Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0311 - Evaluating Abnormalities of the Recto-Anal Inhibitory Reflex in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus vs Healthy Controls
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Rachel Moffett, DO
Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist
Charlotte, NC
Presenting Author(s)
Rachel Moffett, DO1, Sahla Hammad, MD1, Eva Kinzer, NP1, Karla Rocio Garcia Z Rocio Garcia Z, MBBS2, Jose M Remes-Troche, 2, Baha Moshiree, MD3, Jason Baker, MS4
1Atrium Health, Charlotte, NC; 2universidad, Veracruz, Veracruz-Llave, Mexico; 3Atrium Health Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC; 4Anxrobotics, Foley, AL
Introduction: Recto anal inhibitory reflex (RAIR) is part of defecation where the anal canal temporarily relaxes in response to rectal distension. Mediated by the enteric nervous system, RAIR can be abnormal in patients (pts) with neurologic disease, leading to a defecatory disorder. RAIR is part of testing during Anorectal Manometry (ARM) and has been standardized by the International Anorectal Physiology Working Group (IAPWG). Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is associated with peripheral neuropathy and both fecal incontinence (FI) and constipation (CN). Study aim: to evaluate abnormalities in RAIR parameters beyond the present/absent classification in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) compared to healthy controls (HC).
Methods: Retrospective review of 27 pts (16 DM and 11 HC) who completed an ARM and Balloon Expulsion Testing (BET), at two medical centers. All pts underwent ARM with a balloon distension volume of 50cc and evaluation of RAIR, including measurements of Excitation Latency (EL), Amplitude Reduction (AR) (normal ≥25%), Recovery Time (RT), and Duration of Reflex (DR). EL, RT, and DR were measured in seconds, and AR was by %. Normal BET consisted of the ability to expel a 50 ml balloon in ≤ 60 seconds. Analysis consisted of independent t-tests, chi-square test, and logistic regression. A p-value of ≤0.05 was considered significant.
Results: N = 27 pts, mean age of 51.9 (SD = 18.0; Range: 20-78), 74.1% female, and 42.3% Hispanic were analyzed. Indications for ARM and BET in DM pts were: 52.4% CN and 47.6 FI. DM pts mean age was significantly higher than HC: 61.4 (14.1) vs. 37.9 (13.6), p = 0.0002. EL, p = 0.04, AR, p = 0.0001, and DR, p = 0.0002, were significantly different for DM pts vs. HC. [Table 1]. BET results were 63.0% normal and 37.0% abnormal overall. An abnormal BET was significantly different vs. normal BET in the entire sample: EL (4.0 vs. 1.2, p = 0.03); AR (24.0% vs. 43.2%, p = 0.004); DR (12.9 vs. 30.9, p = 0.02). No RAIR differences in BET results in DM patients only. The regression model, including age, EL, DR, and AR, showed no association for DM pts compared to HC.
Discussion: Evaluating specific RAIR parameters, we found significant differences between ARM patient populations versus healthy controls. These parameters should be investigated in populations with a medical history of neuropathy and systemic/autoimmune disorders. Further guidelines should consider classification of RAIR beyond normal and areflexia as RAIR may not be a binary assessment.
