Sunday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P0790 - Increased Diagnoses of IBS and Functional Dyspepsia in Patients With Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Propensity-Matched Cohort Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mohamed Eldesouki, MD
Saint Michael's Medical Center, New York Medical College
Newark, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Mohamed Eldesouki, MD1, Ahmed Ibrahim, MD2, Danny Issa, MD3, Mohammad Kloub, MD4, Khaled Elfert, MD5, Mona Ahmed, 6, Jumana E. Alseidi, 7, Lin Chang, MD8, Firas Bahdi, MD9
1Saint Michael's Medical Center, New York Medical College, Newark, NJ; 2Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC; 3David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, West Hills, CA; 4New York Medical College - Saint Michael's Medical Center, Bloomfield, NJ; 5West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV; 6Mansoura University School of Medicine, East Newark, NJ; 7St michael's Medical Center, Newark, NJ; 8Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, US, Los Angeles, CA; 9David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) are widely used in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. While their gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events are well recognized, their association with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia (FD) remains underexplored. We aim to assess the incidence of IBS and FD diagnoses in patients with uncomplicated T2DM treated with GLP1-RAs compared to matched controls.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed using the TriNetX database. Adults (aged ≥18 years) with uncomplicated T2DM between 2015 and 2020 were included. Patients with complicated DM, gastroparesis, peptic ulcer disease, IBD, celiac disease, GI malignancies, prescription of insulin or chronic opioids, or prior diagnosis of IBS or FD were excluded. Two cohorts were defined: 1) Patients receiving GLP1-RAs (semaglutide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide) with at least 3 documented prescriptions, and 2) Controls receiving oral antihyperglycemic agents. Propensity score matching (PSM) was employed to balance demographic and clinical variables. The primary outcome was new IBS and FD diagnoses at 1-, 3-, and 5-years after continuous GLP-1 RAs. Secondary outcomes included EGD ± colonoscopy and IBS-related medications within 5 years.
Results: After PSM, 8,409 patients were included in each group. BMI was slightly higher in the GLP-1-RAs group compared to controls [36.1 vs. 34.3], while HbA1c was comparable; 8.17 vs. 8.34 (Table 1). While there was no significant difference in new IBS (aOR 1.21; 95% CI 0.71–2.10) or FD diagnoses (aOR 1.08; 95% CI 0.51–2.29) at 1 year, GLP1-RAs were associated with significantly higher incidence of IBS and FD diagnoses at 3 years [IBS (aOR 1.61; 95% CI 1.10–2.69), FD (aOR 1.95; 95% CI 1.14–3.35)] and 5 years [IBS (aOR 1.68; 95% CI 1.16–2.42), FD (aOR 1.67; 95% CI 1.04–2.69)], respectively (Table 2). Within 5 years, GLP1-RAs use was associated with a significant increase in EGD and/or colonoscopy utilization (aOR 1.97; 95% CI 1.71–2.26) along with prescription of IBS-related pharmacotherapy (aOR 1.72; 95% CI 1.51–1.96; Figure).
Discussion: GLP1-RAs are associated with a significantly higher incidence of IBS and FD ICD diagnoses, endoscopic procedures, and IBS-related medications in patients with uncomplicated T2DM. Although absolute rates were low, the relative increases suggest a potential for GLP1-RAs-related GI symptoms to be misclassified as IBS and FD. Further studies are warranted to clarify this association.
