Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0712 - Lymphocytic Esophagitis: Intermittent Dysphagia Masquerading as Untreated Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Noah Fanous, MD
University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School
Austin, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Noah Fanous, MD1, Elias Fanous, MD2, Asher Fanous, BA3
1University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, Austin, TX; 2UT Health Tyler, Tyler, TX; 3University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX
Introduction: Lymphocytic esophagitis (LyE) is a rare esophageal disorder characterized by esophageal intraepithelial lymphocytosis with minimal granulocyte infiltration and intercellular edema. Endoscopic findings can include erosive esophagitis, concentric rings, strictures, linear furrows, strictures and white plaques. Diagnosis is often confused for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) due to similar endoscopic appearance.
Case Description/
Methods: 81 year old female with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), hiatal hernia, and previously diagnosed EoE presented with intermittent dysphagia and reflux. Patient was diagnosed with EoE in 2022 with no evidence of eosinophilia on biopsy. EGD noted a small Zenker’s diverticulum with numerous concentric rings and linear furrows consistent with possible EoE.. Esophageal biopsies were taken from the proximal and distal esophagus and no dilation offered given higher risk of perforation from previously untreated EoE. Patient was started on a daily PPI. Esophageal biopsy showed benign fragments of squamous mucosa with increased intraepithelial lymphocytes ( >20 per high power field (HPF)) consistent with the actual diagnosis of LyE. Repeat EGD 8 weeks later noted numerous concentric rings and distal esophageal narrowing and biopsy showing acute and chronic inflammation with yeast and fungal forms suggestive of candidal esophagitis; patient was started on budesonide and fluconazole and presented with recurrent candidiasis and resolved lymphocytic esophagitis on follow-up EGD and biopsy. Sprue antibodies were negative.
Discussion: Lymphocytic esophagitis (LyE) is a rare esophageal disorder that can be misdiagnosed as EoE. Diagnostic criteria and treatment are not clearly defined, but on average, patients will present with > 10 intraepithelial lymphocytes per HPF, infrequent or absent granulocytes and epithelial damage. Symptomatic treatment has been noted with PPI use, topical steroids such as fluticasone, and esophageal dilation in patients with more prominent esophageal strictures. In addition, immune-mediated diseases such as celiac, Crohn’s disease, and in our patient’s unique case RA are increasingly found to be associated with the disease.
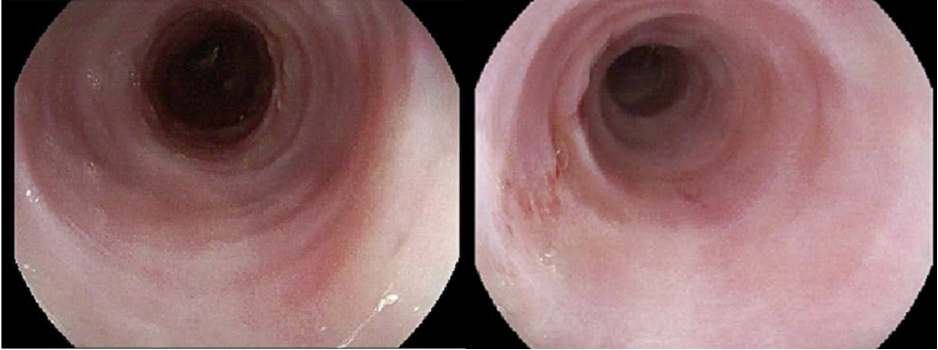
Figure: EGD with numerous concentric rings and linear furrows
Disclosures:
Noah Fanous indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elias Fanous indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asher Fanous indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noah Fanous, MD1, Elias Fanous, MD2, Asher Fanous, BA3. P0712 - Lymphocytic Esophagitis: Intermittent Dysphagia Masquerading as Untreated Eosinophilic Esophagitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School, Austin, TX; 2UT Health Tyler, Tyler, TX; 3University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX
Introduction: Lymphocytic esophagitis (LyE) is a rare esophageal disorder characterized by esophageal intraepithelial lymphocytosis with minimal granulocyte infiltration and intercellular edema. Endoscopic findings can include erosive esophagitis, concentric rings, strictures, linear furrows, strictures and white plaques. Diagnosis is often confused for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) due to similar endoscopic appearance.
Case Description/
Methods: 81 year old female with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), hiatal hernia, and previously diagnosed EoE presented with intermittent dysphagia and reflux. Patient was diagnosed with EoE in 2022 with no evidence of eosinophilia on biopsy. EGD noted a small Zenker’s diverticulum with numerous concentric rings and linear furrows consistent with possible EoE.. Esophageal biopsies were taken from the proximal and distal esophagus and no dilation offered given higher risk of perforation from previously untreated EoE. Patient was started on a daily PPI. Esophageal biopsy showed benign fragments of squamous mucosa with increased intraepithelial lymphocytes ( >20 per high power field (HPF)) consistent with the actual diagnosis of LyE. Repeat EGD 8 weeks later noted numerous concentric rings and distal esophageal narrowing and biopsy showing acute and chronic inflammation with yeast and fungal forms suggestive of candidal esophagitis; patient was started on budesonide and fluconazole and presented with recurrent candidiasis and resolved lymphocytic esophagitis on follow-up EGD and biopsy. Sprue antibodies were negative.
Discussion: Lymphocytic esophagitis (LyE) is a rare esophageal disorder that can be misdiagnosed as EoE. Diagnostic criteria and treatment are not clearly defined, but on average, patients will present with > 10 intraepithelial lymphocytes per HPF, infrequent or absent granulocytes and epithelial damage. Symptomatic treatment has been noted with PPI use, topical steroids such as fluticasone, and esophageal dilation in patients with more prominent esophageal strictures. In addition, immune-mediated diseases such as celiac, Crohn’s disease, and in our patient’s unique case RA are increasingly found to be associated with the disease.

Figure: EGD with numerous concentric rings and linear furrows
Disclosures:
Noah Fanous indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elias Fanous indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asher Fanous indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noah Fanous, MD1, Elias Fanous, MD2, Asher Fanous, BA3. P0712 - Lymphocytic Esophagitis: Intermittent Dysphagia Masquerading as Untreated Eosinophilic Esophagitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
