Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1771 - Valproic Acid–Induced Liver Failure in a Patient With POLG-Related Disorder: A Case Emphasizing Early Diagnosis and Injury Pattern Recognition
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- OA
Omar Al-Radideh, MD
University of Florida College of Medicine
Gainesville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Omar Al-Radideh, MD1, Andreas G. Zori, MD2, Steve Qian, MD1
1University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL; 2University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
Introduction: POLG-Related disorders are mitochondrial disease presenting from childhood to adulthood with seizure, neuropathy, ataxia and stroke-like episodes. Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrom ( AHS ), a severe autosomal recessive condition due to POLG mutation, typically present with intractable epilepsy, psychomotor regression, liver failure and neuropathy. The brain and liver are particularly vulnerable due to the high energy demands. valproic acid exacerbates metacarpal serial dysfunction by increasing oxidative stress, inhibition beta oxidation and impairing the respiratory chain, significantly increase the risk of liver failure. Early recognition is essential to avoid mitochondrial- toxic agent like valproic acid
Case Description/
Methods: A 21- year old woman presented with jaundice, nausea, vomiting and Malaysia. 3 months prior, she was hospitalized for new onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE) and discharged on pregabalin,perampanel and valproic acid. EEG showed left occipital lateralized periodic discharge. Brain MRI relieved restricted diffusion and edema in the left parietal, occipital, posterior temporal lobes and thalamus. On readmission, lab show coagulopathy, hyperbilirubinemia, hypoglycemia and hypoalbuminemia. her condition progress to acute liver failure and worsening mental status. Repeat MRI showed near resolution of CNS lesions; EEG relieve no epileptiform activity. Liver biopsy demonstrate lobular and portal inflammation, marked microvesicular steatosis, foamy cytoplasm and a two- toned hepatocyte pattern. her hospital course was complicated by acute kidney injury requiring CVVHD. Echocardiogram showed a reduced ejection fraction which normalized with the treatment. Cardiac MRI showed myocardial edema. Rapid whole genome sequencing relieved compound heterozygous POLG mutation( c.1399G >A P.A467T and C.2243G >C p.W748S), confirming POLG -related disorder. she underwent successful liver transplantation and was discharged with improved mental status and motor function, without seizure recurrence
