Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1668 - Safety of Percutaneous Liver Biopsy Procedure in Patients on Antithrombotic Therapy: A Comparative Multi-Institutional Cohort Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- ME
Mohanad Elchouemi, BS
Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center
El Paso, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Mohanad Elchouemi, BS1, Mostafa Eysha, MD1, Mutaz Kalas, MD2, Omar Alkasabrah, MD3, Arsalan Asad, BS4, Mona A. Ali, MD5, Anas A. Elsaka, MD5, Kholoud Abdelmoneim, MD5, Alejandro Robles, MD6, Marc J. Zuckerman, MD7, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD2
1Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX; 2Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX; 3Landmark Medical Center, Woonsocket, RI; 4John Sealy School of Medicine, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5Mansoura University, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 6Department of Gastroenterology, Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso, El Paso , TX, El Paso, TX; 7Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX., El Paso, TX
Introduction: Percutaneous liver biopsy is an important diagnostic tool for various liver diseases. Despite its minimally invasive nature, it poses risks, with bleeding being the most concerning complication. Anticoagulants (ACs) and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) are vital for managing cardiovascular and thromboembolic conditions. Their widespread use can impact the risk of bleeding during liver biopsy. This study aims to assess the safety of percutaneous liver biopsy in patients on anticoagulation (AC) or dual antiplatelet medications (DAPT) using a US-based multi-institutional database.
Methods: The study cohorts were identified using the TriNetX US Collaborative Network database based on the CPT code for percutaneous liver biopsy. Patients undergoing these procedures on uninterrupted AC were compared with those who never received any AC prior to or after the procedure. Additionally, patients undergoing this procedure on uninterrupted DAPT were compared with a control group of patients who did not receive any antiplatelets or aspirin prior to or after the procedure. Propensity score matching (1:1) was conducted based on demographics, medications, various comorbidities and labs (INR and platelets count). Hazards Ratios were calculated for outcomes such as post-biopsy bleeding, blood transfusion and mortality within 30 days of the procedure.
Results: A total of 7,726 patients were identified in the AC group and a total of 462 in the DAPT group. After propensity score matching, the rates of post biopsy bleeding (HR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.36-3.02), blood transfusion (HR, 3.66; 95% CI,3.04-4.39) and overall mortality (HR, 2.60; 95% CI, 2.31-2.93) were significantly higher in the liver biopsy with AC group compared with the liver biopsy without AC group. Meanwhile the group on DAPT compared with those not on DAPT had no significant difference in post biopsy bleeding (HR, 0.70; 95% CI,0.22-2.20), blood transfusion(HR, 1.40; 95% CI,0.87-2.26) or overall mortality(HR, 0.92; 95% CI,0.66-1.29) (Table 1).
Discussion: In this multi-institutional database retrospective cohort study, patients who continued AC during liver biopsy experienced significantly higher rates of post-biopsy bleeding and other adverse outcomes. However, no such increase was observed in patients receiving DAPT compared with the control group. Future prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings, particularly in the DAPT group, where the results may have been affected by the relatively small sample size.
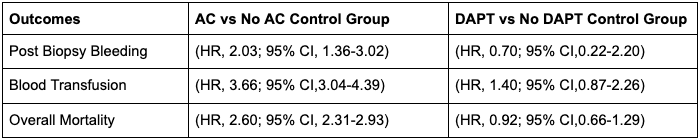
Figure: Table 1. Adverse outcomes post percutaneous liver biopsy procedure in patients on AC and DAPT compared to their control groups.
Disclosures:
Mohanad Elchouemi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mostafa Eysha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mutaz Kalas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Alkasabrah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arsalan Asad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Elsaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kholoud Abdelmoneim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alejandro Robles indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marc Zuckerman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sherif Elhanafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohanad Elchouemi, BS1, Mostafa Eysha, MD1, Mutaz Kalas, MD2, Omar Alkasabrah, MD3, Arsalan Asad, BS4, Mona A. Ali, MD5, Anas A. Elsaka, MD5, Kholoud Abdelmoneim, MD5, Alejandro Robles, MD6, Marc J. Zuckerman, MD7, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD2. P1668 - Safety of Percutaneous Liver Biopsy Procedure in Patients on Antithrombotic Therapy: A Comparative Multi-Institutional Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX; 2Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX; 3Landmark Medical Center, Woonsocket, RI; 4John Sealy School of Medicine, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5Mansoura University, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 6Department of Gastroenterology, Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso, El Paso , TX, El Paso, TX; 7Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX., El Paso, TX
Introduction: Percutaneous liver biopsy is an important diagnostic tool for various liver diseases. Despite its minimally invasive nature, it poses risks, with bleeding being the most concerning complication. Anticoagulants (ACs) and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) are vital for managing cardiovascular and thromboembolic conditions. Their widespread use can impact the risk of bleeding during liver biopsy. This study aims to assess the safety of percutaneous liver biopsy in patients on anticoagulation (AC) or dual antiplatelet medications (DAPT) using a US-based multi-institutional database.
Methods: The study cohorts were identified using the TriNetX US Collaborative Network database based on the CPT code for percutaneous liver biopsy. Patients undergoing these procedures on uninterrupted AC were compared with those who never received any AC prior to or after the procedure. Additionally, patients undergoing this procedure on uninterrupted DAPT were compared with a control group of patients who did not receive any antiplatelets or aspirin prior to or after the procedure. Propensity score matching (1:1) was conducted based on demographics, medications, various comorbidities and labs (INR and platelets count). Hazards Ratios were calculated for outcomes such as post-biopsy bleeding, blood transfusion and mortality within 30 days of the procedure.
Results: A total of 7,726 patients were identified in the AC group and a total of 462 in the DAPT group. After propensity score matching, the rates of post biopsy bleeding (HR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.36-3.02), blood transfusion (HR, 3.66; 95% CI,3.04-4.39) and overall mortality (HR, 2.60; 95% CI, 2.31-2.93) were significantly higher in the liver biopsy with AC group compared with the liver biopsy without AC group. Meanwhile the group on DAPT compared with those not on DAPT had no significant difference in post biopsy bleeding (HR, 0.70; 95% CI,0.22-2.20), blood transfusion(HR, 1.40; 95% CI,0.87-2.26) or overall mortality(HR, 0.92; 95% CI,0.66-1.29) (Table 1).
Discussion: In this multi-institutional database retrospective cohort study, patients who continued AC during liver biopsy experienced significantly higher rates of post-biopsy bleeding and other adverse outcomes. However, no such increase was observed in patients receiving DAPT compared with the control group. Future prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings, particularly in the DAPT group, where the results may have been affected by the relatively small sample size.

Figure: Table 1. Adverse outcomes post percutaneous liver biopsy procedure in patients on AC and DAPT compared to their control groups.
Disclosures:
Mohanad Elchouemi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mostafa Eysha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mutaz Kalas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Alkasabrah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arsalan Asad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Elsaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kholoud Abdelmoneim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alejandro Robles indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marc Zuckerman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sherif Elhanafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohanad Elchouemi, BS1, Mostafa Eysha, MD1, Mutaz Kalas, MD2, Omar Alkasabrah, MD3, Arsalan Asad, BS4, Mona A. Ali, MD5, Anas A. Elsaka, MD5, Kholoud Abdelmoneim, MD5, Alejandro Robles, MD6, Marc J. Zuckerman, MD7, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD2. P1668 - Safety of Percutaneous Liver Biopsy Procedure in Patients on Antithrombotic Therapy: A Comparative Multi-Institutional Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
