Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1150 - Effect of Subcutaneous Guselkumab on Bowel Urgency and Abdominal Pain as Measured by the UC-PRO/SS in Participants With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results From the Phase 3 ASTRO Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Jessica R. Allegretti, MD, MPH, FACG (she/her/hers)
Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Silvio Danese, MD, PhD1, Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet, MD, PhD2, Millie D. Long, MD, FACG3, Matthew Germinaro, MD4, Thomas Baker, MD4, Yelina Alvarez, 4, Mary Kavalam, 4, Chenglong Han, 5, Silke Jorgens, 6, Lingjing Jiang, 4, Hongyan Zhang, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD7, David T. Rubin, MD8, Jessica R.. Allegretti, MD, MPH9
1Gastroenterology and Endoscopy, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele and University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Lombardia, Italy; 2Department of Gastroenterology, CHRU Nancy, INSERM NGERE, Université de Lorraine, France, Vandœuvre-lès-Nancy, Lorraine, France; 3Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, Chapel Hill, NC; 4Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA; 5Johnson & Johnson, Malvern, PA; 6Johnson & Johnson, Neuss, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany; 7Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 8University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL; 9Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Introduction: Guselkumab (GUS), a dual-acting IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor, demonstrated efficacy in participants (pts) with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) treated with GUS subcutaneous (SC) induction and maintenance in the Phase 3 ASTRO study. Here, we present data for bowel urgency and abdominal pain symptoms as measured by the Ulcerative Colitis Patient-Reported Outcomes Signs and Symptoms (UC-PRO/SS) instrument through Week (W) 24.
Methods: Eligible pts had a modified Mayo score of 5 to 9, a rectal bleeding subscore of ≥1, and a Mayo endoscopic subscore (MES) ≥2. Pts had a documented inadequate response/intolerance to biologics, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, and/or sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) inhibitors (BIO/JAKi/S1Pi-IR) or to corticosteroids, 6-mercaptopurine, or azathioprine. Randomization was stratified by baseline BIO/JAKi/S1Pi-IR status and MES with 418 pts allocated 1:1:1 to GUS 400 mg SC every 4 weeks (q4w) (x3)→GUS 200 mg SC q4w (N=140), GUS 400 mg SC q4w (x3)→GUS 100 mg SC every 8 weeks (q8w) (N=139), or placebo (PBO) (N=139). Pts who met rescue criteria at W16 were rescued: PBO pts switched to GUS; GUS pts stayed on their assigned GUS dose regimen (sham rescue). The UC-PRO/SS is a validated instrument to assess the severity of bowel-related symptoms.1 Clinically meaningful improvements (CMI) in bowel signs and symptoms and abdominal symptoms scales were evaluated. Complete resolution of individual core symptoms (bowel urgency and abdominal pain) was assessed.
Results: GUS-treated pts achieved greater improvement from baseline through W24 in domain and individual core symptoms compared with PBO-treated pts (Figure 1A and Figure 2A). The proportions of pts achieving CMI in each domain score were also greater for GUS vs PBO (Figure 1B). Among pts with bowel urgency symptoms at baseline, 45.0% receiving GUS had resolution of bowel urgency by W12 compared with 23.1% for PBO, and these levels were maintained through W24 (Figure 2B). Among pts with abdominal pain symptoms at baseline, 48.8% receiving GUS had resolution of abdominal pain by W12 compared with 23.9% for PBO, and these levels were also maintained through W24. Among all pts, proportions with no bowel urgency or abdominal pain are shown in Figure 2C.
Discussion: Pts with moderately to severely active UC treated with GUS SC experienced clinically meaningful improvements through W24 in UC signs and symptoms as measured by UC-PRO/SS compared with PBO.
