Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1073 - Efficacy and Safety of Curcumin-QingDai (CurQD) in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Clinical and Real-World Studies
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Kobina Essilfie-Quaye, MD (he/him/his)
University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME
Gainesville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Kobina Essilfie-Quaye, MD1, Albert Ohene, MD2, Nana Amma Larbi, MD3, Angela Barnes, MD4, Kofi Clarke, MD5
1University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Gainesville, FL; 2Piedmont Athens Regional, Piedmont, GA; 3Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, RI; 4Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA; 5Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA
Introduction: Curcumin and QingDai are herbal compounds with anti-inflammatory properties. Recent evidence suggests their combination (CurQD) may provide synergistic therapeutic benefit in ulcerative colitis (UC). However, comprehensive evaluation of CurQD’s efficacy and safety across adult UC populations remains limited.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies evaluating CurQD in adults with UC. We searched Google Scholar, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase from inception to 2025 using MeSH terms and keywords. Eligible studies included randomized controlled trials (RCTs), prospective or retrospective cohort studies, and case series (n ≥ 10) that used CurQD as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy in patients with UC. Studies had to report clinical remission, endoscopic response, or relevant safety outcomes. Two reviewers independently screened and selected studies, extracted data, and assessed quality using validated risk-of-bias tools. Outcomes included clinical remission, fecal calprotectin response, and adverse events.
Results: A total of five studies comprising one RCT, one prospective cohort, and three retrospective studies totaling 180 patients met inclusion criteria. Across studies, CurQD was administered either as monotherapy or adjunctively, with doses ranging from 3 g/day to combinations of Curcumin (4–8 g/day) and Qing Dai (0.3–1.3 g/day). Clinical remission rates ranged from 46.5% to 81%, with the highest observed in a prospective cohort combining CurQD with Vedolizumab. The RCT demonstrated a significantly greater remission rate in the CurQD group compared to placebo (50% vs. 8%, p = 0.01). Endoscopic outcomes were reported in three studies. The RCT showed endoscopic improvement in 75% of patients. 36% achieved endoscopic remission (Mayo = 0) in one cohort, and 80% showed mural thickness normalization on ultrasound in another. Fecal calprotectin normalized in 44% to 81% of patients across cohorts. Adverse events were mostly mild. One patient experienced microperforation requiring hospitalization. Other events included headache (n=1), abdominal pain (n=2), and reversible alopecia (n=1). No serious adverse events occurred in the RCT.
Discussion: CurQD appears to be an effective and well-tolerated adjunctive therapy for adult patients with active UC. Evidence supports significant improvements in clinical, biomarker, and endoscopic outcomes. Larger RCTs are warranted to confirm efficacy, establish optimal dosing, and assess long-term safety.
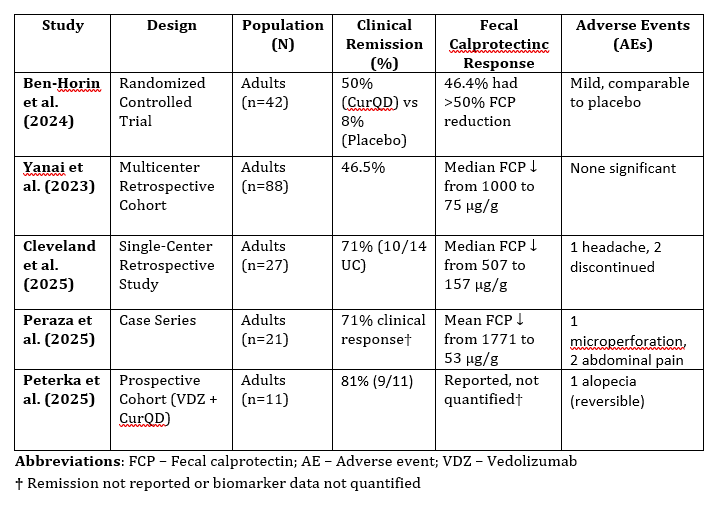
Figure: Summary of Studies Evaluating Curcumin-QingDai (CurQD) in Ulcerative Colitis
Disclosures:
Kobina Essilfie-Quaye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Albert Ohene indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nana Amma Larbi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Angela Barnes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kofi Clarke: Takeda – Clinical Trial Support.
Kobina Essilfie-Quaye, MD1, Albert Ohene, MD2, Nana Amma Larbi, MD3, Angela Barnes, MD4, Kofi Clarke, MD5. P1073 - Efficacy and Safety of Curcumin-QingDai (CurQD) in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Clinical and Real-World Studies, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Gainesville, FL; 2Piedmont Athens Regional, Piedmont, GA; 3Brown University School of Public Health, Providence, RI; 4Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA; 5Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA
Introduction: Curcumin and QingDai are herbal compounds with anti-inflammatory properties. Recent evidence suggests their combination (CurQD) may provide synergistic therapeutic benefit in ulcerative colitis (UC). However, comprehensive evaluation of CurQD’s efficacy and safety across adult UC populations remains limited.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies evaluating CurQD in adults with UC. We searched Google Scholar, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase from inception to 2025 using MeSH terms and keywords. Eligible studies included randomized controlled trials (RCTs), prospective or retrospective cohort studies, and case series (n ≥ 10) that used CurQD as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy in patients with UC. Studies had to report clinical remission, endoscopic response, or relevant safety outcomes. Two reviewers independently screened and selected studies, extracted data, and assessed quality using validated risk-of-bias tools. Outcomes included clinical remission, fecal calprotectin response, and adverse events.
Results: A total of five studies comprising one RCT, one prospective cohort, and three retrospective studies totaling 180 patients met inclusion criteria. Across studies, CurQD was administered either as monotherapy or adjunctively, with doses ranging from 3 g/day to combinations of Curcumin (4–8 g/day) and Qing Dai (0.3–1.3 g/day). Clinical remission rates ranged from 46.5% to 81%, with the highest observed in a prospective cohort combining CurQD with Vedolizumab. The RCT demonstrated a significantly greater remission rate in the CurQD group compared to placebo (50% vs. 8%, p = 0.01). Endoscopic outcomes were reported in three studies. The RCT showed endoscopic improvement in 75% of patients. 36% achieved endoscopic remission (Mayo = 0) in one cohort, and 80% showed mural thickness normalization on ultrasound in another. Fecal calprotectin normalized in 44% to 81% of patients across cohorts. Adverse events were mostly mild. One patient experienced microperforation requiring hospitalization. Other events included headache (n=1), abdominal pain (n=2), and reversible alopecia (n=1). No serious adverse events occurred in the RCT.
Discussion: CurQD appears to be an effective and well-tolerated adjunctive therapy for adult patients with active UC. Evidence supports significant improvements in clinical, biomarker, and endoscopic outcomes. Larger RCTs are warranted to confirm efficacy, establish optimal dosing, and assess long-term safety.

Figure: Summary of Studies Evaluating Curcumin-QingDai (CurQD) in Ulcerative Colitis
Disclosures:
Kobina Essilfie-Quaye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Albert Ohene indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nana Amma Larbi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Angela Barnes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kofi Clarke: Takeda – Clinical Trial Support.
Kobina Essilfie-Quaye, MD1, Albert Ohene, MD2, Nana Amma Larbi, MD3, Angela Barnes, MD4, Kofi Clarke, MD5. P1073 - Efficacy and Safety of Curcumin-QingDai (CurQD) in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review of Clinical and Real-World Studies, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
