize to the bone, brain, adrenal glands and liver. The incidence of pancreatic metastasis is less than 1%, and is most commonly large cell carcinoma. Though squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) has a 3-9% risk of metastasis within 1-2 years following diagnosis, it is very rare to develop in the pancreas and liver independently and, only one other case highlights synchronous pancreatic and hepatic metastasis from primary SqCC of the lung. Herein we present a 58-year-old-man with nausea and jaundice, found to have primary SqCC of the lung with concomitant pancreatic and hepatic metastasis.
Case Description/
Methods: A 58-year-old man with an extensive medical history, presented to the ER with acute intractable nausea and vomiting. On arrival, he was afebrile and hemodynamically stable with an exam remarkable for jaundice and generalized abdominal pain without peritonitis. Initial labs revealed normocytic anemia (Hgb 11 g/dL), hyperbilirubinemia (Tbili 5.5 mg/dL /Dbili 5 mg/dL), and elevated liver enzymes (ALP 718/ALT 213/AST 122). An abdominal US revealed CBD dilation (11.8 mm), intrahepatic duct dilation and gallbladder sludge. An abdominal MRI demonstrated diffuse liver metastases, pancreatic head mass and peripancreatic lymphadenopathy. Poorly differentiated SqCC was diagnosed via liver biopsy. EUS revealed a hypoechoic pancreatic head mass, which was biopsied and returned positive for SqCC. The pancreatic duct and ampulla were unremarkable. The patient underwent biliary sphincterotomy and balloon dilation, and a 10mm x 60mm metallic stent was deployed in the CBD. At this time, a CT of the chest revealed a left lower lobe multinodular mass with central necrosis, which was biopsied and again positive for poorly differentiated SqCC. This was determined to be the primary based on pathology, and the patient was treated with carboplatin, paclitaxel and pembrolizumab for palliative therapy.
Discussion: Primary squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) of the pancreas is an exceedingly rare entity, with an estimated incidence of 0.5–0.7%. When it does occur, it is believed to arise within the pancreatic ducts, often in the setting of chronic inflammation and squamous metaplasia. Pancreatic metastasis commonly infiltrates the pancreatic head and body, consistent with our patient. Though there are other infrequent reports of primary pulmonary SqCC metastasizing to the pancreas, this is the second case highlighting concomitant metastatic disease to both the liver and pancreas.

Figure: A. Coronal MRI showing Ill-defined hypoenhancing lesion in the head of the pancreas
B. Axial MRI showing Ill-defined hypoenhancing lesion in the head of the pancreas
C. Axial MRI showing liver metastases

Figure: Pancreatic lesion biopsy showing metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
Disclosures:
Kathleen Moore indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishnu Yanamaladoddi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ariana Tagliaferri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Fietz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dalbir Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kathleen S. Moore, Vishnu Yanamaladoddi, MD, Ariana R. Tagliaferri, MD, Mary Fietz, MD, Dalbir Sandhu, MD. P4458 - Two for One: A Rare Case of Squamous Cell Lung Cancer With Synchronous Pancreatic and Hepatic Metastases, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
