Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1115 - Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Biologic Therapies in Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SK
Sabah Kulsum, MD (she/her/hers)
St. Mary's General Hospital, New York Medical College
Pine Brook, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Nayanika Tummala, MD1, Sabah Kulsum, MD2, Hakim Wazir, MBBS3, Saniya Ishtiaq, MBBS4, Muhamaad Maaz, MBBS5, M. Rafiqul Islam, 6, Maryam Muzaffar, MD7, Ammarah Tariq, MD4, Nimra Ehsan, 8, Rithish Nimmagadda, MBBS9, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD10
1St. Mary's General Hospital, New York Medical College, Pine Brook, NJ; 2St. Mary's General Hospital, New York Medical College, Poughkeepsie, NY; 3Gajju Khan Medical College,Swabi Pakistan Medicine department, Shahmansor, Swabi, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 4Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Bacha Khan Medical College, Mardan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 6Suhrawardy Medical College Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh, Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh; 7Allama Iqbal medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Khyber Medical College, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 9One Brooklyn Health-Interfaith Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 10NYMC at St. Mary’s General hospital amd st clares health, Parsippany, NJ
Introduction: Biologic therapies have transformed Crohn’s disease (CD) treatment, especially in moderate-to-severe cases. However, selecting the right biologic after anti-TNF failure remains challenging. This review aims to compare the efficacy and safety of various biologics, integrating recent evidence.
Methods: Literature Search & Selection:
Following PRISMA guidelines, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Embase, and ClinicalTrials.gov for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating biologic therapies in moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. Studies were screened using Rayyan, with data extracted into Excel spreadsheets.
Analysis:
Using R 4.4.3 software, a Bayesian network meta-analysis was performed and pooled Odd Ratios (OR) or Relative Risk (RR) with 95% credible intervals (CrIs) were approximated using a random or fixed effects model based on deviance information criteria (DIC). Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) values were calculated to rank interventions across outcomes.
Results: We identified 14 RCTs encompassing 6,360 patients and 23 treatment arms. Risankizumab (RZB) 1200 mg Q4W yielded the highest clinical remission rate compared to placebo (RR: 2.72; 95% CrI: 1.11–7.33), though its SUCRA value was modest (0.379). Ustekinumab (UST), RZB 600 mg, and infliximab also outperformed placebo. Interestingly, vedolizumab (VDZ) 300 mg Q4W achieved the highest SUCRA score (0.874) for remission, despite lower RR values. For clinical response, UST 90 mg Q8W showed the strongest signal (OR: 24.52; 95% CrI: 0.14–7192.58), with UST Q12W and RZB 1200 mg following. Endoscopic healing was most evident with RZB 600 mg (RR: 2.36; 95% CrI: 1.03–5.36), but mirikizumab ranked highest in SUCRA (0.77). On safety outcomes, RZB 600 mg had the highest adverse event rate (RR: 1.19), whereas VDZ, infliximab, and certolizumab (CZP) exhibited lower rates. CZP was particularly notable for safety, with the lowest log RR for serious adverse events (–2.10; 95% CrI: –4.34 to –0.17) and a SUCRA of 0.92. VDZ also showed a favorable safety profile.
Discussion: IL-23 inhibitors such as risankizumab and ustekinumab appear highly effective for inducing both clinical and endoscopic remission. In contrast, vedolizumab and certolizumab stand out for their safety, particularly regarding serious adverse events. These insights support a personalized approach to biologic sequencing, balancing treatment efficacy with safety considerations in managing moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease.
