Sunday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P0826 - Dual Implantable Electronic Device Therapy and Pyloroplasty in the Setting of Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome With Superimposed Gastroparesis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mira Yang, MD (she/her/hers)
Tufts Medical Center
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Mira Yang, MD1, Ritam H. Patel, BS2, Swati Yarlagadda, BS2, Joy Liu, MD2
1Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Gastroparesis (Gp) and cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) are distinct conditions that present with nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Gastric electrical stimulation (GES) is a treatment indicated for medically refractory Gp. Evidence regarding the safety and efficacy of GES when there is a pre-existing implantable electronic device (dual-IED) is limited. We present a case of successful GES implantation in a patient with an automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD).
Case Description/
Methods: A 44-year-old female with ventricular arrhythmia controlled with an AICD, long QT syndrome, and CVS presented for evaluation of superimposed post-viral Gp. After a COVID infection in 2022, vomiting episodes intensified from episodic and once yearly to multiple times daily. The patient was only able to tolerate a liquid diet and lost significant weight. A gastric emptying study showed 39% retention at 4 hours and delayed gastric emptying (T1/2 = 205 minutes). Given contraindications to QTc-prolonging agents, and refractoriness to other pharmacotherapies and diet, robotic Enterra® Therapy placement and pyloroplasty were performed. The GES device was implanted on the side contralateral to the AICD, and impedance was set to 475 Ohms. Device placement was confirmed with fluoroscopy. At eight months post-procedure, the patient was on a regular diet with significantly improved symptom severity (Figure 1). Evaluation of her AICD post-operatively yielded no abnormalities.
Discussion: This case is an example of CVS with superimposed Gp symptoms and demonstrates that treatment of Gp can improve symptoms and restore quality of life. To our knowledge, this is the second reported case of successful GES implantation in a patient with an existing AICD. (PMID: 25031232) Certain precautions are recommended: continuous rhythm monitoring, inactivation of defibrillators during procedures using electrosurgical currents, and post-operative monitoring to ensure there is no crosstalk or artifact sensing. Interdisciplinary communication must occur to ensure complete device information and appropriate GES device selection. As the prevalence of implantable devices increases, careful consideration must be given to ensure safe and efficacious use of dual-IED therapy.
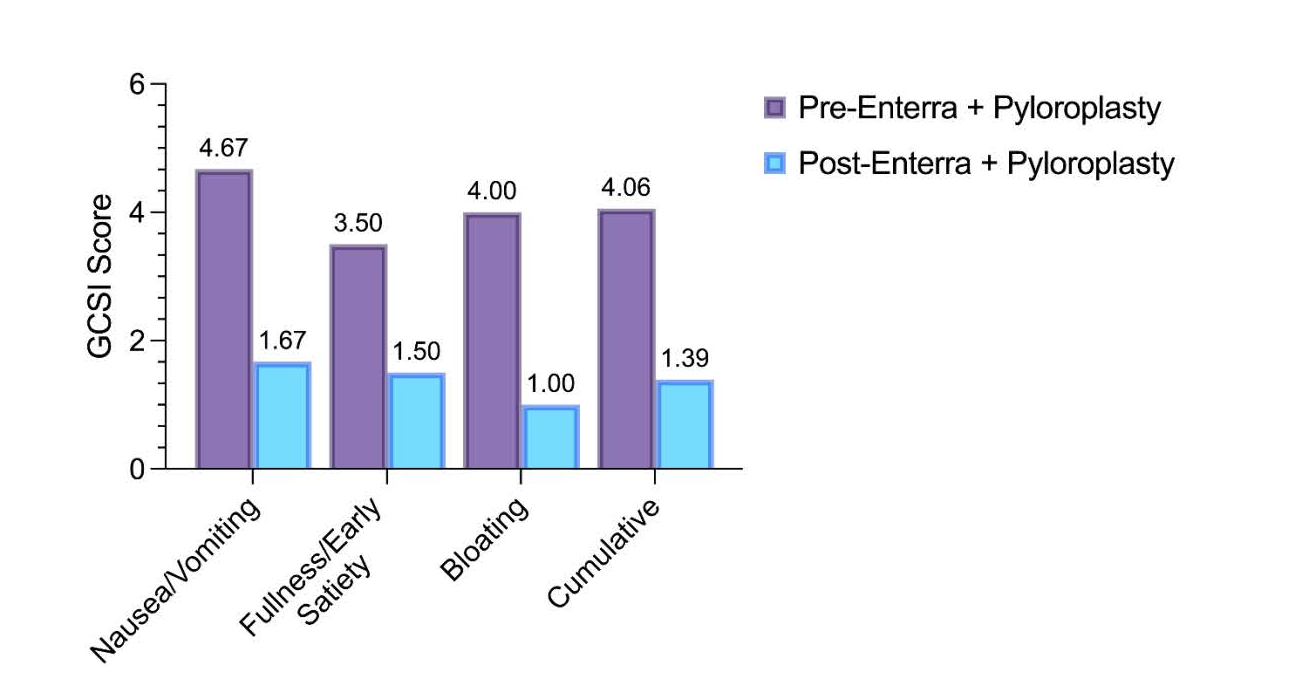
Figure: Figure 1: Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index
Disclosures:
Mira Yang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritam Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swati Yarlagadda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joy Liu: Ironwood – Consultant.
