Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1476 - Treatment of Complicated Post-Operative Esophagopleurocutaneous Fistula Using a Combined Gastroenterology and Interventional Radiology Approach
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Joseph Solomon, BS (he/him/his)
University of Arizona College of Medicine - Phoenix
Phoenix, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Joseph Solomon, BS1, Vanessa Eller, MD2, Pradhan Hariharan, BS1, Patrick Taggart, MD3, Kevin Liu, MD3, Kenneth S. Zurcher, MD3
1University of Arizona College of Medicine - Phoenix, Phoenix, AZ; 2University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, Phoenix, AZ; 3Banner University Medical Center, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Gastrocutaneous fistula is a rare complication of sleeve gastrectomy, occurring in 1–2% of cases. Most require complex multidisciplinary management involving surgical, endoscopic, and/or radiologic interventions. We present a case of a sleeve gastrectomy complicated by esophagopleurocutaneous fistula (EPCF) treated with a combined endoscopic and interventional radiology (IR) approach.
Case Description/
Methods: The patient is a 43-year-old female with a complex surgical history related to a sleeve gastrectomy complicated by early leak, proximal stomach staple line dehiscence, and multiple intra-abdominal abscesses. Initial esophageal stenting failed with refractory leak progressing to a gastropleural fistula and empyema requiring chest tube placements. Due to refractory fistula, she underwent thoracotomy with Ivor Lewis esophagectomy and gastric pull-up. Post-operatively, she developed an anastomotic leak at the esophagogastric anastomosis, resulting in a chronic high output EPCF.
Repeat endoscopy revealed a cratered, fibrotic 6-7 mm fistula at the anastomosis. Endoscopic therapies included argon plasma coagulation of the fistula tract, overstitch closure, and placement of a through-the-scope 20mm by 8cm covered metal stent fixed to the esophagus with endoscopic suturing. Despite initial reduction of fistula output, drainage recurred 3 months after treatment.
Combined IR and endoscopic treatment was attempted. The cutaneous fistula site was accessed with a wire and angled catheter. These were advanced under fluoroscopic guidance through the fistula into the esophagus lumen and grasped endoscopically with a snare.
A 9mm microvascular plug was deployed at the anastomotic fistula orifice under endoscopic and fluoroscopic guidance and bolstered with 6-10mm coils. The remainder of the fistula tract was embolized with Obsidio conformable embolic gel. No further leak was visualized following endoscopic injection of contrast. At 3-month follow-up, a repeat upper GI fluoroscopy study showed no evidence of residual fistula and the patient reported complete resolution of drainage.
Discussion: Refractory enterocutaneous fistulas pose a significant management challenge and often require multidisciplinary intervention. We report a complex EPCF closed with a novel combined endoscopic and IR approach. This case highlights the potential for integrated therapies in treating complex GI fistulas. Further research is needed to define the role of such combined interventions.
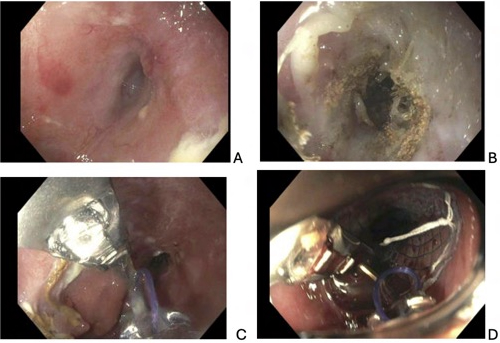
Figure: A) EPCF Opening at the esophagogastric anastomosis
B) APC for de-epithelization of the fistula tract
C) Endoscopic overstitch with closure of the fistula tract
D) Enteral stent placement over the fistula with overstitch fixation