1. Higgins PDR, et al. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2017;2:26.
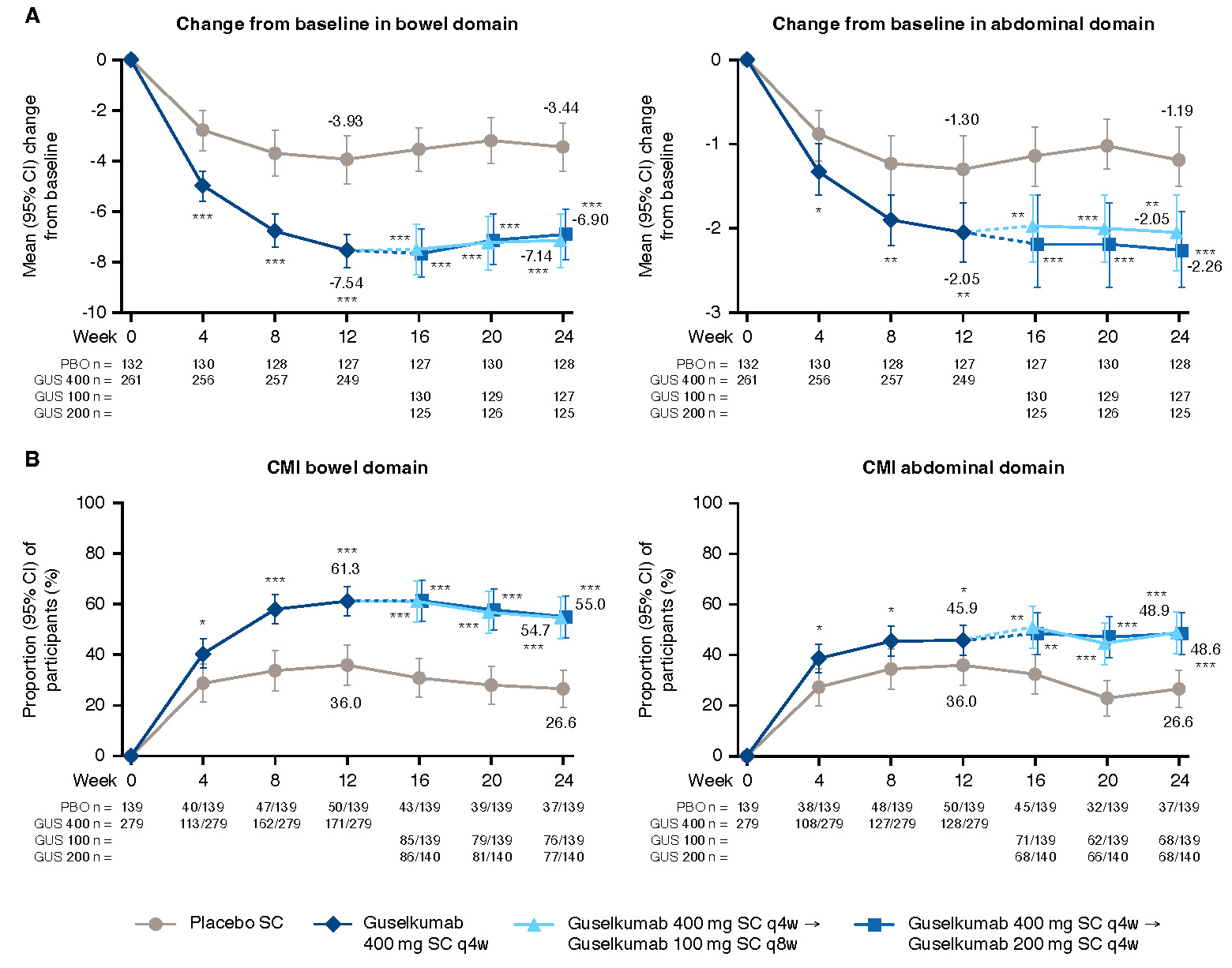
Figure: Figure 1. Change from baseline and clinically meaningful improvement from baseline through Week 24 for UC-PRO/SS domain scores
*nominal p-value <0.05 GUS vs PBO; **nominal p-value <0.01 GUS vs PBO; ***nominal p-value <0.001 GUS vs PBO; values are mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. NOTE: The prespecified analysis plan compared the combined GUS 400 mg SC group to PBO at W12 (both the GUS 100 mg q8w and 200 mg q4w groups received the same induction dosing regimen through W12) and each GUS group to PBO at W24. Participants who, prior to the designated timepoint, had an ostomy or colectomy, a prohibited change in UC medications, discontinued study intervention due to lack of efficacy or an adverse event of worsening of UC, or met rescue criteria had their baseline value carried forward from the time of the event onward or were considered not to have met the dichotomous endpoint. For participants who discontinued study intervention due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis prior to the designated timepoint, their observed values were used, if available. Participants who discontinued study intervention due to reasons other than those described above prior to the designated timepoint had their baseline value carried forward from the time of the event onward or were considered not to have met the dichotomous endpoint.
