Sunday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P0925 - Hidden Links: How Obesity, Race, and Gender Influence Upper GI Bleeding - A Revealing Nationwide Study of 2.8 Million Patients
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AZ
Amina Zafar, MD
Nassau University Medical Center
East Meadow, New York
Presenting Author(s)
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD1, Dilman Natt, MD1, Sai Reshma Magam, MD1, Achal Patel, MD1, Leeza E. Pannikodu, MD1, Wing Hang Lau, DO1, Sindhuja Giridharan, MD1, Sri Harsha Boppana, MD1, Venkata Panchagnula, MD1, Amilcar Guaschino, MD1, Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard, MD1, Amina Zafar, MD1, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD1, Krina Patel, 2, Paul Mustacchia, MD1, Melvin Joy, MD3
1Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY; 2The wardlaw Hartridge school, Edison, NJ; 3HCA Healthcare Citrus Hospital, Inverness, FL
Introduction: Amidst the growing concern over obesity's health effects, particularly on upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB), this study utilizes the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP) to explore how obesity, race, and gender influence UGIB and its readmission rates. Covering 2019 to 2024, the research analyzes over 2.8 million adult hospital admissions, specifically examining 234,024 patients with obesity-related diagnoses. The aim is to assess whether obesity correlates with increased UGIB incidences and subsequent short-term readmissions, thereby providing insights into the demographic and clinical factors that may exacerbate UGIB risks and healthcare burdens.
Methods: From 2019 to 2024, the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP) was accessed to study 2,858,576 adult hospital admissions, analyzing the influence of obesity, race, and gender on upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) and 30-day and 60-day readmission rates. The study stratified patients by obesity status, using chi-square tests and logistic regression to evaluate UGIB incidence and readmission differences. ROC curves with Area Under the Curve (AUC) assessed predictive accuracy, with statistical significance established at p < 0.05.
Results: From 2019 to 2024, the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP) was utilized to analyze 2,858,576 adult hospital admissions, focusing on 234,024 patients diagnosed with diverticulitis, including 112,014 obese individuals (BMI > 30). Chi-square tests revealed no significant difference in UGIB incidence between obese and non-obese groups (p = 0.795). However, among obese patients with UGIB, significant associations were found with 30-day (p = 0.032) and 60-day (p = 0.041) readmissions. African Americans showed a significant association with UGIB incidence (p < 0.001). Logistic regression indicated race impacted 30-day readmissions (p < 0.05 for Black and Hispanic patients) and gender influenced 60-day readmissions, notably in males and Hispanics (p < 0.001 and p = 0.031, respectively). ROC analysis demonstrated moderate predictive accuracy for UGIB (AUC = 0.71) and readmissions, with 60-day predictions showing better performance (AUC = 0.89).
Discussion: This study examines obesity, race, and gender in UGIB outcomes. While obesity didn’t raise initial UGIB risk (p = 0.795), it was linked to higher 30- and 60-day readmissions. African Americans showed notable disparities. Predictive model challenges highlight the need for targeted care and research.
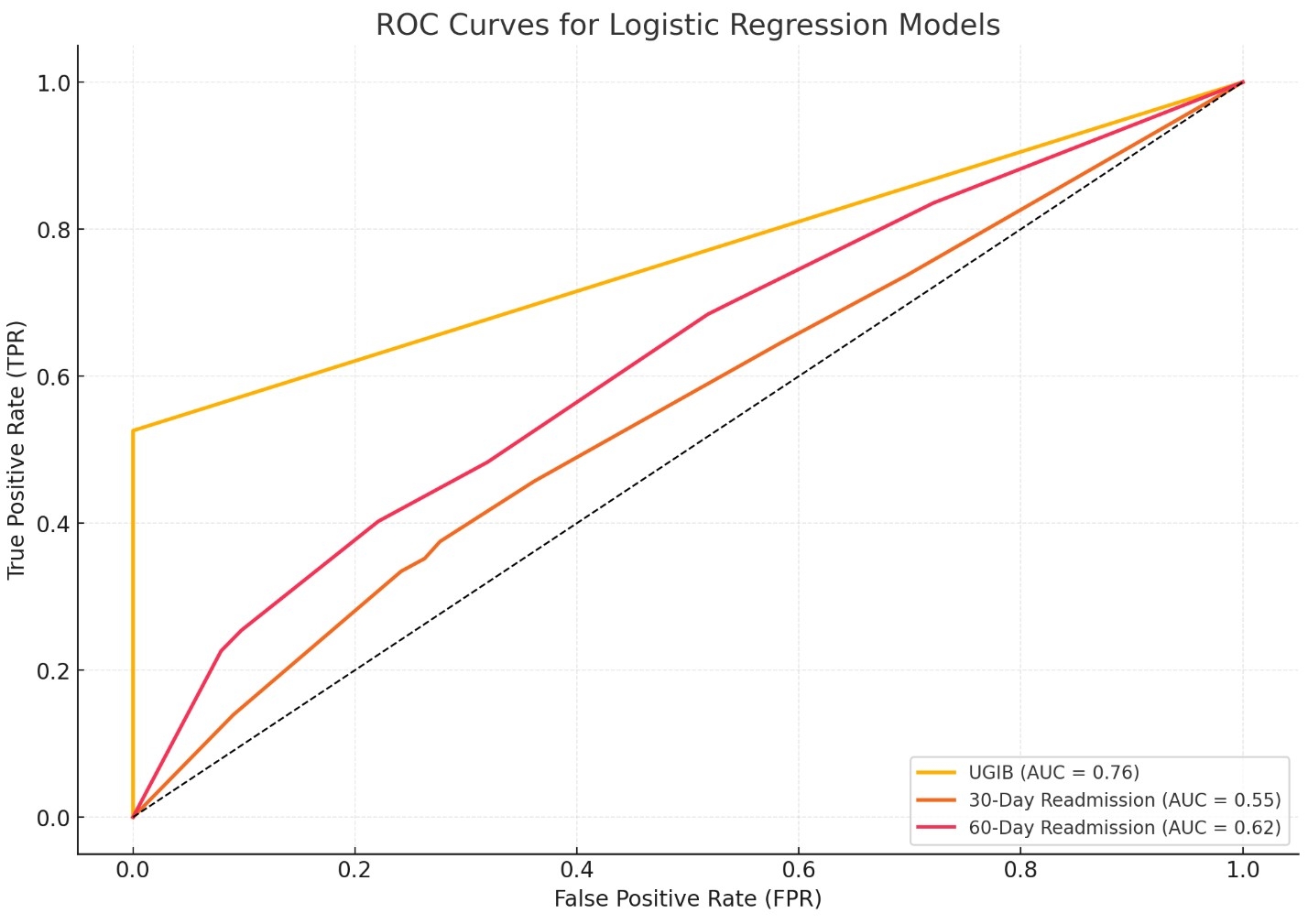
Figure: Figure 1
Disclosures:
Rajmohan Rammohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Achal Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wing Hang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sindhuja Giridharan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sri Harsha Boppana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Venkata Panchagnula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amilcar Guaschino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amina Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnaiyer Subramani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krina Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melvin Joy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD1, Dilman Natt, MD1, Sai Reshma Magam, MD1, Achal Patel, MD1, Leeza E. Pannikodu, MD1, Wing Hang Lau, DO1, Sindhuja Giridharan, MD1, Sri Harsha Boppana, MD1, Venkata Panchagnula, MD1, Amilcar Guaschino, MD1, Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard, MD1, Amina Zafar, MD1, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD1, Krina Patel, 2, Paul Mustacchia, MD1, Melvin Joy, MD3. P0925 - Hidden Links: How Obesity, Race, and Gender Influence Upper GI Bleeding - A Revealing Nationwide Study of 2.8 Million Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY; 2The wardlaw Hartridge school, Edison, NJ; 3HCA Healthcare Citrus Hospital, Inverness, FL
