Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1604 - Twenty-Five-Year Mortality Trends in Older Adults With Coexisting Liver Cirrhosis and Acute Renal Failure in the United States: A CDC Multiple Cause of Death Analysis (1999–2023)
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Abdul Khuram, DO (he/him/his)
University of Connecticut Health
Farmington, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Hakim Wazir, MBBS1, Abdul Khuram, DO2, Abdul Majid, MBBS3, Ali Zubair, MBBS4, Minahil Zaheer, MBBS5, Maliha Khalid, MBBS6, Aman Iqbal, MBBS7, Yukthi Mudiam, MBBS8, Rameesha Zubair, MBBS2, Rakhshanda Khan, MBBS9, Harshawardhan Dhanraj Ramteke, MBBS10
1Gajju Khan Medical College,Swabi Pakistan Medicine department, Shahmansor, Swabi, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 2University of Connecticut Health, Farmington, CT; 3Gujji Khan Medical College Swabi, Shahmansor, Swabi, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Zayed Medical College Raheem Yar Khan, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5HBS Medical and Dental College, Taramri, Islamabad, Pakistan; 6Gomal Medical College, Dera Ismail Khan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 7Gomal Medical College Dera Ismail Khan, Dera Ismail Khan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 8Apollo Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Hyderabad, Telangana, India, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 9Ayaan institute of medical sciences, Moinabad, Telangana, India; 10Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Hefei, Anhui, China
Introduction: Older adults with coexisting liver cirrhosis and acute renal failure face significantly elevated mortality risks due to compounded organ dysfunction, systemic inflammation, and limited treatment options. This study analyzes trends in mortality related to liver cirrhosis and acute renal failure among older adults in the United States from 1999 to 2023.
Methods: We extracted mortality data among adults aged ≥ 55 from the CDC WONDER database utilizing ICD-10 codes K74 (liver cirrhosis) and N17 (acute renal failure). Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) were calculated per 100,000 persons and stratified by sex, race/ethnicity, census region, and urbanization status. Joinpoint regression identified temporal trends, estimating annual percentage changes (APCs) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results: From 1999 to 2023, 41,615 deaths were attributed to coexisting liver cirrhosis and acute renal failure in the United States. AAMR steadily increased till 2019 (APC: 4.50; 95% CI, 3.71 to 5.30; p < 0.000001), then sharply accelerated by 2023 (APC: 20.05; 95% CI, 14.21 to 26.18; p < 0.000001). Although men had a higher AAMR than women, a greater rise in mortality (2019-2023) was seen in men (APC: 18.73; 95% CI, 13.06 to 24.67; p < 0.000001). Regionally, the Northeast (2019-2023) exhibited the most pronounced rise (APC: 22.83; 95% CI, 14.28 to 32.02; p =0.000008). During the same period, the Midwest, West, and South regions showed uptrends with APCs of 22.50 (95% CI, 14.03 to 31.60; p =0.000009), 20.15 (95% CI, 13.05 to 27.69; p =0.000004), and 17.82 (95% CI, 12.30 to 23.63; p =0.000001), respectively. Racially, AAMR increased among all the groups, and the Whites experienced the highest number of deaths (35,673). From 2019 to 2023, the non-Hispanics had a higher APC (21.03; 95% CI, 15.06 to 27.31; p < 0.000001) than the Hispanics (14.23; 95% CI, 6.72 to 22.27; p =0.000580). Micropolitan and Small Metropolitan areas showed consistent uptrends throughout the study period with APCs of 5.47 (95% CI, 4.83 to 6.13; p < 0.000001) and 4.50 (95% CI, 3.76 to 5.24; p < 0.000001), respectively.
Discussion: Mortality from liver cirrhosis and acute renal failure among older adults in the U.S. increased significantly, particularly since 2019, with marked demographic and regional disparities. These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted preventive and therapeutic strategies among the high-risk groups.