A) Change from baseline in domain scores through W24. Baseline scores, mean (SD), bowel domain (0-27): placebo, 13.2 (4.4), N=132; 100 mg SC q8w, 13.1 (4.3), N=131; 200 mg SC q4w, 13.1 (4.1), N=130; 400 mg SC combined, 13.1 (4.2), N=261; abdominal symptoms domain (0-12): placebo, 5.2 (2.5), N=132; 100 mg SC q8w, 5.3 (2.5), N=131; 200 mg SC q4w, 5.1 (2.5), N=130; 400 mg SC combined, 5.2 (2.5), N=261.
B) Clinically meaningful improvement from baseline through W24. Bowel domain CMI was defined as ≥5 point improvement from baseline in the bowel domain. Abdominal domain CMI was defined as ≥1.5 point improvement from baseline in the abdominal symptoms domain.
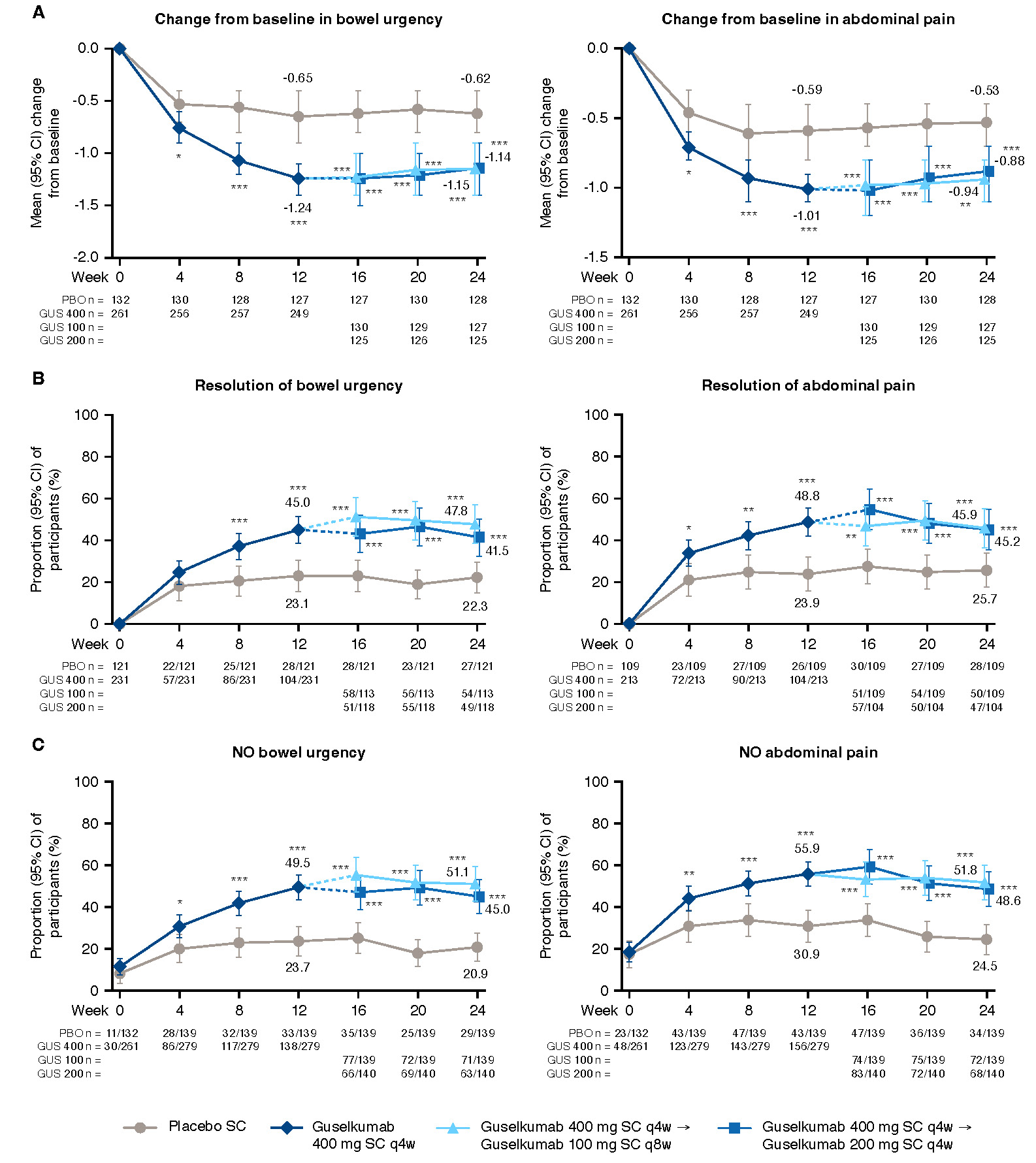
Figure: Figure 2. Change from baseline and resolution of symptoms from baseline through Week 24 for UC-PRO/SS individual symptom scores
*nominal p-value <0.05 GUS vs PBO; **nominal p-value <0.01 GUS vs PBO; ***nominal p-value <0.001 GUS vs PBO; values are mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. NOTE: The prespecified analysis plan compared the combined GUS 400 mg SC group to PBO at W12 (both the GUS 100 mg q8w and 200 mg q4w groups received the same induction dosing regimen through W12) and each GUS group to PBO at W24. Participants who, prior to the designated timepoint, had an ostomy or colectomy, a prohibited change in UC medications, discontinued study intervention due to lack of efficacy or an adverse event of worsening of UC, or met rescue criteria had their baseline value carried forward from the time of the event onward or were considered not to have