Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1070 - Artificial Intelligence Assessment of Linear Endoscope Velocity Improves Standardization of Continuous Assessment of Endoscopic Severity in Ulcerative Colitis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

David T. Rubin, MD
University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL, USA
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Julian Lehrer, 1, Pavel Brodskiy, PhD1, Mohammad Haft-Javaherian, PhD1, Daniel Colucci, 2, Darren Thomason, MBA1, Klaus Gottlieb, MD, PhD, JD3, David T. Rubin, MD4
1Iterative Health Inc, Cambridge, MA; 2Iterative Health Inc, New York, NY; 3Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN; 4University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL, USA, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Artificial Intelligence assessment of Endoscopic Severity and Extent (AI-ESe) is a deep learning approach to continuous assessment of inflammation on endoscopy in ulcerative colitis (UC). Initial approaches assess inflammation via uniform temporal sampling over the procedure video. However, stalling - defined as time during withdrawal where the endoscope pauses in the longitudinal direction, not including panning or rotation - can lead to oversampling of the same mucosal surface. We developed an automated system using deep learning to measure endoscope linear velocity and applied thresholding to detect stalling, aiming to improve sampling uniformity in AI-ESe assessments.
Methods: We evaluated our ability to detect stalling on endoscopic video recordings from the Phase 3 induction trial for mirikizumab in UC (NCT03518086) and routine practice. Five experienced human reviewers were trained to manually identify stalling on withdrawal. To assess human variability, 10 videos were independently reviewed by all five reviewers. An additional 78 videos formed a holdout test set, with stalling labeled by one reviewer and quality-checked by a second. Error was measured to compare the difference in endoscope position between pairs of human reviewers, between human review and the model, and between human review and the null method based on uniform temporal sampling. Mean absolute error (MAE) was computed from error over each video. Confidence intervals (CIs) were computed by bootstrap resampling by videos.