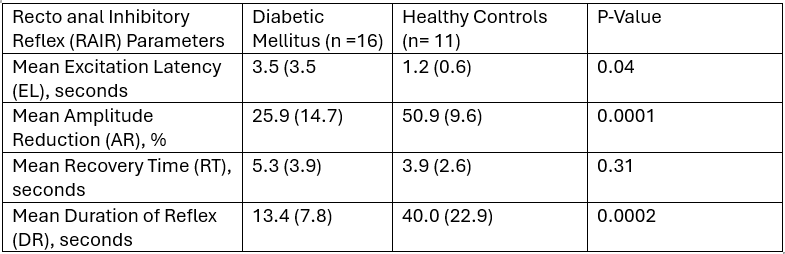
Figure: Table 1
Recto anal Inhibitory Reflex (RAIR) Parameters: Diabetes Mellitus vs. Healthy Controls
Disclosures:
Rachel Moffett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sahla Hammad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eva Kinzer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karla Rocio Garcia Z Rocio Garcia Z indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jose M Remes-Troche indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Baha Moshiree indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Baker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Moffett, DO1, Sahla Hammad, MD1, Eva Kinzer, NP1, Karla Rocio Garcia Z Rocio Garcia Z, MBBS2, Jose M Remes-Troche, 2, Baha Moshiree, MD3, Jason Baker, MS4. P0311 - Evaluating Abnormalities of the Recto-Anal Inhibitory Reflex in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus vs Healthy Controls, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Atrium Health, Charlotte, NC; 2universidad, Veracruz, Veracruz-Llave, Mexico; 3Atrium Health Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC; 4Anxrobotics, Foley, AL
Introduction: Recto anal inhibitory reflex (RAIR) is part of defecation where the anal canal temporarily relaxes in response to rectal distension. Mediated by the enteric nervous system, RAIR can be abnormal in patients (pts) with neurologic disease, leading to a defecatory disorder. RAIR is part of testing during Anorectal Manometry (ARM) and has been standardized by the International Anorectal Physiology Working Group (IAPWG). Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is associated with peripheral neuropathy and both fecal incontinence (FI) and constipation (CN). Study aim: to evaluate abnormalities in RAIR parameters beyond the present/absent classification in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) compared to healthy controls (HC).
Methods: Retrospective review of 27 pts (16 DM and 11 HC) who completed an ARM and Balloon Expulsion Testing (BET), at two medical centers. All pts underwent ARM with a balloon distension volume of 50cc and evaluation of RAIR, including measurements of Excitation Latency (EL), Amplitude Reduction (AR) (normal ≥25%), Recovery Time (RT), and Duration of Reflex (DR). EL, RT, and DR were measured in seconds, and AR was by %. Normal BET consisted of the ability to expel a 50 ml balloon in ≤ 60 seconds. Analysis consisted of independent t-tests, chi-square test, and logistic regression. A p-value of ≤0.05 was considered significant.
Results: N = 27 pts, mean age of 51.9 (SD = 18.0; Range: 20-78), 74.1% female, and 42.3% Hispanic were analyzed. Indications for ARM and BET in DM pts were: 52.4% CN and 47.6 FI. DM pts mean age was significantly higher than HC: 61.4 (14.1) vs. 37.9 (13.6), p = 0.0002. EL, p = 0.04, AR, p = 0.0001, and DR, p = 0.0002, were significantly different for DM pts vs. HC. [Table 1]. BET results were 63.0% normal and 37.0% abnormal overall. An abnormal BET was significantly different vs. normal BET in the entire sample: EL (4.0 vs. 1.2, p = 0.03); AR (24.0% vs. 43.2%, p = 0.004); DR (12.9 vs. 30.9, p = 0.02). No RAIR differences in BET results in DM patients only. The regression model, including age, EL, DR, and AR, showed no association for DM pts compared to HC.
Discussion: Evaluating specific RAIR parameters, we found significant differences between ARM patient populations versus healthy controls. These parameters should be investigated in populations with a medical history of neuropathy and systemic/autoimmune disorders. Further guidelines should consider classification of RAIR beyond normal and areflexia as RAIR may not be a binary assessment.

Figure: Table 1
Recto anal Inhibitory Reflex (RAIR) Parameters: Diabetes Mellitus vs. Healthy Controls
Disclosures:
Rachel Moffett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sahla Hammad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eva Kinzer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karla Rocio Garcia Z Rocio Garcia Z indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jose M Remes-Troche indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Baha Moshiree indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Baker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Moffett, DO1, Sahla Hammad, MD1, Eva Kinzer, NP1, Karla Rocio Garcia Z Rocio Garcia Z, MBBS2, Jose M Remes-Troche, 2, Baha Moshiree, MD3, Jason Baker, MS4. P0311 - Evaluating Abnormalities of the Recto-Anal Inhibitory Reflex in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus vs Healthy Controls, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

