Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1610 - Targeting Liver and Glucose: Comparative Efficacy of SGLT2i and GLP-1RA in NAFLD Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mohamed B. Elnaggar, MD
Hartford Healthcare
Hartford, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Mohamed A. B. Elnaggar, MD1, Omar F. Abbas, 2
1Hartford Healthcare, Hartford, CT; 2Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt
Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a global metabolic disorder marked by decreased insulin sensitivity and impaired insulin secretion, resulting in hyperglycaemia. It is frequently associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent studies suggest that SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists may improve liver enzymes and reduce liver fat in T2DM patients with NAFLD.
Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines. We conducted a comprehensive literature search across five electronic databases: (PubMed, Scopus, Ovid, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science). We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the efficacy of SGLT2 and GLP-1 agonists on NAFLD in T2DM patients. We screened the records to identify eligible studies, extracted and analyzed the data using the meta package (version 4.0.3) in R and STATA MP version 17. We used a random-effects model to calculate the weighted mean difference (WMD) with 95% CI. Heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s Q test and the I² statistic. Sensitivity, subgroup, and publication bias analyses were applied. We used both Galbraith and funnel plots to further assess heterogeneity and publication bias.
Results: Thirty-seven RCTs, with a total of 2,609 patients, were included in this study.SGLT2i significantly reduced ALT (MD= -8.79, 95% CI: -12.80 to -4.79, P < 0.0001) and AST (MD= -10.26, 95% CI: -17.03 to -3.49, P = 0.0030), while GLP-1RA Showed no significant effcet on both enzymes. GGT changes were not changed in both groups. Both treatments significant reduction in body weight