met the dichotomous endpoint. For participants who discontinued study intervention due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis prior to the designated timepoint, their observed values were used, if available. Participants who discontinued study intervention due to reasons other than those described above prior to the designated timepoint had their baseline value carried forward from the time of the event onward or were considered not to have met the dichotomous endpoint.
A) Change from baseline in individual symptom scores through W24. Baseline scores, mean (SD), bowel urgency (0-4): placebo, 2.3 (1.1), N=132; 100 mg SC q8w, 2.2 (1.1), N=131; 200 mg SC q4w, 2.3 (1.0), N=130; 400 mg SC combined, 2.2 (1.1), N=261; abdominal pain (0-4): placebo, 1.7 (1.1), N=132; 100 mg SC q8w, 1.8 (1.1), N=131; 200 mg SC q4w, 1.6 (1.1), N=130; 400 mg SC combined, 1.7 (1.1), N=261.
B) Resolution of individual symptoms from baseline through W24. Resolution of bowel urgency is defined as the rounded weekly average UC-PRO/SS item 7 score = 0 over eligible days within 7 days prior to the designated timepoint when rounded weekly average item 7 score 1 over eligible days within 7 days prior to baseline. Denominator is participants with bowel urgency at baseline. Resolution of abdominal pain is defined as the rounded weekly average UC-PRO/SS item 8 score = 0 over eligible days within 7 days prior to the designated timepoint when rounded weekly average item 8 score 1 over eligible days within 7 days prior to baseline. Denominator is participants with abdominal pain at baseline.
