Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1075 - Comparison of Ustekinumab and Vedolizumab Effectiveness in Perianal Crohn’s Disease: A Matched-Cohort Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mohamed Eldesouki, MD
Saint Michael's Medical Center, New York Medical College
Newark, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Mohamed Eldesouki, MD1, Ahmed Ibrahim, MD2, Mohammed Y. Youssef, MD3, Omar Abdelhalim, MD4, Mohammad Kloub, MD5, Mona Ahmed, 6, Omar Tageldin, MD7, Francis A.. Farraye, MD, MSc, MACG8, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc, FACG8
1Saint Michael's Medical Center, New York Medical College, Newark, NJ; 2Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC; 3Hunt Regional Medical Center, Greenville, TX; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 5New York Medical College - Saint Michael's Medical Center, Bloomfield, NJ; 6Mansoura University School of Medicine, East Newark, NJ; 7university of tennessee medical center, knoxville, Knoxville, TN; 8Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Perianal Crohn’s disease (CD) is a severe and disabling phenotype of CD, frequently needing multidisciplinary medical and surgical care. This study aimed to compare the clinical effectiveness of ustekinumab versus vedolizumab in patients with perianal CD using a real-world database.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX database, to examine adults (≥18 years) with perianal CD (2016-2023). Patients were divided into two cohorts depending on current therapy: ustekinumab versus vedolizumab. After propensity score matching (PSM), 770 patients remained in each group. Outcomes were assessed over 1, and 2-years following treatment initiation. Primary outcomes included the use of oral and IV corticosteroids, antibiotics (metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, or Augmentin), abdominal and anal surgeries. Secondary outcomes included hospitalization and emergency department (ED) visits. Adjusted Odds ratios (aOR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated.
Results: After PSM, 770 patients were included in each group, with well-balanced baseline characteristics and prior biologic use (Table 1). At 1 year, patients treated with ustekinumab were significantly less likely to receive oral steroids (aOR 0.62; 95% CI: 0.51–0.77; p< 0.001), IV steroids (aOR 0.60; 95% CI: 0.49–0.74; p< 0.001), or antibiotics (aOR 0.88; 95% CI: 0.79–0.99; p=0.03) compared to those on vedolizumab (Table 2). Additionally, they had lower odds of hospitalization, emergency department visits, ileostomy/colostomy, and colectomy/enterectomy (Table 2). Anal surgery rates were similar between groups (Table 2).
At 2 years, ustekinumab was consistently associated with reduced use of oral steroids (aOR 0.72; 95% CI: 0.59–0.89; p=0.002), IV steroids (aOR 0.59; 95% CI: 0.48–0.72; p< 0.001), hospitalization (aOR 0.51; 95% CI: 0.41–0.63; p< 0.001), and emergency department visits (aOR 0.64; 95% CI: 0.51–0.80; p< 0.001). No significant differences were observed in antibiotic use, ileostomy/colostomy, colectomy/enterectomy, or anal surgeries (Table 2).
Discussion: Ustekinumab was associated with significantly lower rates of steroids use, antibiotics, abdominal surgeries and hospitalizations compared to vedolizumab over 1 year in patients with perianal CD. However, there was no significant difference in antibiotics and surgeries in 2 years. These findings suggest ustekinumab has superior clinical effectiveness in managing this challenging complicated phenotype.
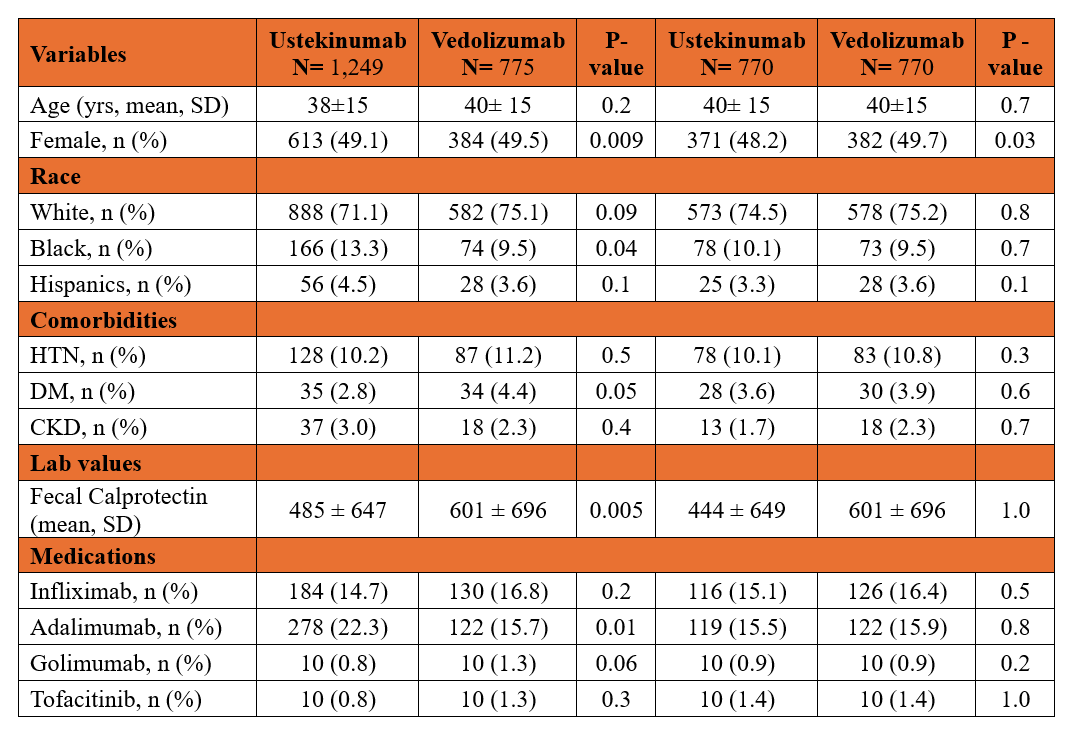
Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients in ustekinumab and vedolizumab cohorts before and after propensity-score matching
Abbreviations- HTN: hypertension; DM: diabetes mellitus; CKD: chronic kidney disease.
