Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0759 - Where There's Smoke, Is There Barrett's Esophagus? A Case Series of EsoGuard Use in Firefighters
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- OB
Owen Battel, MD
University of Virginia
Charlottesville, VA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Owen Battel, MD1, Manavi Bhagwat, MD2, Amy Doran, MD2
1University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA; 2University of Virginia Medical Center, Charlottesville, VA
Introduction: Firefighters are at increased risk of many types of cancers due to work-related exposures, including benzenes, dioxins, asbestos, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and formaldehyde. Research supports a higher rate of esophageal cancers in firefighters, but specific incidence of Barrett’s esophagus (BE) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) compared to the general population are unknown. EsoGuard® is a noninvasive DNA-based screening assay that analyzes cells collected by Esocheck®, a nonendoscopic esophageal balloon sampling device, for BE and EAC. We describe positive findings on esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) among firefighters with positive EsoGuard® screens.
Case Description/
Methods: Asymptomatic firefighters (n=120) underwent EsoGuard® testing in the community as part of a health screening event. Seven men tested positive and were referred by their primary care physician for EGD, and 5 had notable findings. Patient 1, a 64 year old with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and obesity was found to have an esophageal nodule positive for Barrett’s esophagus, benign fundic gland polyps, gastric erythema consistent with reactive changes on biopsy, and nodular duodenal mucosa positive for gastric heterotopia. EGD of patient 2, a 54 year old former smoker, revealed a low grade Schatzki ring, 3 cm hiatal hernia, and erythematous antral mucosa positive for reactive gastropathy and erosions. Patient 3, a 35 year old with obesity, had gastritis on EGD with normal pathology. Patient 4, a 53 year old, was found to have an esophageal nodule positive for Barrett’s esophagus without dysplasia. EGD of patient 5, a 62 year old, revealed erythematous gastric mucosa with normal pathology. None of the five were on a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) prior to endoscopy, and patients 1, 2 and 4 were started on PPI therapy following EGD results.
Discussion: The Esoguard® screening test detected BE in 1.7% of asymptomatic firefighter participants. This case series provides valuable insight into BE rate and endoscopic findings in this high risk population, but is limited by its homogenous cohort and small sample size. Detailed and more longitudinal data in this high risk cohort is needed to help guide personalized screening and treatment recommendations.

Figure: Table 1. Characteristics of patients with positive Esoguard(R) test results
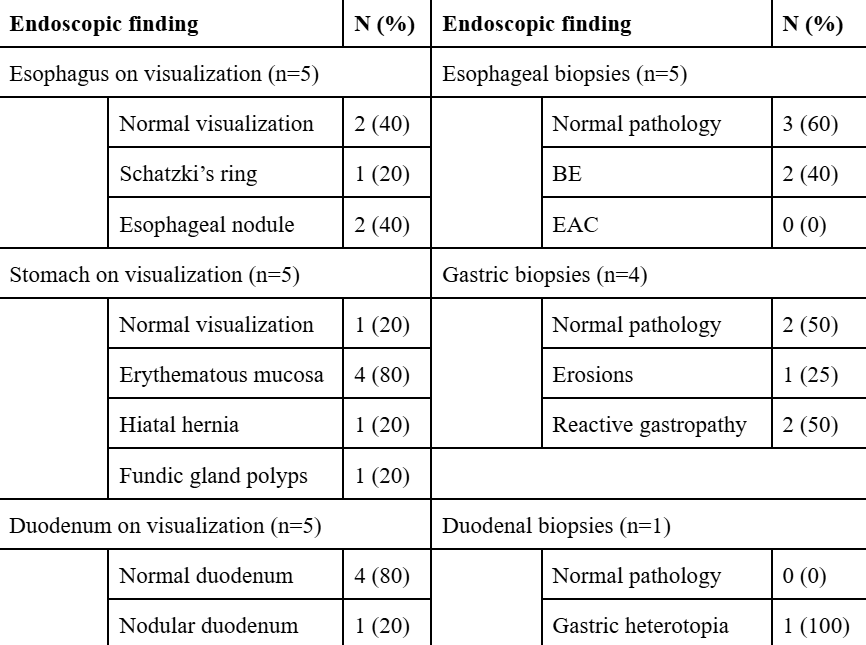
Figure: Table 2. Endoscopic findings in firefighters with positive Esoguard(R) tests
Disclosures:
Owen Battel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manavi Bhagwat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amy Doran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Owen Battel, MD1, Manavi Bhagwat, MD2, Amy Doran, MD2. P0759 - Where There's Smoke, Is There Barrett's Esophagus? A Case Series of EsoGuard Use in Firefighters, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Owen Battel, MD1, Manavi Bhagwat, MD2, Amy Doran, MD2
1University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA; 2University of Virginia Medical Center, Charlottesville, VA
Introduction: Firefighters are at increased risk of many types of cancers due to work-related exposures, including benzenes, dioxins, asbestos, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and formaldehyde. Research supports a higher rate of esophageal cancers in firefighters, but specific incidence of Barrett’s esophagus (BE) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) compared to the general population are unknown. EsoGuard® is a noninvasive DNA-based screening assay that analyzes cells collected by Esocheck®, a nonendoscopic esophageal balloon sampling device, for BE and EAC. We describe positive findings on esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) among firefighters with positive EsoGuard® screens.
Case Description/
Methods: Asymptomatic firefighters (n=120) underwent EsoGuard® testing in the community as part of a health screening event. Seven men tested positive and were referred by their primary care physician for EGD, and 5 had notable findings. Patient 1, a 64 year old with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and obesity was found to have an esophageal nodule positive for Barrett’s esophagus, benign fundic gland polyps, gastric erythema consistent with reactive changes on biopsy, and nodular duodenal mucosa positive for gastric heterotopia. EGD of patient 2, a 54 year old former smoker, revealed a low grade Schatzki ring, 3 cm hiatal hernia, and erythematous antral mucosa positive for reactive gastropathy and erosions. Patient 3, a 35 year old with obesity, had gastritis on EGD with normal pathology. Patient 4, a 53 year old, was found to have an esophageal nodule positive for Barrett’s esophagus without dysplasia. EGD of patient 5, a 62 year old, revealed erythematous gastric mucosa with normal pathology. None of the five were on a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) prior to endoscopy, and patients 1, 2 and 4 were started on PPI therapy following EGD results.
Discussion: The Esoguard® screening test detected BE in 1.7% of asymptomatic firefighter participants. This case series provides valuable insight into BE rate and endoscopic findings in this high risk population, but is limited by its homogenous cohort and small sample size. Detailed and more longitudinal data in this high risk cohort is needed to help guide personalized screening and treatment recommendations.

Figure: Table 1. Characteristics of patients with positive Esoguard(R) test results

Figure: Table 2. Endoscopic findings in firefighters with positive Esoguard(R) tests
Disclosures:
Owen Battel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manavi Bhagwat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amy Doran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Owen Battel, MD1, Manavi Bhagwat, MD2, Amy Doran, MD2. P0759 - Where There's Smoke, Is There Barrett's Esophagus? A Case Series of EsoGuard Use in Firefighters, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