C) No individual symptom pain from baseline through W24. No bowel urgency is defined as the rounded weekly average UC-PRO/SS item 7 score = 0 over eligible days within 7 days prior to the designated timepoint. UC-PRO/SS Question 7: In the past 24 hours, did you feel the need to have a bowel movement right away? No abdominal pain is defined as the rounded weekly average UC-PRO/SS item 8 score = 0 over eligible days within 7 days prior to the designated timepoint. UC-PRO/SS Question 8: In the past 24 hours, did you feel pain in your belly?
Disclosures:
Silvio Danese: AbbVie – Consultant, Lecture fees. Alimentiv – Consultant. Allergan – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant, Lecture fees. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Athos Therapeutics – Consultant. Biogen – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Lecture fees. Gilead – Consultant, Lecture fees. Hospira – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. MSD – Consultant. Mundipharma – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant, Lecture fees. Pfizer – Consultant, Lecture fees. Sandoz – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Lecture fees. TiGenix – Consultant. UCB Inc. – Consultant. Vifor (International) Ltd. – Consultant.
Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet: AbbVie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Abivax – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Adacyte – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Alfasigma – Speakers Bureau. Alimentiv – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Amgen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Applied Molecular Transport – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Arena – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Banook – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Biogen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Connect Biopharm – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Cytoki Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Enthera – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Fresenius Kabi – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria. Galapagos – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Genentech – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Gilead – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Gossamer Bio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. GSK – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. IAC Image Analysis – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Index Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Inotrem – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Janssen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Medac – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Mopac – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Morphic – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. MSD – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Nordic Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Novartis – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Oncodesign Precision Medicine – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. ONO Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. OSE Immunotherapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Pandion Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Par' Immune – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Prometheus – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Protagonist – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Samsung – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Sandoz – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Satisfay – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Takeda – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Telavant – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Theravance – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Thermo Fischer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Tigenix – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Tillots – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Vectivbio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Ventyx – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Viatris – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Ysopia – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria.
Millie Long: AbbVie – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Intercept – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant. Lilly – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Merck – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus – Consultant. Roivant – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Target RWE – Consultant.
Matthew Germinaro: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Thomas Baker: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Yelina Alvarez: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Mary Kavalam: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options.
Chenglong Han: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Silke Jorgens: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Lingjing Jiang: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Hongyan Zhang: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Tadakazu Hisamatsu: AbbVie GK – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Boston Scientific Corporation – Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Honararium. EA Pharma Co. Ltd. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. JIMRO Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. Kissei Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Lilly – Consultant. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Mochida Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Nichi-Iko Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd – Consultant. Nippon Kayaku Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Zeria Pharmaceutical Co – Grant/Research Support.
