Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1057 - Impact of Social Determinants of Health on Clinical Outcomes and Treatment Patterns in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Large Propensity-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SS
Saad Saadat, MD
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, IN
Presenting Author(s)
Saad Saadat, MD1, Adel Hajj Ali, MD1, AbdiGhani Ismail, MD1, Hareem Syed, MD1, Indira Bhavsar-Burke, MD2, John Guardiola, MD1, Monika Fischer, MD, MS3, Satya Kurada, MD4
1Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 2University of Texas Southwestern School of Medicine, Dallas, TX; 3Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis, Indianapolis, IN; 4Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolus, IN
Introduction: While therapies for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) continue to advance, previous studies highlight disparities in treatment outcomes persist across socioeconomic and racial lines. Social determinants of health (SDOH) are environmental conditions that affect an individual’s health outcomes. We aim to perform the largest retrospective cohort study to investigate the impact of common SDOH on the outcomes and complications of IBD.
Methods: This large retrospective cohort study used de-identified data from the TriNetX database through May 2025. Adult patients with both IBD and at least one International Classification of Diseases (ICD) code identifying SDOH (IBD+SDOH) was compared to patients with IBD without any ICD code relevant to SDOH (IBD–SDOH). SDOH ICD-10 codes and sub-codes were classified pertinent to: education and literacy (Z55.5/6), physical environment (Z58.6/8), housing conditions (Z59), upbringing (Z62) and support circumstances (Z63-65). 1:1 propensity score matching was performed for 28 covariates including age, race, sex, tobacco use, and IBD type. Outcomes analyzed included IBD complications, emergency department (ED) visits, IBD therapies, opioid use, and inflammatory biomarkers.
Results: After PS matching, a total of 12,715 patients were included in the cohort with IBD+SDOH, and 12,715 patients were included in IBD–SDOH. IBD+SDOH patients were found to have a significantly higher risk ratio (RR) (p< 0.05) for ED visits, inpatient admissions, intensive care unit admissions, and mortality (Table 1). IBD+SDOH patients also had significantly higher RR for intestinal complications including fistulation, obstruction, perforation, and opioid use. The IBD+SDOH group more often received steroids, but received significantly less immunomodulators and biologic drugs. There was no significant difference between these groups in receiving 5-aminosalicylates or small molecules. Those with SDOH also had significantly higher risk of elevated biomarkers.
Discussion: Patients with IBD in the presence of SDOH have significantly higher risks of complications of IBD, higher healthcare utilization, and increased use of steroids while receiving less advanced therapies compared to patients with IBD without identified SDOH. These disparities highlight the importance for clinicians to be cognizant of systemic barriers that affect access to advanced therapies for IBD and poorer outcomes in patients with IBD.
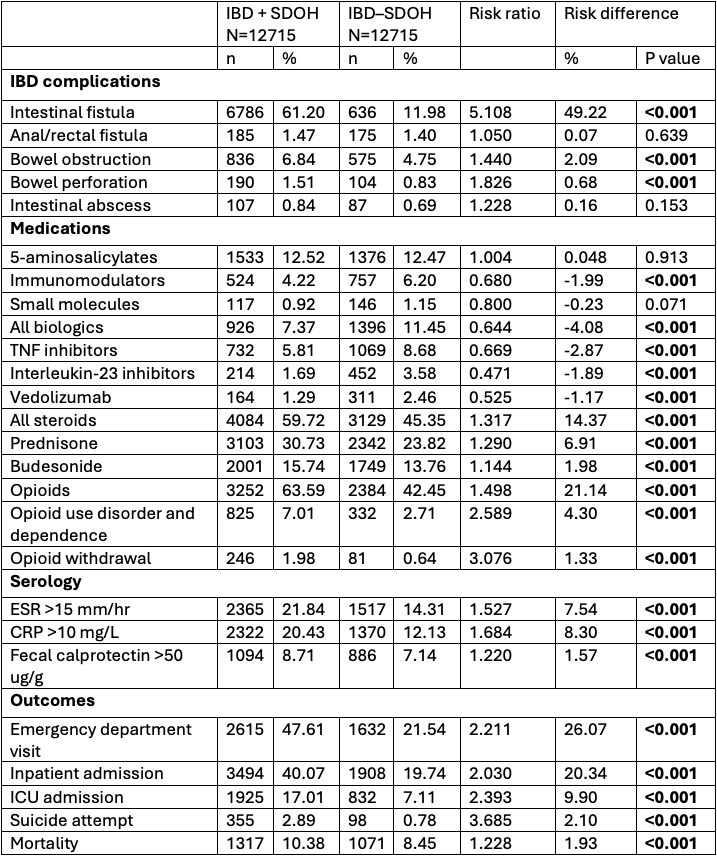
Figure: Table 1. Outcomes of patients with IBD in the presence of social determinants of health compared to those without social determinants of health.
IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentary rate, CRP: C-reactive protein, ICU: Intensive care unit.
Disclosures:
Saad Saadat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adel Hajj Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
AbdiGhani Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hareem Syed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Indira Bhavsar-Burke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Guardiola indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monika Fischer: abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Criscot – DSMB chair. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Ferring – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Johnson and Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. seres – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Satya Kurada: Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Saad Saadat, MD1, Adel Hajj Ali, MD1, AbdiGhani Ismail, MD1, Hareem Syed, MD1, Indira Bhavsar-Burke, MD2, John Guardiola, MD1, Monika Fischer, MD, MS3, Satya Kurada, MD4. P1057 - Impact of Social Determinants of Health on Clinical Outcomes and Treatment Patterns in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Large Propensity-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 2University of Texas Southwestern School of Medicine, Dallas, TX; 3Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis, Indianapolis, IN; 4Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolus, IN
Introduction: While therapies for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) continue to advance, previous studies highlight disparities in treatment outcomes persist across socioeconomic and racial lines. Social determinants of health (SDOH) are environmental conditions that affect an individual’s health outcomes. We aim to perform the largest retrospective cohort study to investigate the impact of common SDOH on the outcomes and complications of IBD.
Methods: This large retrospective cohort study used de-identified data from the TriNetX database through May 2025. Adult patients with both IBD and at least one International Classification of Diseases (ICD) code identifying SDOH (IBD+SDOH) was compared to patients with IBD without any ICD code relevant to SDOH (IBD–SDOH). SDOH ICD-10 codes and sub-codes were classified pertinent to: education and literacy (Z55.5/6), physical environment (Z58.6/8), housing conditions (Z59), upbringing (Z62) and support circumstances (Z63-65). 1:1 propensity score matching was performed for 28 covariates including age, race, sex, tobacco use, and IBD type. Outcomes analyzed included IBD complications, emergency department (ED) visits, IBD therapies, opioid use, and inflammatory biomarkers.
Results: After PS matching, a total of 12,715 patients were included in the cohort with IBD+SDOH, and 12,715 patients were included in IBD–SDOH. IBD+SDOH patients were found to have a significantly higher risk ratio (RR) (p< 0.05) for ED visits, inpatient admissions, intensive care unit admissions, and mortality (Table 1). IBD+SDOH patients also had significantly higher RR for intestinal complications including fistulation, obstruction, perforation, and opioid use. The IBD+SDOH group more often received steroids, but received significantly less immunomodulators and biologic drugs. There was no significant difference between these groups in receiving 5-aminosalicylates or small molecules. Those with SDOH also had significantly higher risk of elevated biomarkers.
Discussion: Patients with IBD in the presence of SDOH have significantly higher risks of complications of IBD, higher healthcare utilization, and increased use of steroids while receiving less advanced therapies compared to patients with IBD without identified SDOH. These disparities highlight the importance for clinicians to be cognizant of systemic barriers that affect access to advanced therapies for IBD and poorer outcomes in patients with IBD.

Figure: Table 1. Outcomes of patients with IBD in the presence of social determinants of health compared to those without social determinants of health.
IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentary rate, CRP: C-reactive protein, ICU: Intensive care unit.
Disclosures:
Saad Saadat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adel Hajj Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
AbdiGhani Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hareem Syed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Indira Bhavsar-Burke indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Guardiola indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monika Fischer: abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Criscot – DSMB chair. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Ferring – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Johnson and Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. seres – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Satya Kurada: Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Saad Saadat, MD1, Adel Hajj Ali, MD1, AbdiGhani Ismail, MD1, Hareem Syed, MD1, Indira Bhavsar-Burke, MD2, John Guardiola, MD1, Monika Fischer, MD, MS3, Satya Kurada, MD4. P1057 - Impact of Social Determinants of Health on Clinical Outcomes and Treatment Patterns in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Large Propensity-Matched Retrospective Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