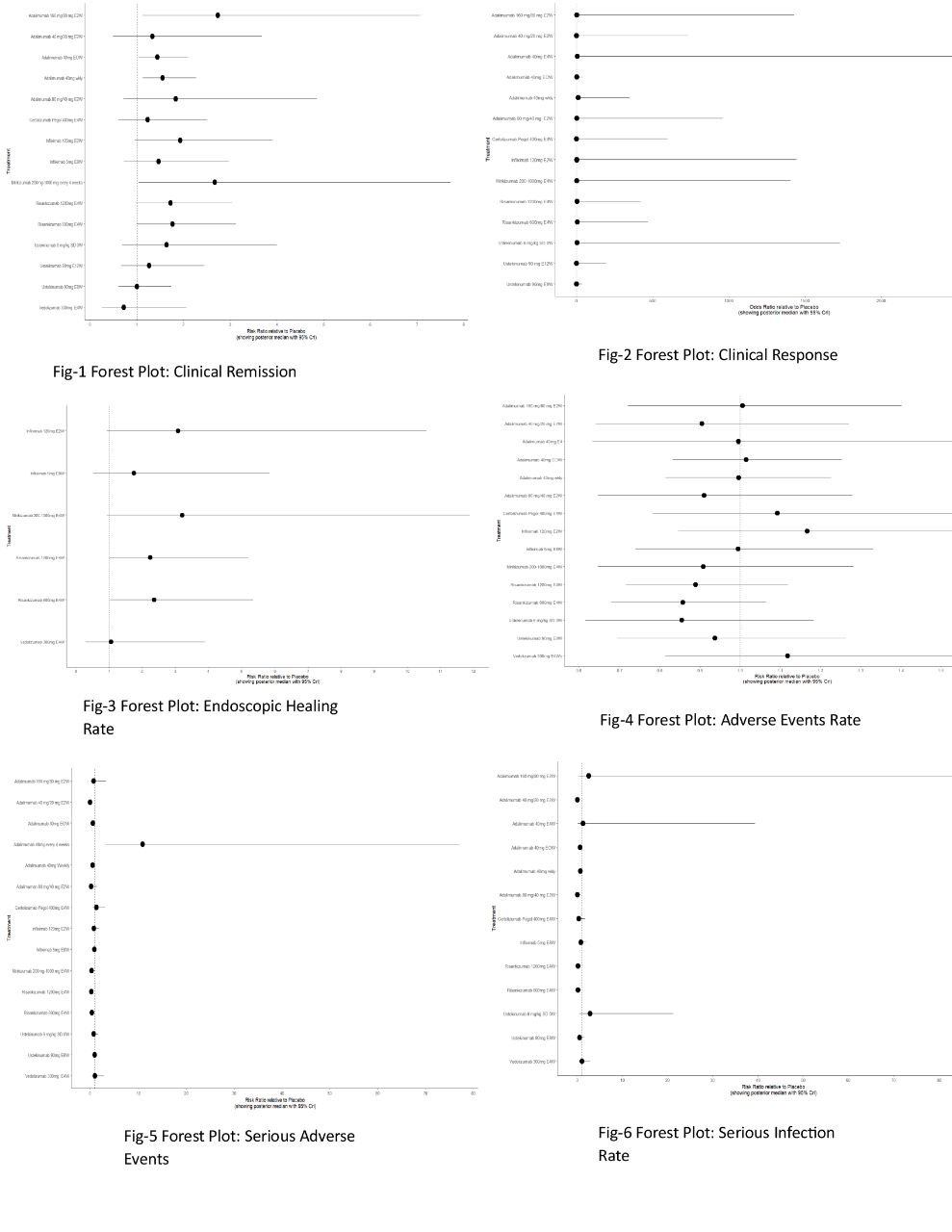
Figure: Figure: Forest plots depicting key efficacy and safety outcomes of microbiota-targeted therapies in biologic-refractory ulcerative colitis.
Fig. 1–3 show clinical remission, clinical response, and endoscopic healing rates; Fig. 4–6 represent overall adverse events, serious adverse events, and serious infection rates.