and BMI. Fasting glucose and HOMA-IR improved in both groups, with a greater reduction in glucose seen in SGLT2i group. GLP-1RA group reduced HbA1c but not in SGLT2i group. No significant changes were observed in total cholesterol, HDL, or LDL. Triglycerides were significantly reduced in both groups, with a greater effect in SGLT2i. Postprandial glucose was reduced significantly with GLP-1RA
Discussion: Both GLP-1 and SGLT2 showed benefits in patients with NAFLD and T2DM. SGLT2 showed greater effects on liver enzymes, while GLP-1 showed improved weight loss and glycemic control. Still, the choice of treatment should be based on the patient’s goals and the main clinical needs.
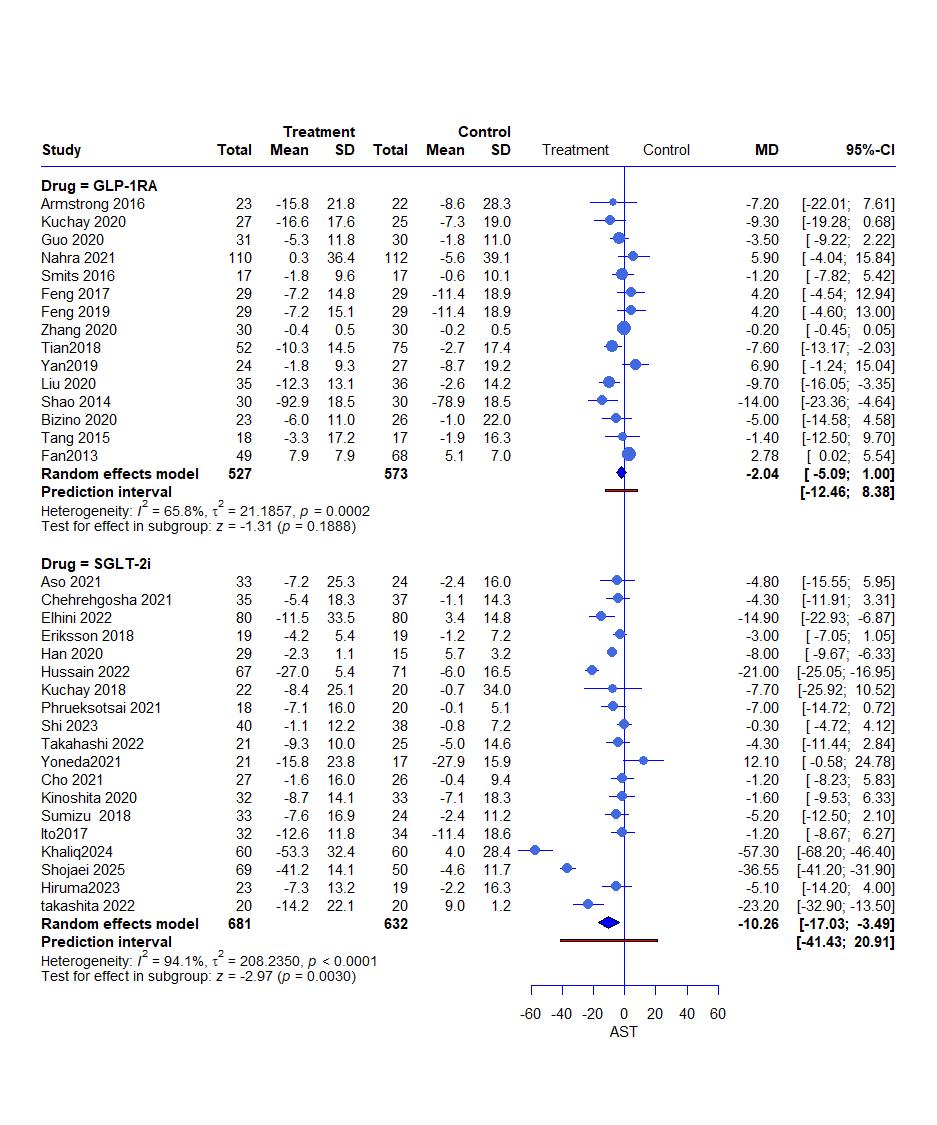
Figure: Effect of GLP 1 agonist and SGLTi on AST (Aspartate Transferase)
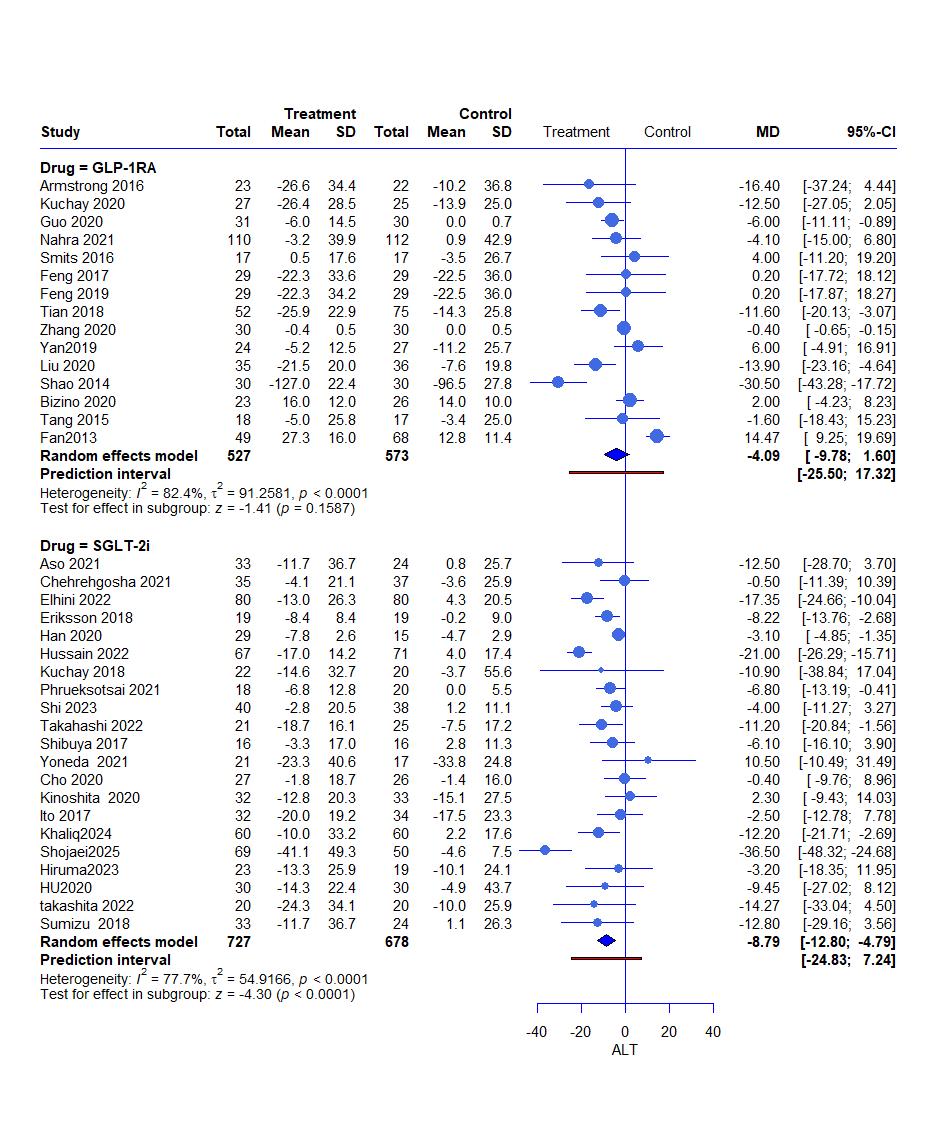
Figure: Effect of GLP 1 agonist and SGLTi on ALT (Alanine Transaminase)
Disclosures:
Mohamed A. Elnaggar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar F. Abbas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed A. B. Elnaggar, MD1, Omar F. Abbas, 2. P1610 - Targeting Liver and Glucose: Comparative Efficacy of SGLT2i and GLP-1RA in NAFLD Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Hartford Healthcare, Hartford, CT; 2Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt
Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a global metabolic disorder marked by decreased insulin sensitivity and impaired insulin secretion, resulting in hyperglycaemia. It is frequently associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent studies suggest that SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists may improve liver enzymes and reduce liver fat in T2DM patients with NAFLD.
Methods: This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines. We conducted a comprehensive literature search across five electronic databases: (PubMed, Scopus, Ovid, the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science). We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the efficacy of SGLT2 and GLP-1 