Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1198 - Ustekinumab vs Vedolizumab and Ustekinumab vs Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Agent Infectious Adverse Effects in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Short Report Based on Real-World Data
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Hussam Almasri, MD, MRCP(UK)
University of North Dakota, School of Medicine and Health Sciences
Fargo, ND
Presenting Author(s)
Hussam Almasri, MD, MRCP(UK)1, Abdellatif Ismail, MD2, Guneet Sidhu, MD1, Himsikhar Khataniar, MD3, Muhammad Ali Butt, MD4, Rahul Karna, MD5, John Bassett, MD6, Daphne Moutsoglou, MD, PhD7
1University of North Dakota, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Fargo, ND; 2University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD; 3Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA; 4Beth Israel Lahey Health, Burlington, MA; 5University of Minnesota Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN; 6Sanford Health, Fargo, ND; 7University of Minnesota and Minneapolis VA Health Care System, Minneapolis, MN
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC), a chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the colon, often requires immunomodulatory therapies that balance efficacy with safety. Among biologics, vedolizumab and ustekinumab have emerged as alternatives to anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) agents. We aim to address the incidence of specific infectious adverse events associated with these agents outside clinical trials using a real-world database.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX database. Three cohorts were defined as adult patients with UC, each treated with one of the following: ustekinumab, anti-TNFα agents, or vedolizumab. We used propensity score matching to balance groups regarding demographics, comorbidities, body mass index, and the use of other immunosuppressive medications. Outcomes included a new diagnosis of pneumonia, urinary tract infections, cellulitis, shingles, meningitis, Clostridioides difficile infection, or sepsis.
Results: After propensity score matching, 11,228 participants were included in each cohort comparing ustekinumab- and anti-TNFα-treated individuals, and 11.576 participants were included in each cohort comparing ustekinumab- and vedolizumab-treated individuals. Participants receiving ustekinumab demonstrated a significantly lower risk of several infections compared to those on anti-TNFα therapy, including pneumonia with an odds ratio (OR) of 0.72 (95%CI 0.58–0.89), any urinary tract infection OR 0.64 (95%CI 0.53–0.78), cellulitis OR 0.61 (95%CI 0.50–0.74), Clostridioides difficile infection OR 0.74 (95%CI 0.62–0.89), infectious diarrhea OR 0.63 (95%CI 0.47–0.85), and sepsis OR 0.70 (95%CI 0.577–0.842), (Table 1). Compared to vedolizumab, ustekinumab was associated with a reduced risk of cellulitis OR 0.77 (95%CI 0.62, 0.95) and Clostridioides difficile infection OR 0.80 (95%CI 0.67–0.95). However, no significant difference was detected for the risk of other infections (Table 2).