Results: Comparison of pairs of human reviewers in assessing stalling yielded an MAE in endoscope position of 17 seconds (95% CI 9-29 seconds). Use of the velocity model to assess stalling compared to human assessment showed a comparable MAE of 22 seconds (95% CI 17-27 seconds). In contrast, uniform temporal sampling had roughly double the MAE compared to stalling adjustment (40 seconds, 95% CI 32-49 seconds), primarily due to overcounting of the same mucosal surface during stalling.
Discussion: We present a novel deep learning approach to measure the velocity of the endoscope and apply this model to detect stalling during procedure recordings in UC. These results demonstrate that adjusting for stalling improves the consistency of spatial sampling, and that our model can effectively identify these periods at a human level of accuracy. This approach can help standardize more granular AI-based endoscopic scoring in UC by ensuring uniform assessment of the mucosal surface.
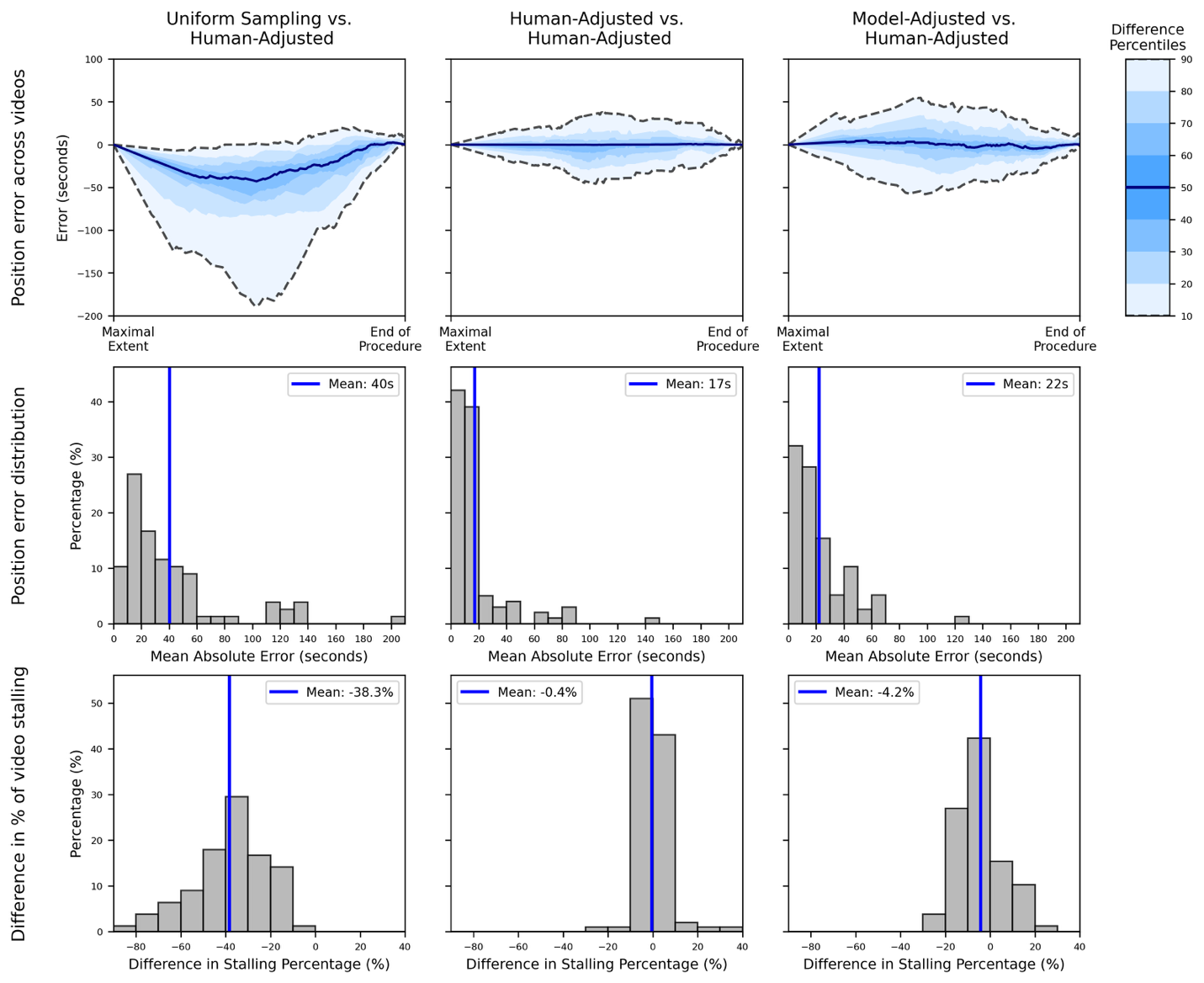
Figure: Figure 1. Row 1 measures the difference in position of the endoscope in seconds between human adjustment of stalling compared to (A) uniform temporal sampling, (B) another human, and (C) our velocity model. Row 2 shows the distribution of the mean absolute error in position per video across the three methods. Row 3 shows the difference in the fraction of video duration determined to be stalling between the three methods.
Disclosures:
Julian Lehrer: Iterative Health Inc – Employee.
Pavel Brodskiy: Iterative Health Inc – Employee.
Mohammad Haft-Javaherian: Iterative Health Inc – Employee.
Daniel Colucci: Iterative Health Inc – Employee.
Darren Thomason: Iterative Health – Employee.
Klaus Gottlieb: Eli Lilly – Employee.