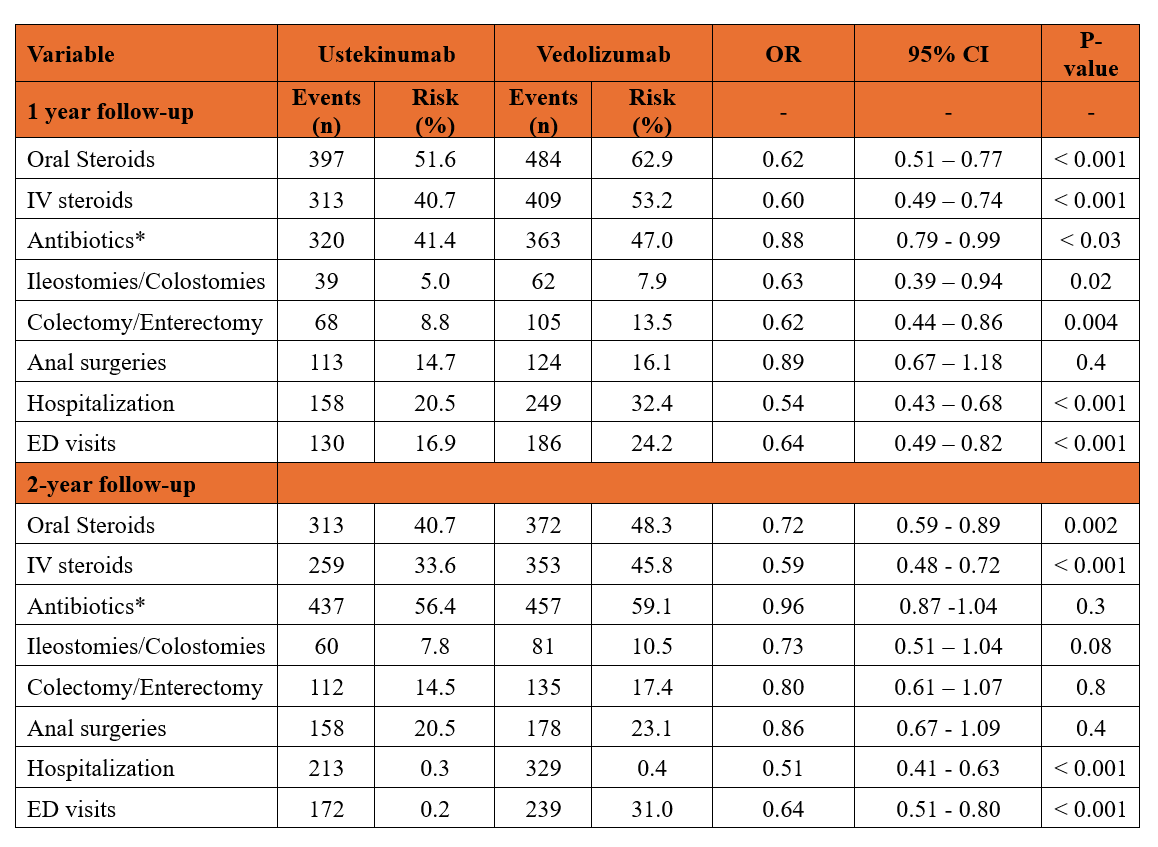
Figure: Table.2 Outcomes comparison between study groups after one, and two years of follow-up.
*Antibiotics included metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, and augmentin.
Abbreviations- IV: intravenous; ED: emergency department.