Discussion: this case highlight the need to consider POLG- related disorders in NORSE. valproic acid must be avoided until POLG status is known due to its potential to triggered fetal liver failure. EEG, liver biopsy and medication history were crucial in diagnosis. Microvesicular steatosis should raised suspicion for mitochondrial disease. POLG testing is essential in acute liver failure with valproate exposure. early diagnosis is critical given the risk of multi system progression
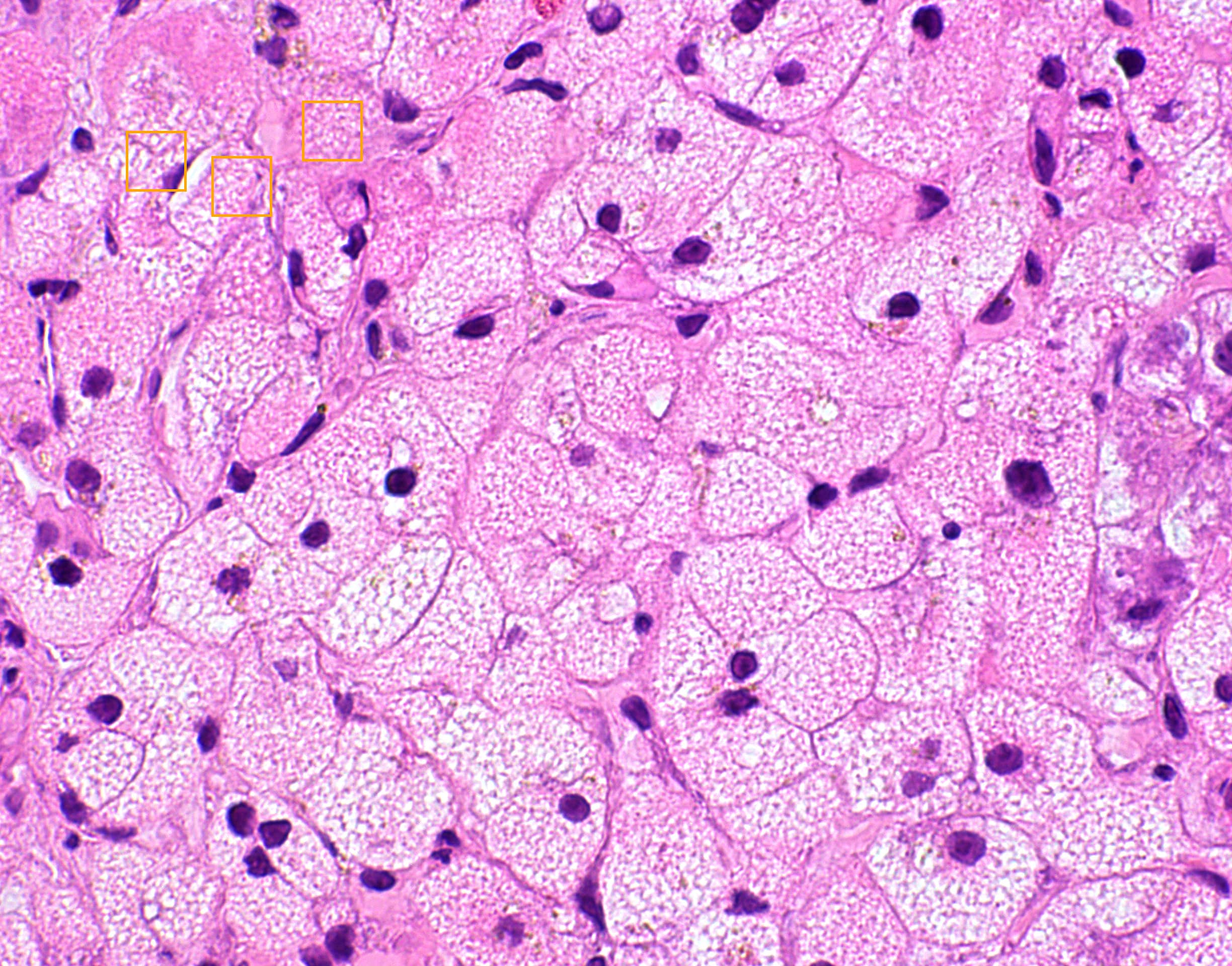
Figure: Liver biopsy showing acute hepatitis with two-toned hepatocytes and foamy cytoplasm.
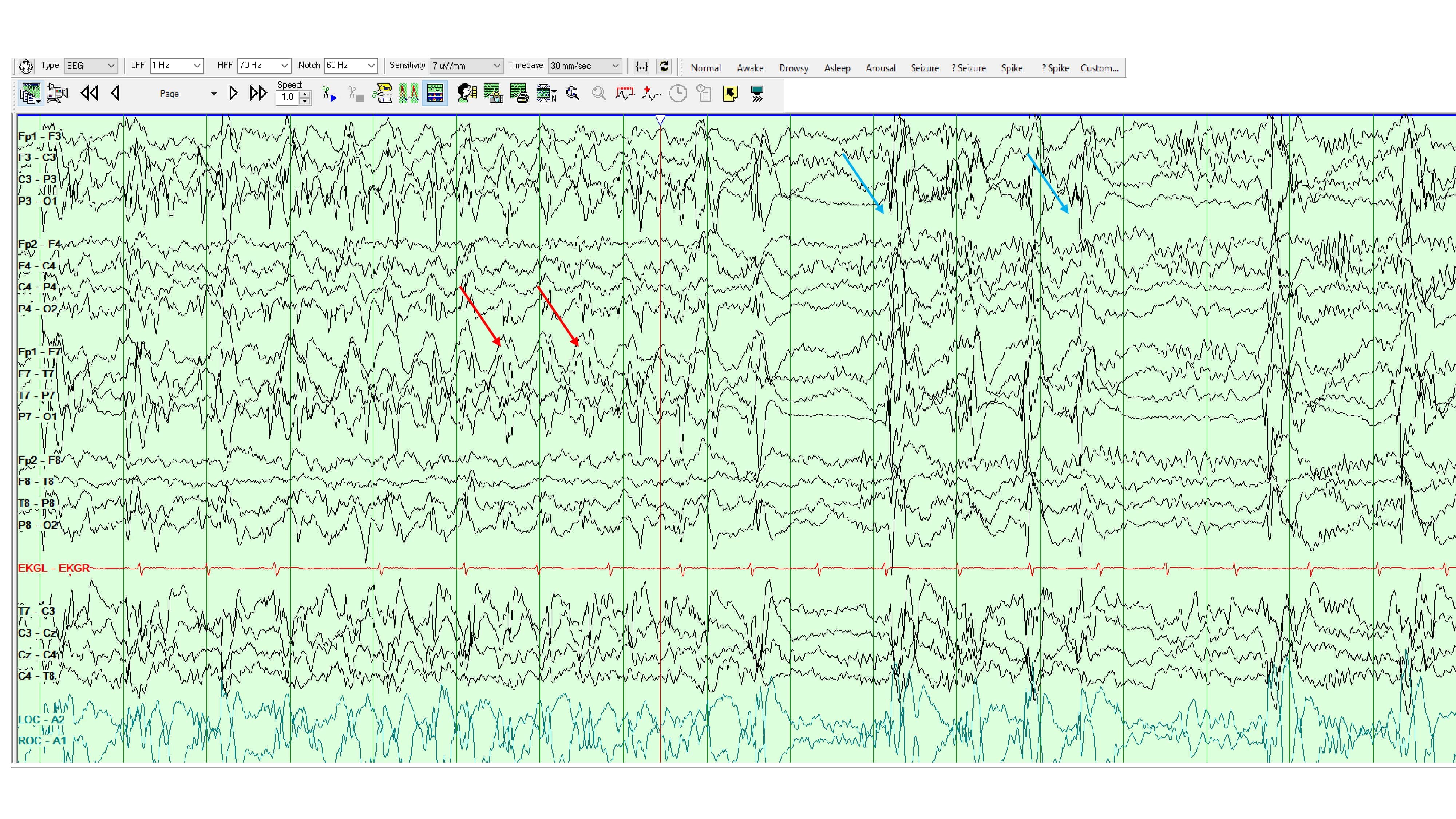
Figure: EEG showing continuous left occipital lateralized periodic discharges consistent with RHADS.
Disclosures:
Omar Al-Radideh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andreas Zori indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steve Qian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al-Radideh, MD1, Andreas G. Zori, MD2, Steve Qian, MD1. P1771 - Valproic Acid–Induced Liver Failure in a Patient With POLG-Related Disorder: A Case Emphasizing Early Diagnosis and Injury Pattern Recognition, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL; 2University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
Introduction: POLG-Related disorders are mitochondrial disease presenting from childhood to adulthood with seizure, neuropathy, ataxia and stroke-like episodes. Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrom ( AHS ), a severe autosomal recessive condition due to POLG mutation, typically present with intractable epilepsy, psychomotor regression, liver failure and neuropathy. The brain and liver are particularly vulnerable due to the high energy demands. valproic acid exacerbates metacarpal serial dysfunction by increasing oxidative stress, inhibition beta oxidation and impairing the respiratory chain, significantly increase the risk of liver failure. Early recognition is essential to avoid mitochondrial- toxic agent like valproic acid
Case Description/
