Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0266 - Efficacy and Safety of Sintilimab (PD-1 Inhibitor) Combined With Anti-VEGF Therapy as Neoadjuvant Treatment in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Proportional Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Ayesha Ishtiaq, MBBS (she/her/hers)
Federal Medical and Dental College
Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan
Presenting Author(s)
Haris Mumtaz Malik, MBBS1, Beenish Sabir, MBBS1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Waseem Nabi, MD3, Omar Al-Radideh, MD4, Ayesha Ishtiaq, MBBS5
1Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 2University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 3Wyckoff Heights Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL; 5Federal Medical and Dental College, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan
Introduction: Metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) remains a major contributor to cancer mortality, particularly in RAS-mutant and microsatellite-stable (MSS) tumors, which respond poorly to immunotherapy. Combining PD-1 inhibitors like sintilimab with anti-VEGF agents may enhance immune response by improving T-cell infiltration and vascular normalization. This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of this combination as neoadjuvant therapy in colorectal cancer.
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane was conducted for clinical trials published up to April 3, 2025, assessing sintilimab with anti-VEGF agents in neoadjuvant colorectal cancer treatment. Primary outcomes included adverse events (AEs), grade ≥3 AEs, progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and stable disease (SD). Random-effects meta-analysis and leave-one-out sensitivity analysis were performed using R Studio.
Results: Four trials (205 patients) were included. One-year PFS was 25% (95% CI: 9%–45%) with high heterogeneity (I² = 82.1%), resolved to 0% after excluding Liu 2025. Two-year PFS was 9% (95% CI: 5%–14%) with no heterogeneity. ORR was 55% (95% CI: 32%–76%; I² = 89.3%), dropping to 45.4% upon omitting Guo 2023. Stable disease was 42% (95% CI: 25%–60%; I² = 82.4%), reduced to 58.0% excluding Guo 2023. AEs occurred in 90% (95% CI: 65%–100%; I² = 94.0%), mainly influenced by Wang 2025 (I² dropped to 25.4%). Grade ≥3 AEs were 21% (95% CI: 3%–48%; I² = 92.4%), lowered to 9% (95% CI: 5%–15%) upon excluding Guo 2023.
Discussion: Neoadjuvant sintilimab plus anti-VEGF therapy demonstrates modest efficacy and manageable toxicity in colorectal cancer. High heterogeneity underscores the need for standardized approaches and biomarker-driven trials, particularly for MSS/RAS-mutant subgroups.
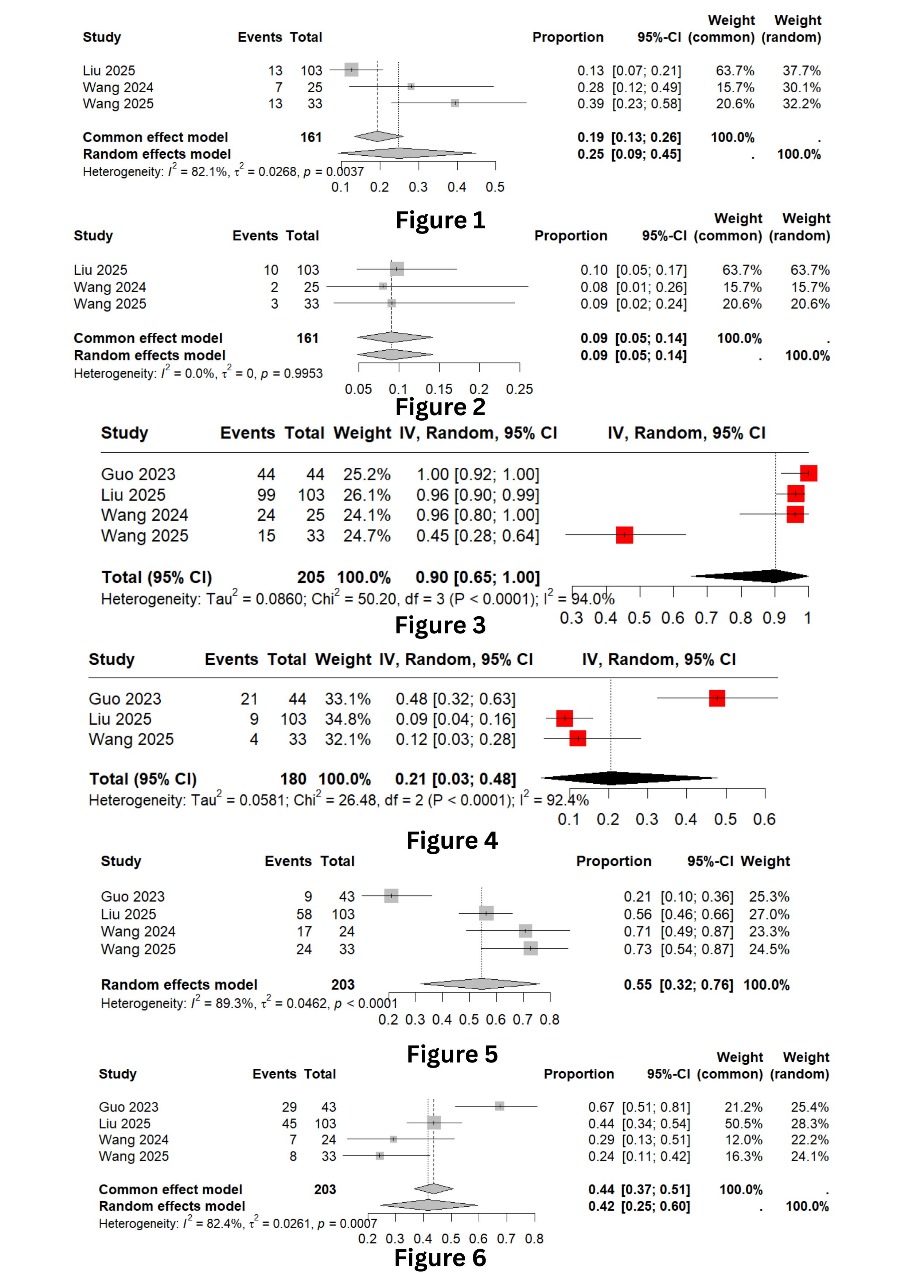
Figure: Title: Forest Plots
Figure 1: PFS at 1 Year
Figure 2: PFS at 2 Year
Figure 3: Adverse Events
Figure 4: Adverse Events (Grade 3 or >Grade 3)
Figure 5: Objective Response Rate
Figure 6: Stable Disease
Disclosures:
