Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1122 - Evaluating Effectiveness and Safety of a GLP-1 Agonist in Obese Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Moulika kari, MBBS
Maimonides Medical Center
New York City, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Moulika Kari, MBBS1, Pratiksha Shankarlal Nathani, MBBS2, Anushka Dhabuwala, MBBS3, Vaishnavi Kanisetti, MBBS4, Helai Hussaini, MD5, Shashank Gupta, MBBS6, Ankitkumar R. Patel, MBBS7, Shrutik P. Borda, MBBS8, Rupak Desai, MBBS9
1Maimonides Medical Center, New York City, NY; 2St. Barbanbas Hospital, New York City, NY; 3Government Medical College, Surat, Valhalla, NY; 4Bhaskar Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 5west anaheim medical center, Anaheim, CA; 6Mayo Clinic, Brentwood, CA; 7Narendra Modi medical college, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 8Narendra Modi Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 9Independent Outcomes Researcher, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: Obesity is rising among people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), complicating management and treatment response. GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are widely used for weight loss and glycemic control, but their safety and effects on IBD are unclear. This study aims to assess the safety and efficacy of GLP-1 RAs in obese IBD patients by evaluating changes in body weight, disease activity, inflammatory markers (e.g., CRP), and adverse events.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar for studies published up to May 2025 that evaluated the use of GLP-1 RAs in obese patients with IBD. Search terms included: “Semaglutide,” “glucagon-like peptide,” “Inflammatory Bowel Disease,” “IBD,” “ulcerative colitis,” and “Crohn’s.” We included retrospective and observational studies published in English in peer-reviewed journals that assessed the impact of GLP-1 agonists on weight change, inflammatory markers, and adverse events in the target population. Studies were included if they involved obese (BMI >30 kg/m²) patients with IBD receiving GLP-1-based therapies. Exclusion criteria were studies involving non-obese IBD patients, animal or in vitro models, and reviews without original data. Study selection followed the PICO framework, and all eligible articles were independently reviewed and extracted using a standardized data collection form.
Results: Five studies (n = 546 patients) met inclusion criteria. GLP-1 receptor agonists were consistently associated with reductions in body weight and BMI. One study reported that 58.3% of patients achieved >5% weight loss at six months, while others demonstrated statistically significant reductions in weight without reporting thresholds. No study reported increased rates of IBD exacerbations, hospitalizations, or need for escalation of therapy. Improvements in CRP were noted in some cohorts. Adverse events were primarily gastrointestinal, including nausea and constipation, and were generally mild.
Discussion: This review supports the potential role of GLP-1 receptor agonists as a safe and effective treatment option for weight reduction in obese patients with IBD, without exacerbating disease activity. These agents may offer a dual therapeutic benefit by addressing both metabolic and inflammatory pathways. Future prospective studies and randomized controlled trials are needed to establish long-term efficacy, clarify their role in disease modulation, and inform clinical guidelines.
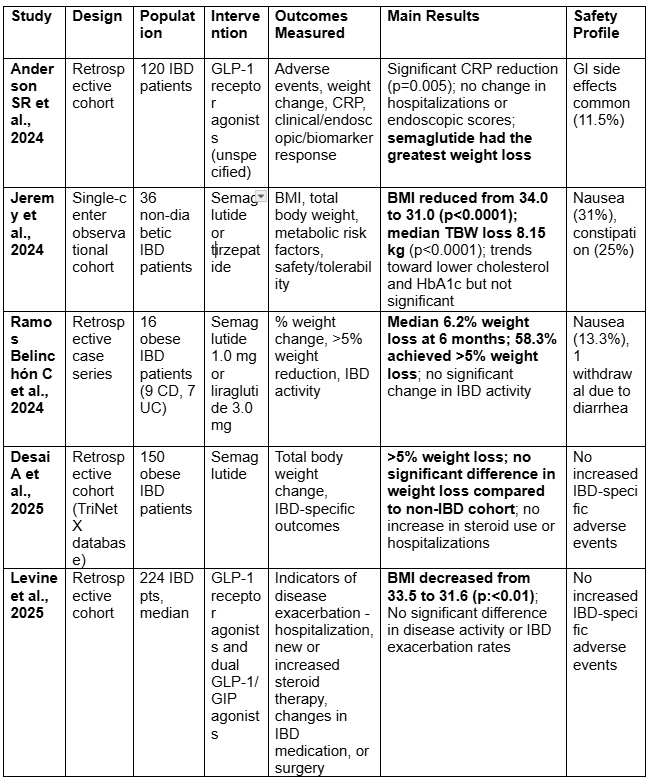
Figure: Summary of Studies Evaluating GLP-1 RA in Obese Patients with IBD
Disclosures:
Moulika Kari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pratiksha Shankarlal Nathani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anushka Dhabuwala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vaishnavi Kanisetti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Helai Hussaini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shashank Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ankitkumar R. Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shrutik P. Borda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rupak Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moulika Kari, MBBS1, Pratiksha Shankarlal Nathani, MBBS2, Anushka Dhabuwala, MBBS3, Vaishnavi Kanisetti, MBBS4, Helai Hussaini, MD5, Shashank Gupta, MBBS6, Ankitkumar R. Patel, MBBS7, Shrutik P. Borda, MBBS8, Rupak Desai, MBBS9. P1122 - Evaluating Effectiveness and Safety of a GLP-1 Agonist in Obese Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Maimonides Medical Center, New York City, NY; 2St. Barbanbas Hospital, New York City, NY; 3Government Medical College, Surat, Valhalla, NY; 4Bhaskar Medical College, Hyderabad, Telangana, India; 5west anaheim medical center, Anaheim, CA; 6Mayo Clinic, Brentwood, CA; 7Narendra Modi medical college, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 8Narendra Modi Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 9Independent Outcomes Researcher, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: Obesity is rising among people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), complicating management and treatment response. GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are widely used for weight loss and glycemic control, but their safety and effects on IBD are unclear. This study aims to assess the safety and efficacy of GLP-1 RAs in obese IBD patients by evaluating changes in body weight, disease activity, inflammatory markers (e.g., CRP), and adverse events.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar for studies published up to May 2025 that evaluated the use of GLP-1 RAs in obese patients with IBD. Search terms included: “Semaglutide,” “glucagon-like peptide,” “Inflammatory Bowel Disease,” “IBD,” “ulcerative colitis,” and “Crohn’s.” We included retrospective and observational studies published in English in peer-reviewed journals that assessed the impact of GLP-1 agonists on weight change, inflammatory markers, and adverse events in the target population. Studies were included if they involved obese (BMI >30 kg/m²) patients with IBD receiving GLP-1-based therapies. Exclusion criteria were studies involving non-obese IBD patients, animal or in vitro models, and reviews without original data. Study selection followed the PICO framework, and all eligible articles were independently reviewed and extracted using a standardized data collection form.
Results: Five studies (n = 546 patients) met inclusion criteria. GLP-1 receptor agonists were consistently associated with reductions in body weight and BMI. One study reported that 58.3% of patients achieved >5% weight loss at six months, while others demonstrated statistically significant reductions in weight without reporting thresholds. No study reported increased rates of IBD exacerbations, hospitalizations, or need for escalation of therapy. Improvements in CRP were noted in some cohorts. Adverse events were primarily gastrointestinal, including nausea and constipation, and were generally mild.
Discussion: This review supports the potential role of GLP-1 receptor agonists as a safe and effective treatment option for weight reduction in obese patients with IBD, without exacerbating disease activity. These agents may offer a dual therapeutic benefit by addressing both metabolic and inflammatory pathways. Future prospective studies and randomized controlled trials are needed to establish long-term efficacy, clarify their role in disease modulation, and inform clinical guidelines.

Figure: Summary of Studies Evaluating GLP-1 RA in Obese Patients with IBD
Disclosures:
Moulika Kari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pratiksha Shankarlal Nathani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anushka Dhabuwala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vaishnavi Kanisetti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Helai Hussaini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shashank Gupta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ankitkumar R. Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shrutik P. Borda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rupak Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moulika Kari, MBBS1, Pratiksha Shankarlal Nathani, MBBS2, Anushka Dhabuwala, MBBS3, Vaishnavi Kanisetti, MBBS4, Helai Hussaini, MD5, Shashank Gupta, MBBS6, Ankitkumar R. Patel, MBBS7, Shrutik P. Borda, MBBS8, Rupak Desai, MBBS9. P1122 - Evaluating Effectiveness and Safety of a GLP-1 Agonist in Obese Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