Methods: A 21- year old woman presented with jaundice, nausea, vomiting and Malaysia. 3 months prior, she was hospitalized for new onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE) and discharged on pregabalin,perampanel and valproic acid. EEG showed left occipital lateralized periodic discharge. Brain MRI relieved restricted diffusion and edema in the left parietal, occipital, posterior temporal lobes and thalamus. On readmission, lab show coagulopathy, hyperbilirubinemia, hypoglycemia and hypoalbuminemia. her condition progress to acute liver failure and worsening mental status. Repeat MRI showed near resolution of CNS lesions; EEG relieve no epileptiform activity. Liver biopsy demonstrate lobular and portal inflammation, marked microvesicular steatosis, foamy cytoplasm and a two- toned hepatocyte pattern. her hospital course was complicated by acute kidney injury requiring CVVHD. Echocardiogram showed a reduced ejection fraction which normalized with the treatment. Cardiac MRI showed myocardial edema. Rapid whole genome sequencing relieved compound heterozygous POLG mutation( c.1399G >A P.A467T and C.2243G >C p.W748S), confirming POLG -related disorder. she underwent successful liver transplantation and was discharged with improved mental status and motor function, without seizure recurrence
Discussion: this case highlight the need to consider POLG- related disorders in NORSE. valproic acid must be avoided until POLG status is known due to its potential to triggered fetal liver failure. EEG, liver biopsy and medication history were crucial in diagnosis. Microvesicular steatosis should raised suspicion for mitochondrial disease. POLG testing is essential in acute liver failure with valproate exposure. early diagnosis is critical given the risk of multi system progression

Figure: Liver biopsy showing acute hepatitis with two-toned hepatocytes and foamy cytoplasm.

Figure: EEG showing continuous left occipital lateralized periodic discharges consistent with RHADS.
Disclosures:
Omar Al-Radideh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andreas Zori indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steve Qian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al-Radideh, MD1, Andreas G. Zori, MD2, Steve Qian, MD1. P1771 - Valproic Acid–Induced Liver Failure in a Patient With POLG-Related Disorder: A Case Emphasizing Early Diagnosis and Injury Pattern Recognition, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