Figure: A) Percutaneous access of EPCF with 035” glidewire and 5 French Bern catheter.
B) Embolization of fistula with microvascular plug (black arrow) and fibered metallic coils (white arrow). Endoscopic contrast injection confirms no residual leak.
C) Embolization of remaining fistula tract with Obsidio conformable gel embolic
Disclosures:
Joseph Solomon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vanessa Eller indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pradhan Hariharan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patrick Taggart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kenneth Zurcher: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Joseph Solomon, BS1, Vanessa Eller, MD2, Pradhan Hariharan, BS1, Patrick Taggart, MD3, Kevin Liu, MD3, Kenneth S. Zurcher, MD3. P1476 - Treatment of Complicated Post-Operative Esophagopleurocutaneous Fistula Using a Combined Gastroenterology and Interventional Radiology Approach, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Joseph Solomon, BS1, Vanessa Eller, MD2, Pradhan Hariharan, BS1, Patrick Taggart, MD3, Kevin Liu, MD3, Kenneth S. Zurcher, MD3
1University of Arizona College of Medicine - Phoenix, Phoenix, AZ; 2University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, Phoenix, AZ; 3Banner University Medical Center, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Gastrocutaneous fistula is a rare complication of sleeve gastrectomy, occurring in 1–2% of cases. Most require complex multidisciplinary management involving surgical, endoscopic, and/or radiologic interventions. We present a case of a sleeve gastrectomy complicated by esophagopleurocutaneous fistula (EPCF) treated with a combined endoscopic and interventional radiology (IR) approach.
Case Description/
Methods: The patient is a 43-year-old female with a complex surgical history related to a sleeve gastrectomy complicated by early leak, proximal stomach staple line dehiscence, and multiple intra-abdominal abscesses. Initial esophageal stenting failed with refractory leak progressing to a gastropleural fistula and empyema requiring chest tube placements. Due to refractory fistula, she underwent thoracotomy with Ivor Lewis esophagectomy and gastric pull-up. Post-operatively, she developed an anastomotic leak at the esophagogastric anastomosis, resulting in a chronic high output EPCF.
Repeat endoscopy revealed a cratered, fibrotic 6-7 mm fistula at the anastomosis. Endoscopic therapies included argon plasma coagulation of the fistula tract, overstitch closure, and placement of a through-the-scope 20mm by 8cm covered metal stent fixed to the esophagus with endoscopic suturing. Despite initial reduction of fistula output, drainage recurred 3 months after treatment.
Combined IR and endoscopic treatment was attempted. The cutaneous fistula site was accessed with a wire and angled catheter. These were advanced under fluoroscopic guidance through the fistula into the esophagus lumen and grasped endoscopically with a snare.
A 9mm microvascular plug was deployed at the anastomotic fistula orifice under endoscopic and fluoroscopic guidance and bolstered with 6-10mm coils. The remainder of the fistula tract was embolized with Obsidio conformable embolic gel. No further leak was visualized following endoscopic injection of contrast. At 3-month follow-up, a repeat upper GI fluoroscopy study showed no evidence of residual fistula and the patient reported complete resolution of drainage.
Discussion: Refractory enterocutaneous fistulas pose a significant management challenge and often require multidisciplinary intervention. We report a complex EPCF closed with a novel combined endoscopic and IR approach. This case highlights the potential for integrated therapies in treating complex GI fistulas. Further research is needed to define the role of such combined interventions.

Figure: A) EPCF Opening at the esophagogastric anastomosis
B) APC for de-epithelization of the fistula tract
C) Endoscopic overstitch with closure of the fistula tract
D) Enteral stent placement over the fistula with overstitch fixation

Figure: A) Percutaneous access of EPCF with 035” glidewire and 5 French Bern catheter.
B) Embolization of fistula with microvascular plug (black arrow) and fibered metallic coils (white arrow). Endoscopic contrast injection confirms no residual leak.
C) Embolization of remaining fistula tract with Obsidio conformable gel embolic
Disclosures:
Joseph Solomon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vanessa Eller indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pradhan Hariharan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patrick Taggart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kenneth Zurcher: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Joseph Solomon, BS1, Vanessa Eller, MD2, Pradhan Hariharan, BS1, Patrick Taggart, MD3, Kevin Liu, MD3, Kenneth S. Zurcher, MD3. P1476 - Treatment of Complicated Post-Operative Esophagopleurocutaneous Fistula Using a Combined Gastroenterology and Interventional Radiology Approach, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