Introduction: Amidst the growing concern over obesity's health effects, particularly on upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB), this study utilizes the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP) to explore how obesity, race, and gender influence UGIB and its readmission rates. Covering 2019 to 2024, the research analyzes over 2.8 million adult hospital admissions, specifically examining 234,024 patients with obesity-related diagnoses. The aim is to assess whether obesity correlates with increased UGIB incidences and subsequent short-term readmissions, thereby providing insights into the demographic and clinical factors that may exacerbate UGIB risks and healthcare burdens.
Methods: From 2019 to 2024, the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP) was accessed to study 2,858,576 adult hospital admissions, analyzing the influence of obesity, race, and gender on upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) and 30-day and 60-day readmission rates. The study stratified patients by obesity status, using chi-square tests and logistic regression to evaluate UGIB incidence and readmission differences. ROC curves with Area Under the Curve (AUC) assessed predictive accuracy, with statistical significance established at p < 0.05.
Results: From 2019 to 2024, the Nationwide Admission Database (HCUP) was utilized to analyze 2,858,576 adult hospital admissions, focusing on 234,024 patients diagnosed with diverticulitis, including 112,014 obese individuals (BMI > 30). Chi-square tests revealed no significant difference in UGIB incidence between obese and non-obese groups (p = 0.795). However, among obese patients with UGIB, significant associations were found with 30-day (p = 0.032) and 60-day (p = 0.041) readmissions. African Americans showed a significant association with UGIB incidence (p < 0.001). Logistic regression indicated race impacted 30-day readmissions (p < 0.05 for Black and Hispanic patients) and gender influenced 60-day readmissions, notably in males and Hispanics (p < 0.001 and p = 0.031, respectively). ROC analysis demonstrated moderate predictive accuracy for UGIB (AUC = 0.71) and readmissions, with 60-day predictions showing better performance (AUC = 0.89).
Discussion: This study examines obesity, race, and gender in UGIB outcomes. While obesity didn’t raise initial UGIB risk (p = 0.795), it was linked to higher 30- and 60-day readmissions. African Americans showed notable disparities. Predictive model challenges highlight the need for targeted care and research.

Figure: Figure 1
Disclosures:
Rajmohan Rammohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Achal Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wing Hang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sindhuja Giridharan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sri Harsha Boppana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Venkata Panchagnula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amilcar Guaschino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amina Zafar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnaiyer Subramani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krina Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melvin Joy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD1, Dilman Natt, MD1, Sai Reshma Magam, MD1, Achal Patel, MD1, Leeza E. Pannikodu, MD1, Wing Hang Lau, DO1, Sindhuja Giridharan, MD1, Sri Harsha Boppana, MD1, Venkata Panchagnula, MD1, Amilcar Guaschino, MD1, Cesar Orlando Ortiz Bernard, MD1, Amina Zafar, MD1, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD1, Krina Patel, 2, Paul Mustacchia, MD1, Melvin Joy, MD3. P0925 - Hidden Links: How Obesity, Race, and Gender Influence Upper GI Bleeding - A Revealing Nationwide Study of 2.8 Million Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