Mira Yang, MD1, Ritam H. Patel, BS2, Swati Yarlagadda, BS2, Joy Liu, MD2. P0826 - Dual Implantable Electronic Device Therapy and Pyloroplasty in the Setting of Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome With Superimposed Gastroparesis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mira Yang, MD1, Ritam H. Patel, BS2, Swati Yarlagadda, BS2, Joy Liu, MD2
1Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Gastroparesis (Gp) and cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) are distinct conditions that present with nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Gastric electrical stimulation (GES) is a treatment indicated for medically refractory Gp. Evidence regarding the safety and efficacy of GES when there is a pre-existing implantable electronic device (dual-IED) is limited. We present a case of successful GES implantation in a patient with an automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (AICD).
Case Description/
Methods: A 44-year-old female with ventricular arrhythmia controlled with an AICD, long QT syndrome, and CVS presented for evaluation of superimposed post-viral Gp. After a COVID infection in 2022, vomiting episodes intensified from episodic and once yearly to multiple times daily. The patient was only able to tolerate a liquid diet and lost significant weight. A gastric emptying study showed 39% retention at 4 hours and delayed gastric emptying (T1/2 = 205 minutes). Given contraindications to QTc-prolonging agents, and refractoriness to other pharmacotherapies and diet, robotic Enterra® Therapy placement and pyloroplasty were performed. The GES device was implanted on the side contralateral to the AICD, and impedance was set to 475 Ohms. Device placement was confirmed with fluoroscopy. At eight months post-procedure, the patient was on a regular diet with significantly improved symptom severity (Figure 1). Evaluation of her AICD post-operatively yielded no abnormalities.
Discussion: This case is an example of CVS with superimposed Gp symptoms and demonstrates that treatment of Gp can improve symptoms and restore quality of life. To our knowledge, this is the second reported case of successful GES implantation in a patient with an existing AICD. (PMID: 25031232) Certain precautions are recommended: continuous rhythm monitoring, inactivation of defibrillators during procedures using electrosurgical currents, and post-operative monitoring to ensure there is no crosstalk or artifact sensing. Interdisciplinary communication must occur to ensure complete device information and appropriate GES device selection. As the prevalence of implantable devices increases, careful consideration must be given to ensure safe and efficacious use of dual-IED therapy.

Figure: Figure 1: Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index
Disclosures:
Mira Yang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritam Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swati Yarlagadda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joy Liu: Ironwood – Consultant.
Mira Yang, MD1, Ritam H. Patel, BS2, Swati Yarlagadda, BS2, Joy Liu, MD2. P0826 - Dual Implantable Electronic Device Therapy and Pyloroplasty in the Setting of Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome With Superimposed Gastroparesis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