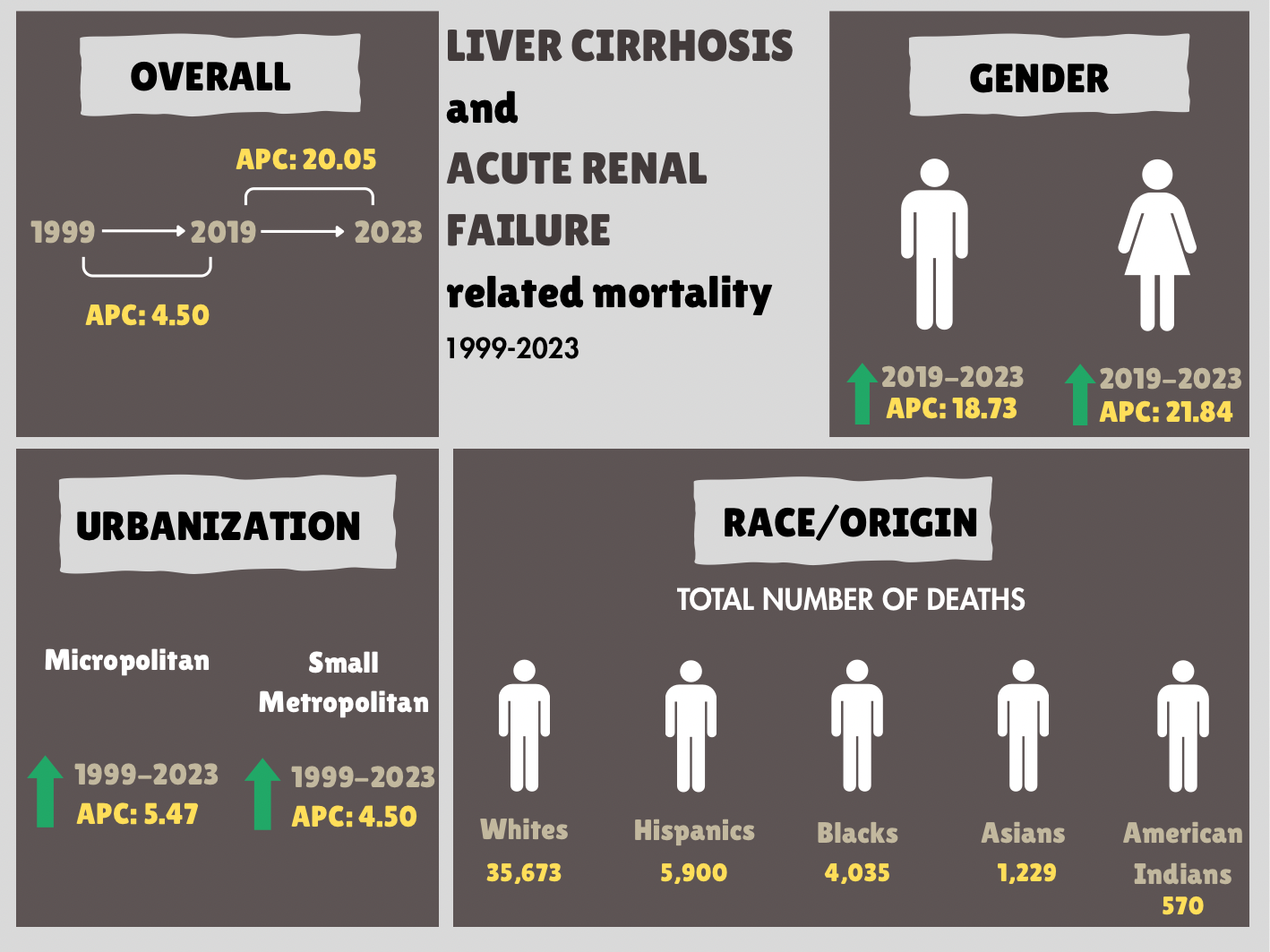
Figure: Figure 1: Twenty-Five-Year Mortality Trends in Older Adults With Coexisting Liver Cirrhosis and Acute Renal Failure in the United States: Stratification by year, sex, race/ethnicity, and urbanization
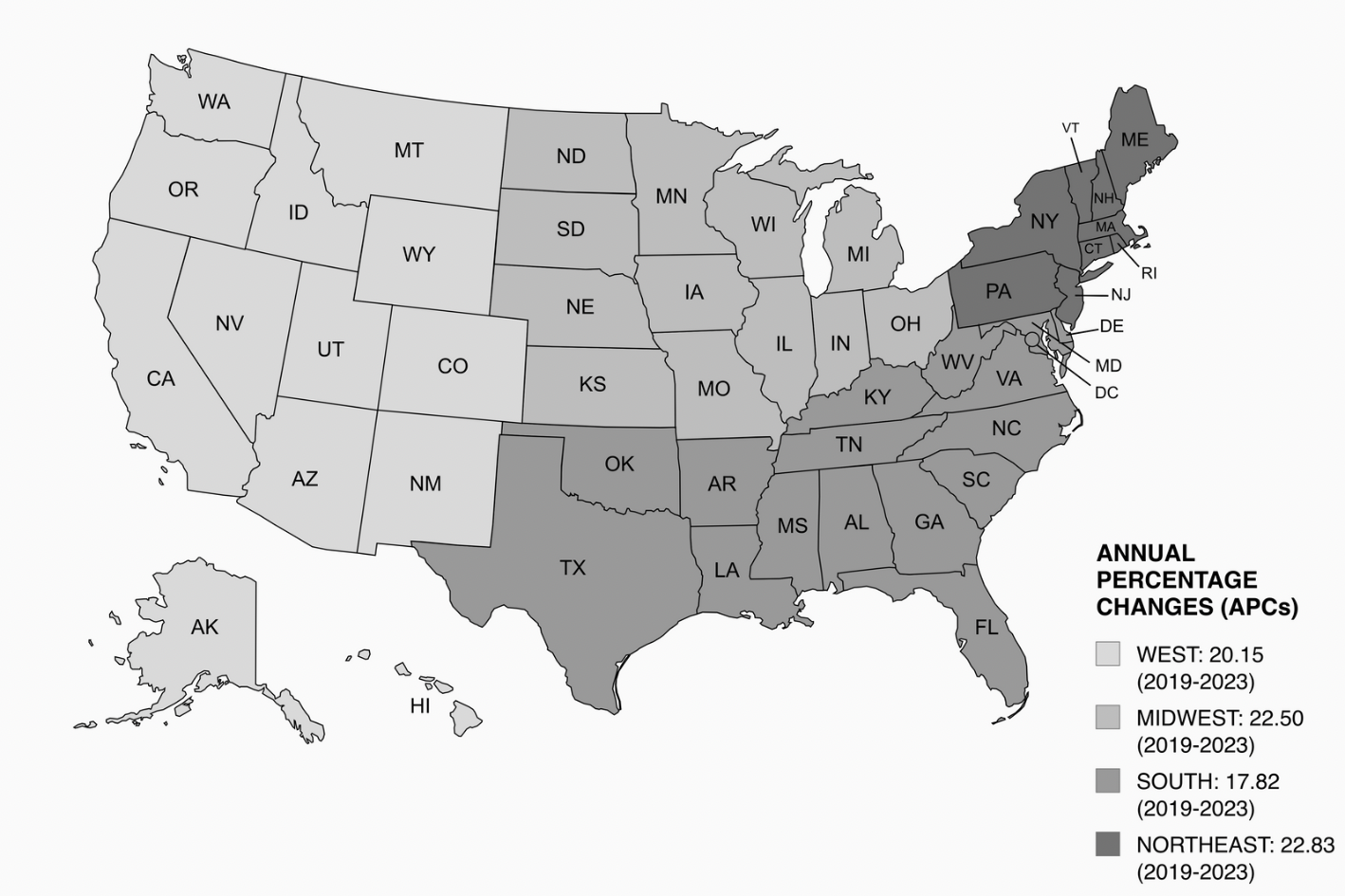
Figure: Figure 2: Twenty-Five-Year Mortality Trends in Older Adults With Coexisting Liver Cirrhosis and Acute Renal Failure in the United States: Census region wise trends
Disclosures:
Hakim Wazir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Khuram indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Majid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Zubair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minahil Zaheer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maliha Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aman Iqbal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yukthi Mudiam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rameesha Zubair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rakhshanda Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harshawardhan Dhanraj Ramteke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hakim Wazir, MBBS1, Abdul Khuram, DO2, Abdul Majid, MBBS3, Ali Zubair, MBBS4, Minahil Zaheer, MBBS5, Maliha Khalid, MBBS6, Aman Iqbal, MBBS7, Yukthi Mudiam, MBBS8, Rameesha Zubair, MBBS2, Rakhshanda Khan, MBBS9, Harshawardhan Dhanraj Ramteke, MBBS10. P1604 - Twenty-Five-Year Mortality Trends in Older Adults With Coexisting Liver Cirrhosis and Acute Renal Failure in the United States: A CDC Multiple Cause of Death Analysis (1999–2023), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Gajju Khan Medical College,Swabi Pakistan Medicine department, Shahmansor, Swabi, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 2University of Connecticut Health, Farmington, CT; 3Gujji Khan Medical College Swabi, Shahmansor, Swabi, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 4Sheikh Zayed Medical College Raheem Yar Khan, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 5HBS Medical and Dental College, Taramri, Islamabad, Pakistan; 6Gomal Medical College, Dera Ismail Khan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 7Gomal Medical College Dera Ismail Khan, Dera Ismail Khan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 8Apollo Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Hyderabad, Telangana, India, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 9Ayaan institute of medical sciences, Moinabad, Telangana, India; 10Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Hefei, Anhui, China
Introduction: Older adults with coexisting liver cirrhosis and acute renal failure face significantly elevated mortality risks due to compounded organ dysfunction, systemic inflammation, and limited treatment options. This study analyzes trends in mortality related to liver cirrhosis and acute renal failure among older adults in the United States from 1999 to 2023.