Disclosures:
Mohamed Eldesouki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Ibrahim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Y. Youssef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Abdelhalim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Kloub indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Tageldin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Francis Farraye: Astellas – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bausch – Advisory Committee/Board Member. BMS – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Braintree Labs – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Fresenius Kabi – Advisory Committee/Board Member. GI Reviewers – Independent Contractor. IBD Educational Group – Independent Contractor. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Stock Options. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Lilly – DSMB. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pharmacosmos – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Viatris – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Jana Hashash: BMS – Ad Board.
Mohamed Eldesouki, MD1, Ahmed Ibrahim, MD2, Mohammed Y. Youssef, MD3, Omar Abdelhalim, MD4, Mohammad Kloub, MD5, Mona Ahmed, 6, Omar Tageldin, MD7, Francis A.. Farraye, MD, MSc, MACG8, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc, FACG8. P1075 - Comparison of Ustekinumab and Vedolizumab Effectiveness in Perianal Crohn’s Disease: A Matched-Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Saint Michael's Medical Center, New York Medical College, Newark, NJ; 2Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC; 3Hunt Regional Medical Center, Greenville, TX; 4Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 5New York Medical College - Saint Michael's Medical Center, Bloomfield, NJ; 6Mansoura University School of Medicine, East Newark, NJ; 7university of tennessee medical center, knoxville, Knoxville, TN; 8Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Perianal Crohn’s disease (CD) is a severe and disabling phenotype of CD, frequently needing multidisciplinary medical and surgical care. This study aimed to compare the clinical effectiveness of ustekinumab versus vedolizumab in patients with perianal CD using a real-world database.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX database, to examine adults (≥18 years) with perianal CD (2016-2023). Patients were divided into two cohorts depending on current therapy: ustekinumab versus vedolizumab. After propensity score matching (PSM), 770 patients remained in each group. Outcomes were assessed over 1, and 2-years following treatment initiation. Primary outcomes included the use of oral and IV corticosteroids, antibiotics (metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, or Augmentin), abdominal and anal surgeries. Secondary outcomes included hospitalization and emergency department (ED) visits. Adjusted Odds ratios (aOR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated.
Results: After PSM, 770 patients were included in each group, with well-balanced baseline characteristics and prior biologic use (Table 1). At 1 year, patients treated with ustekinumab were significantly less likely to receive oral steroids (aOR 0.62; 95% CI: 0.51–0.77; p< 0.001), IV steroids (aOR 0.60; 95% CI: 0.49–0.74; p< 0.001), or antibiotics (aOR 0.88; 95% CI: 0.79–0.99; p=0.03) compared to those on vedolizumab (Table 2). Additionally, they had lower odds of hospitalization, emergency department visits, ileostomy/colostomy, and colectomy/enterectomy (Table 2). Anal surgery rates were similar between groups (Table 2).
At 2 years, ustekinumab was consistently associated with reduced use of oral steroids (aOR 0.72; 95% CI: 0.59–0.89; p=0.002), IV steroids (aOR 0.59; 95% CI: 0.48–0.72; p< 0.001), hospitalization (aOR 0.51; 95% CI: 0.41–0.63; p< 0.001), and emergency department visits (aOR 0.64; 95% CI: 0.51–0.80; p< 0.001). No significant differences were observed in antibiotic use, ileostomy/colostomy, colectomy/enterectomy, or anal surgeries (Table 2).
Discussion: Ustekinumab was associated with significantly lower rates of steroids use, antibiotics, abdominal surgeries and hospitalizations compared to vedolizumab over 1 year in patients with perianal CD. However, there was no significant difference in antibiotics and surgeries in 2 years. These findings suggest ustekinumab has superior clinical effectiveness in managing this challenging complicated phenotype.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients in ustekinumab and vedolizumab cohorts before and after propensity-score matching
Abbreviations- HTN: hypertension; DM: diabetes mellitus; CKD: chronic kidney disease.

Figure: Table.2 Outcomes comparison between study groups after one, and two years of follow-up.
*Antibiotics included metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, and augmentin.
Abbreviations- IV: intravenous; ED: emergency department.
Disclosures:
Mohamed Eldesouki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Ibrahim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Y. Youssef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Abdelhalim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Kloub indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Tageldin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Francis Farraye: Astellas – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bausch – Advisory Committee/Board Member. BMS – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Braintree Labs – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Fresenius Kabi – Advisory Committee/Board Member. GI Reviewers – Independent Contractor. IBD Educational Group – Independent Contractor. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Stock Options. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Lilly – DSMB. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pharmacosmos – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Viatris – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Jana Hashash: BMS – Ad Board.
Mohamed Eldesouki, MD1, Ahmed Ibrahim, MD2, Mohammed Y. Youssef, MD3, Omar Abdelhalim, MD4, Mohammad Kloub, MD5, Mona Ahmed, 6, Omar Tageldin, MD7, Francis A.. Farraye, MD, MSc, MACG8, Jana G. Hashash, MD, MSc, FACG8. P1075 - Comparison of Ustekinumab and Vedolizumab Effectiveness in Perianal Crohn’s Disease: A Matched-Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