Discussion: Our findings demonstrate that ustekinumab is associated with a significantly lower risk of several infections and even severe infectious processes within one year when compared with anti-TNFα; however, there is a less prominent difference in infectious risk between vedolizumab and anti-TNFα agents. These results suggest that ustekinumab may offer a safer alternative, compared to anti-TNFα agents and possibly to vedolizumab, particularly those at higher risk of infections.
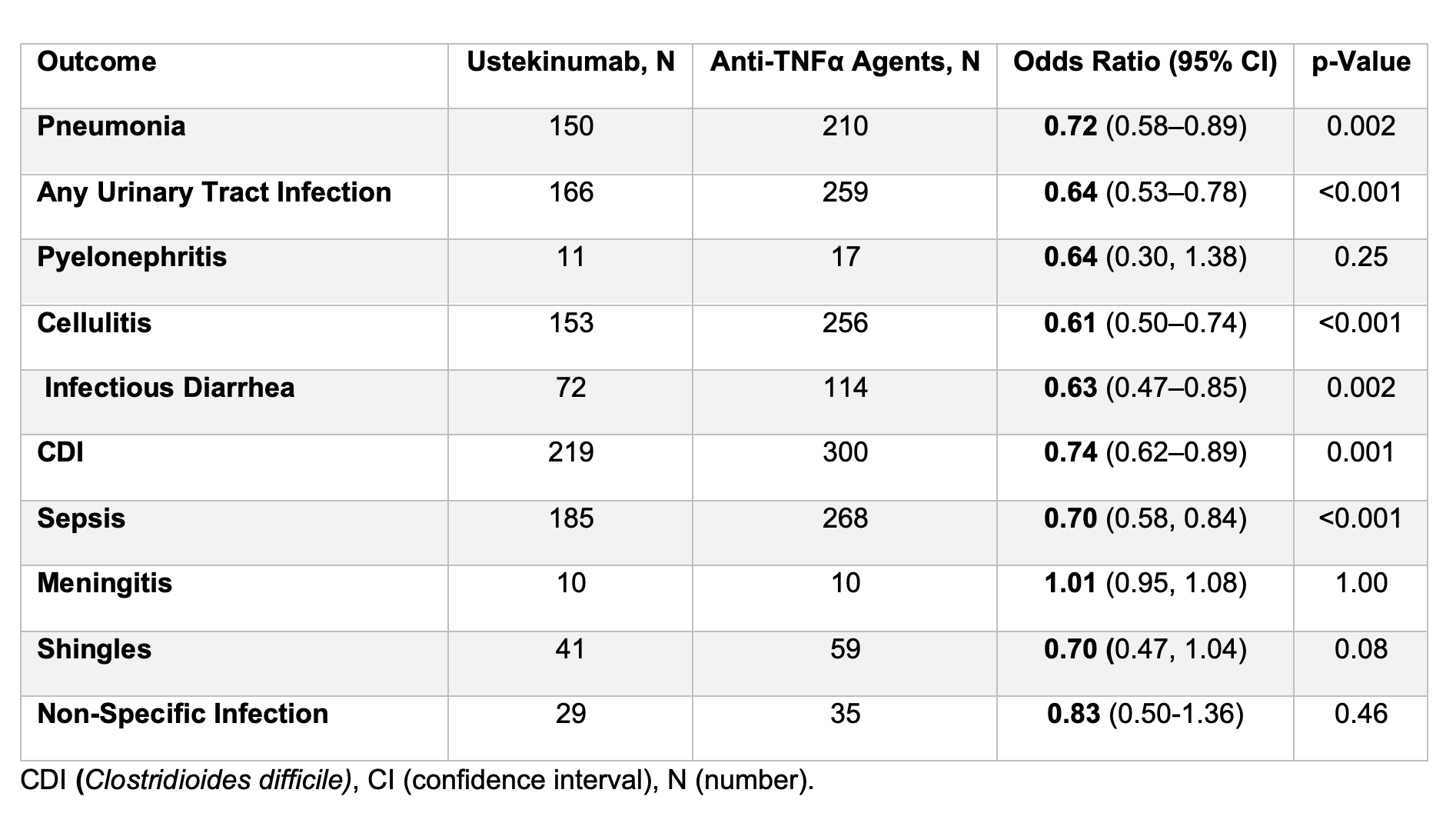
Figure: Table 1. Infectious adverse events between ustekinumab versus anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha in ulcerative colitis participants
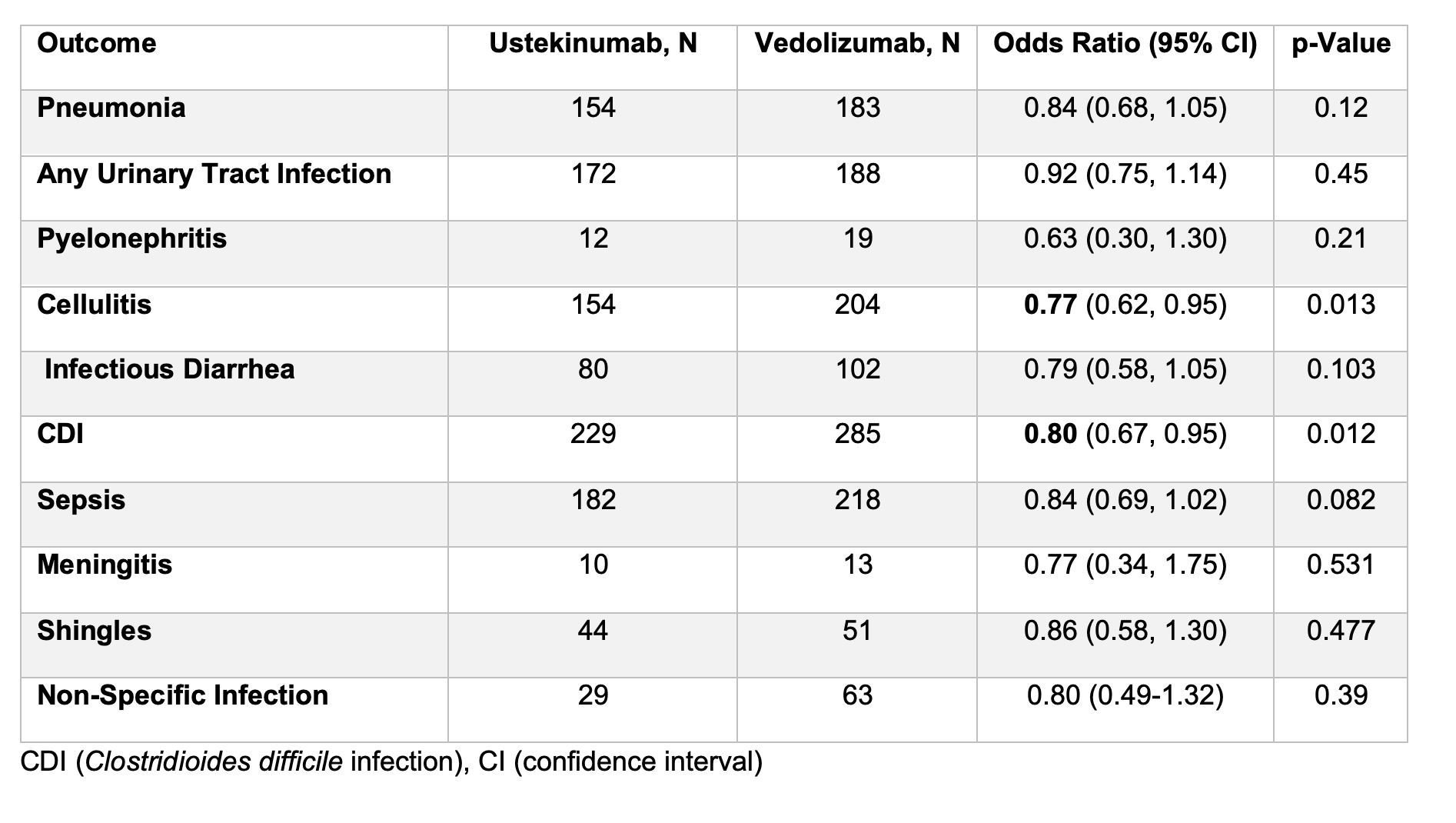
Figure: Table 2. Infectious adverse events between ustekinumab versus vedolizumab in ulcerative colitis participants
Disclosures:
Hussam Almasri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdellatif Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guneet Sidhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Himsikhar Khataniar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali Butt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Karna indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Bassett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daphne Moutsoglou indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hussam Almasri, MD, MRCP(UK)1, Abdellatif Ismail, MD2, Guneet Sidhu, MD1, Himsikhar Khataniar, MD3, Muhammad Ali Butt, MD4, Rahul Karna, MD5, John Bassett, MD6, Daphne Moutsoglou, MD, PhD7. P1198 - Ustekinumab vs Vedolizumab and Ustekinumab vs Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Agent Infectious Adverse Effects in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Short Report Based on Real-World Data, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of North Dakota, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Fargo, ND; 2University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD; 3Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA; 4Beth Israel Lahey Health, Burlington, MA; 5University of Minnesota Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN; 6Sanford Health, Fargo, ND; 7University of Minnesota and Minneapolis VA Health Care System, Minneapolis, MN
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC), a chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the colon, often requires immunomodulatory therapies that balance efficacy with safety. Among biologics, vedolizumab and ustekinumab have emerged as alternatives to anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) agents. We aim to address the incidence of specific infectious adverse events associated with these agents outside clinical trials using a real-world database.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX database. Three cohorts were defined as adult patients with UC, each treated with one of the following: ustekinumab, anti-TNFα agents, or vedolizumab. We used propensity score matching to balance groups regarding demographics, comorbidities, body mass index, and the use of other immunosuppressive medications. Outcomes included a new diagnosis of pneumonia, urinary tract infections, cellulitis, shingles, meningitis, Clostridioides difficile infection, or sepsis.