Each plot includes risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals across included studies, highlighting favorable efficacy and comparable safety of intervention arms
Disclosures:
Nayanika Tummala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sabah Kulsum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hakim Wazir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saniya Ishtiaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhamaad Maaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
M. Rafiqul Islam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maryam Muzaffar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ammarah Tariq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nimra Ehsan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rithish Nimmagadda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwith Reddy Gaddam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nayanika Tummala, MD1, Sabah Kulsum, MD2, Hakim Wazir, MBBS3, Saniya Ishtiaq, MBBS4, Muhamaad Maaz, MBBS5, M. Rafiqul Islam, 6, Maryam Muzaffar, MD7, Ammarah Tariq, MD4, Nimra Ehsan, 8, Rithish Nimmagadda, MBBS9, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD10. P1115 - Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Biologic Therapies in Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1St. Mary's General Hospital, New York Medical College, Pine Brook, NJ; 2St. Mary's General Hospital, New York Medical College, Poughkeepsie, NY; 3Gajju Khan Medical College,Swabi Pakistan Medicine department, Shahmansor, Swabi, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 4Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 5Bacha Khan Medical College, Mardan, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 6Suhrawardy Medical College Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh, Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh; 7Allama Iqbal medical college, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 8Khyber Medical College, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 9One Brooklyn Health-Interfaith Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 10NYMC at St. Mary’s General hospital amd st clares health, Parsippany, NJ
Introduction: Biologic therapies have transformed Crohn’s disease (CD) treatment, especially in moderate-to-severe cases. However, selecting the right biologic after anti-TNF failure remains challenging. This review aims to compare the efficacy and safety of various biologics, integrating recent evidence.
Methods: Literature Search & Selection:
Following PRISMA guidelines, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Embase, and ClinicalTrials.gov for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating biologic therapies in moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease. Studies were screened using Rayyan, with data extracted into Excel spreadsheets.
Analysis:
Using R 4.4.3 software, a Bayesian network meta-analysis was performed and pooled Odd Ratios (OR) or Relative Risk (RR) with 95% credible intervals (CrIs) were approximated using a random or fixed effects model based on deviance information criteria (DIC). Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) values were calculated to rank interventions across outcomes.
Results: We identified 14 RCTs encompassing 6,360 patients and 23 treatment arms. Risankizumab (RZB) 1200 mg Q4W yielded the highest clinical remission rate compared to placebo (RR: 2.72; 95% CrI: 1.11–7.33), though its SUCRA value was modest (0.379). Ustekinumab (UST), RZB 600 mg, and infliximab also outperformed placebo. Interestingly, vedolizumab (VDZ) 300 mg Q4W achieved the highest SUCRA score (0.874) for remission, despite lower RR values. For clinical response, UST 90 mg Q8W showed the strongest signal (OR: 24.52; 95% CrI: 0.14–7192.58), with UST Q12W and RZB 1200 mg following. Endoscopic healing was most evident with RZB 600 mg (RR: 2.36; 95% CrI: 1.03–5.36), but mirikizumab ranked highest in SUCRA (0.77). On safety outcomes, RZB 600 mg had the highest adverse event rate (RR: 1.19), whereas VDZ, infliximab, and certolizumab (CZP) exhibited lower rates. CZP was particularly notable for safety, with the lowest log RR for serious adverse events (–2.10; 95% CrI: –4.34 to –0.17) and a SUCRA of 0.92. VDZ also showed a favorable safety profile.
Discussion: IL-23 inhibitors such as risankizumab and ustekinumab appear highly effective for inducing both clinical and endoscopic remission. In contrast, vedolizumab and certolizumab stand out for their safety, particularly regarding serious adverse events. These insights support a personalized approach to biologic sequencing, balancing treatment efficacy with safety considerations in managing moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease.

Figure: Figure: Forest plots depicting key efficacy and safety outcomes of microbiota-targeted therapies in biologic-refractory ulcerative colitis.
Fig. 1–3 show clinical remission, clinical response, and endoscopic healing rates; Fig. 4–6 represent overall adverse events, serious adverse events, and serious infection rates.
Each plot includes risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals across included studies, highlighting favorable efficacy and comparable safety of intervention arms
Disclosures:
Nayanika Tummala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sabah Kulsum indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hakim Wazir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saniya Ishtiaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhamaad Maaz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
M. Rafiqul Islam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maryam Muzaffar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ammarah Tariq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nimra Ehsan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rithish Nimmagadda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwith Reddy Gaddam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nayanika Tummala, MD1, Sabah Kulsum, MD2, Hakim Wazir, MBBS3, Saniya Ishtiaq, MBBS4, Muhamaad Maaz, MBBS5, M. Rafiqul Islam, 6, Maryam Muzaffar, MD7, Ammarah Tariq, MD4, Nimra Ehsan, 8, Rithish Nimmagadda, MBBS9, Ashwith Reddy Gaddam, MD10. P1115 - Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Biologic Therapies in Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