David Rubin: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Abivax SA – Consultant. Altrubio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker feees, Stock Options. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Bausch Health – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Buhlmann Diagnostics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Connect BioPharma – Consultant. Cornerstones Health, Inc – Board of Directors membership. Douglas Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Co. – Consultant. Foresee, Genentech (Roche) Inc. – Consultant. Image Analysis Group – Consultant. InDex Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Intouch Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Stock Options. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Sanofi – Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker fees. Throne – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Julian Lehrer, 1, Pavel Brodskiy, PhD1, Mohammad Haft-Javaherian, PhD1, Daniel Colucci, 2, Darren Thomason, MBA1, Klaus Gottlieb, MD, PhD, JD3, David T. Rubin, MD4. P1070 - Artificial Intelligence Assessment of Linear Endoscope Velocity Improves Standardization of Continuous Assessment of Endoscopic Severity in Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Iterative Health Inc, Cambridge, MA; 2Iterative Health Inc, New York, NY; 3Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN; 4University of Chicago Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Chicago, IL, USA, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Artificial Intelligence assessment of Endoscopic Severity and Extent (AI-ESe) is a deep learning approach to continuous assessment of inflammation on endoscopy in ulcerative colitis (UC). Initial approaches assess inflammation via uniform temporal sampling over the procedure video. However, stalling - defined as time during withdrawal where the endoscope pauses in the longitudinal direction, not including panning or rotation - can lead to oversampling of the same mucosal surface. We developed an automated system using deep learning to measure endoscope linear velocity and applied thresholding to detect stalling, aiming to improve sampling uniformity in AI-ESe assessments.
Methods: We evaluated our ability to detect stalling on endoscopic video recordings from the Phase 3 induction trial for mirikizumab in UC (NCT03518086) and routine practice. Five experienced human reviewers were trained to manually identify stalling on withdrawal. To assess human variability, 10 videos were independently reviewed by all five reviewers. An additional 78 videos formed a holdout test set, with stalling labeled by one reviewer and quality-checked by a second. Error was measured to compare the difference in endoscope position between pairs of human reviewers, between human review and the model, and between human review and the null method based on uniform temporal sampling. Mean absolute error (MAE) was computed from error over each video. Confidence intervals (CIs) were computed by bootstrap resampling by videos.
Results: Comparison of pairs of human reviewers in assessing stalling yielded an MAE in endoscope position of 17 seconds (95% CI 9-29 seconds). Use of the velocity model to assess stalling compared to human assessment showed a comparable MAE of 22 seconds (95% CI 17-27 seconds). In contrast, uniform temporal sampling had roughly double the MAE compared to stalling adjustment (40 seconds, 95% CI 32-49 seconds), primarily due to overcounting of the same mucosal surface during stalling.
Discussion: We present a novel deep learning approach to measure the velocity of the endoscope and apply this model to detect stalling during procedure recordings in UC. These results demonstrate that adjusting for stalling improves the consistency of spatial sampling, and that our model can effectively identify these periods at a human level of accuracy. This approach can help standardize more granular AI-based endoscopic scoring in UC by ensuring uniform assessment of the mucosal surface.

Figure: Figure 1. Row 1 measures the difference in position of the endoscope in seconds between human adjustment of stalling compared to (A) uniform temporal sampling, (B) another human, and (C) our velocity model. Row 2 shows the distribution of the mean absolute error in position per video across the three methods. Row 3 shows the difference in the fraction of video duration determined to be stalling between the three methods.
Disclosures:
Julian Lehrer: Iterative Health Inc – Employee.
Pavel Brodskiy: Iterative Health Inc – Employee.
Mohammad Haft-Javaherian: Iterative Health Inc – Employee.
Daniel Colucci: Iterative Health Inc – Employee.
Darren Thomason: Iterative Health – Employee.
Klaus Gottlieb: Eli Lilly – Employee.
David Rubin: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Abivax SA – Consultant. Altrubio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker feees, Stock Options. Avalo – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Bausch Health – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Buhlmann Diagnostics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Connect BioPharma – Consultant. Cornerstones Health, Inc – Board of Directors membership. Douglas Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eli Lilly & Co. – Consultant. Foresee, Genentech (Roche) Inc. – Consultant. Image Analysis Group – Consultant. InDex Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Intouch Group – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Iterative Health – Stock Options. Janssen Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker fees. Sanofi – Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker fees. Throne – Consultant. Vedanta – Consultant.
Julian Lehrer, 1, Pavel Brodskiy, PhD1, Mohammad Haft-Javaherian, PhD1, Daniel Colucci, 2, Darren Thomason, MBA1, Klaus Gottlieb, MD, PhD, JD3, David T. Rubin, MD4. P1070 - Artificial Intelligence Assessment of Linear Endoscope Velocity Improves Standardization of Continuous Assessment of Endoscopic Severity in Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