Results: After propensity score matching, 11,228 participants were included in each cohort comparing ustekinumab- and anti-TNFα-treated individuals, and 11.576 participants were included in each cohort comparing ustekinumab- and vedolizumab-treated individuals. Participants receiving ustekinumab demonstrated a significantly lower risk of several infections compared to those on anti-TNFα therapy, including pneumonia with an odds ratio (OR) of 0.72 (95%CI 0.58–0.89), any urinary tract infection OR 0.64 (95%CI 0.53–0.78), cellulitis OR 0.61 (95%CI 0.50–0.74), Clostridioides difficile infection OR 0.74 (95%CI 0.62–0.89), infectious diarrhea OR 0.63 (95%CI 0.47–0.85), and sepsis OR 0.70 (95%CI 0.577–0.842), (Table 1). Compared to vedolizumab, ustekinumab was associated with a reduced risk of cellulitis OR 0.77 (95%CI 0.62, 0.95) and Clostridioides difficile infection OR 0.80 (95%CI 0.67–0.95). However, no significant difference was detected for the risk of other infections (Table 2).
Discussion: Our findings demonstrate that ustekinumab is associated with a significantly lower risk of several infections and even severe infectious processes within one year when compared with anti-TNFα; however, there is a less prominent difference in infectious risk between vedolizumab and anti-TNFα agents. These results suggest that ustekinumab may offer a safer alternative, compared to anti-TNFα agents and possibly to vedolizumab, particularly those at higher risk of infections.

Figure: Table 1. Infectious adverse events between ustekinumab versus anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha in ulcerative colitis participants

Figure: Table 2. Infectious adverse events between ustekinumab versus vedolizumab in ulcerative colitis participants
Disclosures:
Hussam Almasri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdellatif Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guneet Sidhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Himsikhar Khataniar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali Butt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Karna indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Bassett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daphne Moutsoglou indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hussam Almasri, MD, MRCP(UK)1, Abdellatif Ismail, MD2, Guneet Sidhu, MD1, Himsikhar Khataniar, MD3, Muhammad Ali Butt, MD4, Rahul Karna, MD5, John Bassett, MD6, Daphne Moutsoglou, MD, PhD7. P1198 - Ustekinumab vs Vedolizumab and Ustekinumab vs Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Agent Infectious Adverse Effects in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Short Report Based on Real-World Data, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