David Rubin: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Altrubio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau, Stock Options. Apex – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Buhlmann Diagnostics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Connect BioPharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Cornerstones Health, Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Crohn's & Colitis Foundation – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Datos Health – Stock Options. Intouch Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau, Stock Options. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Samsung Neurologica – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Jessica Allegretti: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker, Speakers Bureau. Adiso – Consultant. Bristol Myer Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Finch – Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Iterative Scopes – Consultant. Janssen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker. Merck – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Roivant – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roivant Adiso – Consultant. Seres Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Shattuck Labs – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. TRXBio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Vedanta – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Silvio Danese, MD, PhD1, Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet, MD, PhD2, Millie D. Long, MD, FACG3, Matthew Germinaro, MD4, Thomas Baker, MD4, Yelina Alvarez, 4, Mary Kavalam, 4, Chenglong Han, 5, Silke Jorgens, 6, Lingjing Jiang, 4, Hongyan Zhang, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD7, David T. Rubin, MD8, Jessica R.. Allegretti, MD, MPH9. P1150 - Effect of Subcutaneous Guselkumab on Bowel Urgency and Abdominal Pain as Measured by the UC-PRO/SS in Participants With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results From the Phase 3 ASTRO Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Gastroenterology and Endoscopy, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele and University Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Lombardia, Italy; 2Department of Gastroenterology, CHRU Nancy, INSERM NGERE, Université de Lorraine, France, Vandœuvre-lès-Nancy, Lorraine, France; 3Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, Chapel Hill, NC; 4Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA; 5Johnson & Johnson, Malvern, PA; 6Johnson & Johnson, Neuss, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany; 7Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 8University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL; 9Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Introduction: Guselkumab (GUS), a dual-acting IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor, demonstrated efficacy in participants (pts) with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) treated with GUS subcutaneous (SC) induction and maintenance in the Phase 3 ASTRO study. Here, we present data for bowel urgency and abdominal pain symptoms as measured by the Ulcerative Colitis Patient-Reported Outcomes Signs and Symptoms (UC-PRO/SS) instrument through Week (W) 24.
Methods: Eligible pts had a modified Mayo score of 5 to 9, a rectal bleeding subscore of ≥1, and a Mayo endoscopic subscore (MES) ≥2. Pts had a documented inadequate response/intolerance to biologics, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, and/or sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) inhibitors (BIO/JAKi/S1Pi-IR) or to corticosteroids, 6-mercaptopurine, or azathioprine. Randomization was stratified by baseline BIO/JAKi/S1Pi-IR status and MES with 418 pts allocated 1:1:1 to GUS 400 mg SC every 4 weeks (q4w) (x3)→GUS 200 mg SC q4w (N=140), GUS 400 mg SC q4w (x3)→GUS 100 mg SC every 8 weeks (q8w) (N=139), or placebo (PBO) (N=139). Pts who met rescue criteria at W16 were rescued: PBO pts switched to GUS; GUS pts stayed on their assigned GUS dose regimen (sham rescue). The UC-PRO/SS is a validated instrument to assess the severity of bowel-related symptoms.1 Clinically meaningful improvements (CMI) in bowel signs and symptoms and abdominal symptoms scales were evaluated. Complete resolution of individual core symptoms (bowel urgency and abdominal pain) was assessed.
Results: GUS-treated pts achieved greater improvement from baseline through W24 in domain and individual core symptoms compared with PBO-treated pts (Figure 1A and Figure 2A). The proportions of pts achieving CMI in each domain score were also greater for GUS vs PBO (Figure 1B). Among pts with bowel urgency symptoms at baseline, 45.0% receiving GUS had resolution of bowel urgency by W12 compared with 23.1% for PBO, and these levels were maintained through W24 (Figure 2B). Among pts with abdominal pain symptoms at baseline, 48.8% receiving GUS had resolution of abdominal pain by W12 compared with 23.9% for PBO, and these levels were also maintained through W24. Among all pts, proportions with no bowel urgency or abdominal pain are shown in Figure 2C.
Discussion: Pts with moderately to severely active UC treated with GUS SC experienced clinically meaningful improvements through W24 in UC signs and symptoms as measured by UC-PRO/SS compared with PBO.
1. Higgins PDR, et al. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2017;2:26.

Figure: Figure 1. Change from baseline and clinically meaningful improvement from baseline through Week 24 for UC-PRO/SS domain scores
*nominal p-value <0.05 GUS vs PBO; **nominal p-value <0.01 GUS vs PBO; ***nominal p-value <0.001 GUS vs PBO; values are mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. NOTE: The prespecified analysis plan compared the combined GUS 400 mg SC group to PBO at W12 (both the GUS 100 mg q8w and 200 mg q4w groups received the same induction dosing regimen through W12) and each GUS group to PBO at W24. Participants who, prior to the designated timepoint, had an ostomy or colectomy, a prohibited change in UC medications, discontinued study intervention due to lack of efficacy or an adverse event of worsening of UC, or met rescue criteria had their baseline value carried forward from the time of the event onward or were considered not to have met the dichotomous endpoint. For participants who discontinued study intervention due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis prior to the designated timepoint, their observed values were used, if available. Participants who discontinued study intervention due to reasons other than those described above prior to the designated timepoint had their baseline value carried forward from the time of the event onward or were considered not to have met the dichotomous endpoint.