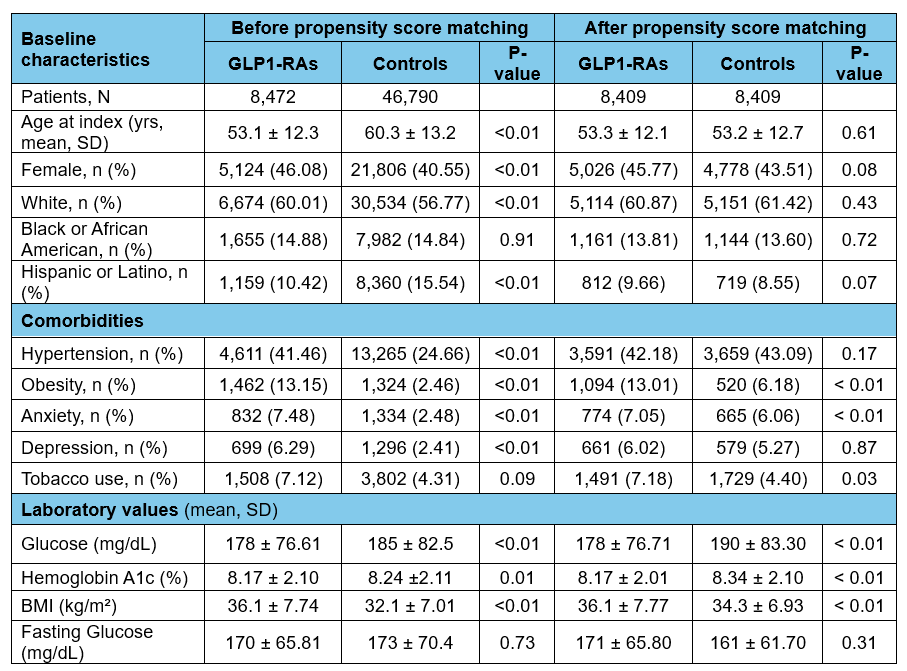
Figure: Table 1. Baseline patients’ characteristics before and after propensity score matching.
Abbreviations: GLP1-RAs: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; BMI: body mass index.
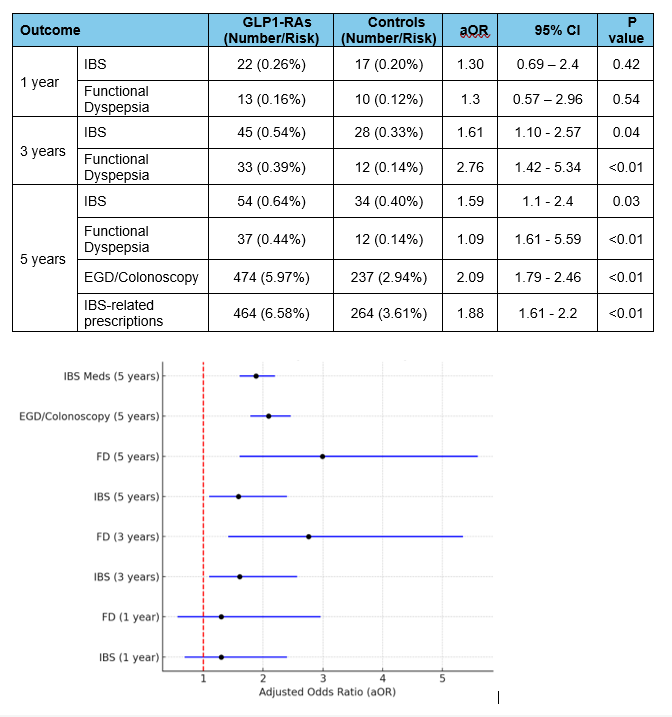
Figure: Table 2. Primary and secondary outcomes
Figure. Forest plot depicting the odds ratios of primary and secondary outcomes
Abbreviations: IBS: inflammatory bowel disease; EGD: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy; GLP1-RAs: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; FD: functional dyspepsia; OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval.