Methods: We extracted mortality data among adults aged ≥ 55 from the CDC WONDER database utilizing ICD-10 codes K74 (liver cirrhosis) and N17 (acute renal failure). Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) were calculated per 100,000 persons and stratified by sex, race/ethnicity, census region, and urbanization status. Joinpoint regression identified temporal trends, estimating annual percentage changes (APCs) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results: From 1999 to 2023, 41,615 deaths were attributed to coexisting liver cirrhosis and acute renal failure in the United States. AAMR steadily increased till 2019 (APC: 4.50; 95% CI, 3.71 to 5.30; p < 0.000001), then sharply accelerated by 2023 (APC: 20.05; 95% CI, 14.21 to 26.18; p < 0.000001). Although men had a higher AAMR than women, a greater rise in mortality (2019-2023) was seen in men (APC: 18.73; 95% CI, 13.06 to 24.67; p < 0.000001). Regionally, the Northeast (2019-2023) exhibited the most pronounced rise (APC: 22.83; 95% CI, 14.28 to 32.02; p =0.000008). During the same period, the Midwest, West, and South regions showed uptrends with APCs of 22.50 (95% CI, 14.03 to 31.60; p =0.000009), 20.15 (95% CI, 13.05 to 27.69; p =0.000004), and 17.82 (95% CI, 12.30 to 23.63; p =0.000001), respectively. Racially, AAMR increased among all the groups, and the Whites experienced the highest number of deaths (35,673). From 2019 to 2023, the non-Hispanics had a higher APC (21.03; 95% CI, 15.06 to 27.31; p < 0.000001) than the Hispanics (14.23; 95% CI, 6.72 to 22.27; p =0.000580). Micropolitan and Small Metropolitan areas showed consistent uptrends throughout the study period with APCs of 5.47 (95% CI, 4.83 to 6.13; p < 0.000001) and 4.50 (95% CI, 3.76 to 5.24; p < 0.000001), respectively.
Discussion: Mortality from liver cirrhosis and acute renal failure among older adults in the U.S. increased significantly, particularly since 2019, with marked demographic and regional disparities. These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted preventive and therapeutic strategies among the high-risk groups.

Figure: Figure 1: Twenty-Five-Year Mortality Trends in Older Adults With Coexisting Liver Cirrhosis and Acute Renal Failure in the United States: Stratification by year, sex, race/ethnicity, and urbanization

Figure: Figure 2: Twenty-Five-Year Mortality Trends in Older Adults With Coexisting Liver Cirrhosis and Acute Renal Failure in the United States: Census region wise trends
Disclosures:
Hakim Wazir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Khuram indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul Majid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Zubair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minahil Zaheer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maliha Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aman Iqbal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yukthi Mudiam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rameesha Zubair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rakhshanda Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harshawardhan Dhanraj Ramteke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hakim Wazir, MBBS1, Abdul Khuram, DO2, Abdul Majid, MBBS3, Ali Zubair, MBBS4, Minahil Zaheer, MBBS5, Maliha Khalid, MBBS6, Aman Iqbal, MBBS7, Yukthi Mudiam, MBBS8, Rameesha Zubair, MBBS2, Rakhshanda Khan, MBBS9, Harshawardhan Dhanraj Ramteke, MBBS10. P1604 - Twenty-Five-Year Mortality Trends in Older Adults With Coexisting Liver Cirrhosis and Acute Renal Failure in the United States: A CDC Multiple Cause of Death Analysis (1999–2023), ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