A) Change from baseline in domain scores through W24. Baseline scores, mean (SD), bowel domain (0-27): placebo, 13.2 (4.4), N=132; 100 mg SC q8w, 13.1 (4.3), N=131; 200 mg SC q4w, 13.1 (4.1), N=130; 400 mg SC combined, 13.1 (4.2), N=261; abdominal symptoms domain (0-12): placebo, 5.2 (2.5), N=132; 100 mg SC q8w, 5.3 (2.5), N=131; 200 mg SC q4w, 5.1 (2.5), N=130; 400 mg SC combined, 5.2 (2.5), N=261.
B) Clinically meaningful improvement from baseline through W24. Bowel domain CMI was defined as ≥5 point improvement from baseline in the bowel domain. Abdominal domain CMI was defined as ≥1.5 point improvement from baseline in the abdominal symptoms domain.

Figure: Figure 2. Change from baseline and resolution of symptoms from baseline through Week 24 for UC-PRO/SS individual symptom scores
*nominal p-value <0.05 GUS vs PBO; **nominal p-value <0.01 GUS vs PBO; ***nominal p-value <0.001 GUS vs PBO; values are mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. NOTE: The prespecified analysis plan compared the combined GUS 400 mg SC group to PBO at W12 (both the GUS 100 mg q8w and 200 mg q4w groups received the same induction dosing regimen through W12) and each GUS group to PBO at W24. Participants who, prior to the designated timepoint, had an ostomy or colectomy, a prohibited change in UC medications, discontinued study intervention due to lack of efficacy or an adverse event of worsening of UC, or met rescue criteria had their baseline value carried forward from the time of the event onward or were considered not to have met the dichotomous endpoint. For participants who discontinued study intervention due to COVID-19 related reasons (excluding COVID-19 infection) or regional crisis prior to the designated timepoint, their observed values were used, if available. Participants who discontinued study intervention due to reasons other than those described above prior to the designated timepoint had their baseline value carried forward from the time of the event onward or were considered not to have met the dichotomous endpoint.
A) Change from baseline in individual symptom scores through W24. Baseline scores, mean (SD), bowel urgency (0-4): placebo, 2.3 (1.1), N=132; 100 mg SC q8w, 2.2 (1.1), N=131; 200 mg SC q4w, 2.3 (1.0), N=130; 400 mg SC combined, 2.2 (1.1), N=261; abdominal pain (0-4): placebo, 1.7 (1.1), N=132; 100 mg SC q8w, 1.8 (1.1), N=131; 200 mg SC q4w, 1.6 (1.1), N=130; 400 mg SC combined, 1.7 (1.1), N=261.
B) Resolution of individual symptoms from baseline through W24. Resolution of bowel urgency is defined as the rounded weekly average UC-PRO/SS item 7 score = 0 over eligible days within 7 days prior to the designated timepoint when rounded weekly average item 7 score 1 over eligible days within 7 days prior to baseline. Denominator is participants with bowel urgency at baseline. Resolution of abdominal pain is defined as the rounded weekly average UC-PRO/SS item 8 score = 0 over eligible days within 7 days prior to the designated timepoint when rounded weekly average item 8 score 1 over eligible days within 7 days prior to baseline. Denominator is participants with abdominal pain at baseline.