Disclosures:
Mohamed Eldesouki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Ibrahim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danny Issa: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Mohammad Kloub indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khaled Elfert indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jumana Alseidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lin Chang: AnX Robotica – Grant/Research Support. Ardelyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Atmo BioSciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bausch Health – Consultant. FoodMarble Digestive Health – Consultant, Stock Options. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Ironwood Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Lilly – Consultant. ModifyHealth – Stock Options. Trellus Health – Consultant, Stock Options. Vibrant Gastro – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Firas Bahdi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Eldesouki, MD1, Ahmed Ibrahim, MD2, Danny Issa, MD3, Mohammad Kloub, MD4, Khaled Elfert, MD5, Mona Ahmed, 6, Jumana E. Alseidi, 7, Lin Chang, MD8, Firas Bahdi, MD9. P0790 - Increased Diagnoses of IBS and Functional Dyspepsia in Patients With Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Propensity-Matched Cohort Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Saint Michael's Medical Center, New York Medical College, Newark, NJ; 2Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC; 3David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, West Hills, CA; 4New York Medical College - Saint Michael's Medical Center, Bloomfield, NJ; 5West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV; 6Mansoura University School of Medicine, East Newark, NJ; 7St michael's Medical Center, Newark, NJ; 8Vatche and Tamar Manoukian Division of Digestive Diseases, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, US, Los Angeles, CA; 9David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP1-RAs) are widely used in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. While their gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events are well recognized, their association with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia (FD) remains underexplored. We aim to assess the incidence of IBS and FD diagnoses in patients with uncomplicated T2DM treated with GLP1-RAs compared to matched controls.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was performed using the TriNetX database. Adults (aged ≥18 years) with uncomplicated T2DM between 2015 and 2020 were included. Patients with complicated DM, gastroparesis, peptic ulcer disease, IBD, celiac disease, GI malignancies, prescription of insulin or chronic opioids, or prior diagnosis of IBS or FD were excluded. Two cohorts were defined: 1) Patients receiving GLP1-RAs (semaglutide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide) with at least 3 documented prescriptions, and 2) Controls receiving oral antihyperglycemic agents. Propensity score matching (PSM) was employed to balance demographic and clinical variables. The primary outcome was new IBS and FD diagnoses at 1-, 3-, and 5-years after continuous GLP-1 RAs. Secondary outcomes included EGD ± colonoscopy and IBS-related medications within 5 years.
Results: After PSM, 8,409 patients were included in each group. BMI was slightly higher in the GLP-1-RAs group compared to controls [36.1 vs. 34.3], while HbA1c was comparable; 8.17 vs. 8.34 (Table 1). While there was no significant difference in new IBS (aOR 1.21; 95% CI 0.71–2.10) or FD diagnoses (aOR 1.08; 95% CI 0.51–2.29) at 1 year, GLP1-RAs were associated with significantly higher incidence of IBS and FD diagnoses at 3 years [IBS (aOR 1.61; 95% CI 1.10–2.69), FD (aOR 1.95; 95% CI 1.14–3.35)] and 5 years [IBS (aOR 1.68; 95% CI 1.16–2.42), FD (aOR 1.67; 95% CI 1.04–2.69)], respectively (Table 2). Within 5 years, GLP1-RAs use was associated with a significant increase in EGD and/or colonoscopy utilization (aOR 1.97; 95% CI 1.71–2.26) along with prescription of IBS-related pharmacotherapy (aOR 1.72; 95% CI 1.51–1.96; Figure).
Discussion: GLP1-RAs are associated with a significantly higher incidence of IBS and FD ICD diagnoses, endoscopic procedures, and IBS-related medications in patients with uncomplicated T2DM. Although absolute rates were low, the relative increases suggest a potential for GLP1-RAs-related GI symptoms to be misclassified as IBS and FD. Further studies are warranted to clarify this association.

Figure: Table 1. Baseline patients’ characteristics before and after propensity score matching.
Abbreviations: GLP1-RAs: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; BMI: body mass index.

Figure: Table 2. Primary and secondary outcomes
Figure. Forest plot depicting the odds ratios of primary and secondary outcomes
Abbreviations: IBS: inflammatory bowel disease; EGD: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy; GLP1-RAs: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; FD: functional dyspepsia; OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval.
Disclosures:
Mohamed Eldesouki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Ibrahim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danny Issa: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
Mohammad Kloub indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khaled Elfert indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jumana Alseidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lin Chang: AnX Robotica – Grant/Research Support. Ardelyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Atmo BioSciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bausch Health – Consultant. FoodMarble Digestive Health – Consultant, Stock Options. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Ironwood Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Lilly – Consultant. ModifyHealth – Stock Options. Trellus Health – Consultant, Stock Options. Vibrant Gastro – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Firas Bahdi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Eldesouki, MD1, Ahmed Ibrahim, MD2, Danny Issa, MD3, Mohammad Kloub, MD4, Khaled Elfert, MD5, Mona Ahmed, 6, Jumana E. Alseidi, 7, Lin Chang, MD8, Firas Bahdi, MD9. P0790 - Increased Diagnoses of IBS and Functional Dyspepsia in Patients With Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Propensity-Matched Cohort Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