agonists on NAFLD in T2DM patients. We screened the records to identify eligible studies, extracted and analyzed the data using the meta package (version 4.0.3) in R and STATA MP version 17. We used a random-effects model to calculate the weighted mean difference (WMD) with 95% CI. Heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s Q test and the I² statistic. Sensitivity, subgroup, and publication bias analyses were applied. We used both Galbraith and funnel plots to further assess heterogeneity and publication bias.
Results: Thirty-seven RCTs, with a total of 2,609 patients, were included in this study.SGLT2i significantly reduced ALT (MD= -8.79, 95% CI: -12.80 to -4.79, P < 0.0001) and AST (MD= -10.26, 95% CI: -17.03 to -3.49, P = 0.0030), while GLP-1RA Showed no significant effcet on both enzymes. GGT changes were not changed in both groups. Both treatments significant reduction in body weight and BMI. Fasting glucose and HOMA-IR improved in both groups, with a greater reduction in glucose seen in SGLT2i group. GLP-1RA group reduced HbA1c but not in SGLT2i group. No significant changes were observed in total cholesterol, HDL, or LDL. Triglycerides were significantly reduced in both groups, with a greater effect in SGLT2i. Postprandial glucose was reduced significantly with GLP-1RA
Discussion: Both GLP-1 and SGLT2 showed benefits in patients with NAFLD and T2DM. SGLT2 showed greater effects on liver enzymes, while GLP-1 showed improved weight loss and glycemic control. Still, the choice of treatment should be based on the patient’s goals and the main clinical needs.

Figure: Effect of GLP 1 agonist and SGLTi on AST (Aspartate Transferase)

Figure: Effect of GLP 1 agonist and SGLTi on ALT (Alanine Transaminase)
Disclosures:
Mohamed A. Elnaggar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar F. Abbas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed A. B. Elnaggar, MD1, Omar F. Abbas, 2. P1610 - Targeting Liver and Glucose: Comparative Efficacy of SGLT2i and GLP-1RA in NAFLD Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