C) No individual symptom pain from baseline through W24. No bowel urgency is defined as the rounded weekly average UC-PRO/SS item 7 score = 0 over eligible days within 7 days prior to the designated timepoint. UC-PRO/SS Question 7: In the past 24 hours, did you feel the need to have a bowel movement right away? No abdominal pain is defined as the rounded weekly average UC-PRO/SS item 8 score = 0 over eligible days within 7 days prior to the designated timepoint. UC-PRO/SS Question 8: In the past 24 hours, did you feel pain in your belly?
Disclosures:
Silvio Danese: AbbVie – Consultant, Lecture fees. Alimentiv – Consultant. Allergan – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant, Lecture fees. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Athos Therapeutics – Consultant. Biogen – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Consultant, Lecture fees. Gilead – Consultant, Lecture fees. Hospira – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. MSD – Consultant. Mundipharma – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant, Lecture fees. Pfizer – Consultant, Lecture fees. Sandoz – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Lecture fees. TiGenix – Consultant. UCB Inc. – Consultant. Vifor (International) Ltd. – Consultant.
Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet: AbbVie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Abivax – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Adacyte – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Alfasigma – Speakers Bureau. Alimentiv – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Amgen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Applied Molecular Transport – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Arena – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Banook – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Biogen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Connect Biopharm – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Cytoki Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Enthera – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Fresenius Kabi – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria. Galapagos – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Genentech – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Gilead – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Gossamer Bio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. GSK – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. IAC Image Analysis – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Index Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Inotrem – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Janssen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Medac – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Mopac – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Morphic – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. MSD – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Nordic Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Novartis – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Oncodesign Precision Medicine – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. ONO Pharma – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. OSE Immunotherapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Pandion Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Par' Immune – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Prometheus – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Protagonist – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Samsung – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Sandoz – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Satisfay – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Takeda – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Telavant – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Theravance – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Thermo Fischer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support. Tigenix – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Tillots – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, meeting attendance/travel support, Speakers Bureau. Vectivbio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Ventyx – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria. Viatris – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Ysopia – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Honoraria.
Millie Long: AbbVie – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Intercept – Consultant. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant. Lilly – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Merck – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus – Consultant. Roivant – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Target RWE – Consultant.
Matthew Germinaro: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Thomas Baker: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Yelina Alvarez: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Mary Kavalam: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options.
Chenglong Han: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Silke Jorgens: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Lingjing Jiang: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Hongyan Zhang: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Tadakazu Hisamatsu: AbbVie GK – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Boston Scientific Corporation – Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Honararium. EA Pharma Co. Ltd. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. JIMRO Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Lecture fees. Kissei Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Lilly – Consultant. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Mochida Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Nichi-Iko Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd – Consultant. Nippon Kayaku Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer Inc. – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. – Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Zeria Pharmaceutical Co – Grant/Research Support.
David Rubin: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Altrubio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau, Stock Options. Apex – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Buhlmann Diagnostics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Connect BioPharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Cornerstones Health, Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Crohn's & Colitis Foundation – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Datos Health – Stock Options. Intouch Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau, Stock Options. Johnson & Johnson – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Samsung Neurologica – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Jessica Allegretti: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker, Speakers Bureau. Adiso – Consultant. Bristol Myer Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Finch – Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Iterative Scopes – Consultant. Janssen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker. Merck – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Roivant – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roivant Adiso – Consultant. Seres Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Shattuck Labs – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. TRXBio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Vedanta – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Silvio Danese, MD, PhD1, Laurent Peyrin-Biroulet, MD, PhD2, Millie D. Long, MD, FACG3, Matthew Germinaro, MD4, Thomas Baker, MD4, Yelina Alvarez, 4, Mary Kavalam, 4, Chenglong Han, 5, Silke Jorgens, 6, Lingjing Jiang, 4, Hongyan Zhang, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD7, David T. Rubin, MD8, Jessica R.. Allegretti, MD, MPH9. P1150 - Effect of Subcutaneous Guselkumab on Bowel Urgency and Abdominal Pain as Measured by the UC-PRO/SS in Participants With Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results From the Phase 3 ASTRO Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