Haris Mumtaz Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Beenish Sabir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Waseem Nabi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al-Radideh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Ishtiaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haris Mumtaz Malik, MBBS1, Beenish Sabir, MBBS1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Waseem Nabi, MD3, Omar Al-Radideh, MD4, Ayesha Ishtiaq, MBBS5. P0266 - Efficacy and Safety of Sintilimab (PD-1 Inhibitor) Combined With Anti-VEGF Therapy as Neoadjuvant Treatment in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Proportional Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rawalpindi Medical University, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan; 2University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 3Wyckoff Heights Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 4University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL; 5Federal Medical and Dental College, Islamabad, Islamabad, Pakistan
Introduction: Metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) remains a major contributor to cancer mortality, particularly in RAS-mutant and microsatellite-stable (MSS) tumors, which respond poorly to immunotherapy. Combining PD-1 inhibitors like sintilimab with anti-VEGF agents may enhance immune response by improving T-cell infiltration and vascular normalization. This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of this combination as neoadjuvant therapy in colorectal cancer.
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane was conducted for clinical trials published up to April 3, 2025, assessing sintilimab with anti-VEGF agents in neoadjuvant colorectal cancer treatment. Primary outcomes included adverse events (AEs), grade ≥3 AEs, progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and stable disease (SD). Random-effects meta-analysis and leave-one-out sensitivity analysis were performed using R Studio.
Results: Four trials (205 patients) were included. One-year PFS was 25% (95% CI: 9%–45%) with high heterogeneity (I² = 82.1%), resolved to 0% after excluding Liu 2025. Two-year PFS was 9% (95% CI: 5%–14%) with no heterogeneity. ORR was 55% (95% CI: 32%–76%; I² = 89.3%), dropping to 45.4% upon omitting Guo 2023. Stable disease was 42% (95% CI: 25%–60%; I² = 82.4%), reduced to 58.0% excluding Guo 2023. AEs occurred in 90% (95% CI: 65%–100%; I² = 94.0%), mainly influenced by Wang 2025 (I² dropped to 25.4%). Grade ≥3 AEs were 21% (95% CI: 3%–48%; I² = 92.4%), lowered to 9% (95% CI: 5%–15%) upon excluding Guo 2023.
Discussion: Neoadjuvant sintilimab plus anti-VEGF therapy demonstrates modest efficacy and manageable toxicity in colorectal cancer. High heterogeneity underscores the need for standardized approaches and biomarker-driven trials, particularly for MSS/RAS-mutant subgroups.

Figure: Title: Forest Plots
Figure 1: PFS at 1 Year
Figure 2: PFS at 2 Year
Figure 3: Adverse Events
Figure 4: Adverse Events (Grade 3 or >Grade 3)
Figure 5: Objective Response Rate
Figure 6: Stable Disease
Disclosures:
Haris Mumtaz Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Beenish Sabir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adnan Bhat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Waseem Nabi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Al-Radideh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Ishtiaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haris Mumtaz Malik, MBBS1, Beenish Sabir, MBBS1, Adnan Bhat, MD2, Waseem Nabi, MD3, Omar Al-Radideh, MD4, Ayesha Ishtiaq, MBBS5. P0266 - Efficacy and Safety of Sintilimab (PD-1 Inhibitor) Combined With Anti-VEGF Therapy as Neoadjuvant Treatment in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Proportional Meta-Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
