Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0251 - A Rare Manifestation of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicity
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SF
Scott Farley, MD
Prisma Health, University of South Carolina School of Medicine
Greenville, SC
Presenting Author(s)
Scott Farley, MD1, Aayush Purohit, BS1, Joseph R. Baber, DO2
1Prisma Health, University of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville, SC; 2Prisma Health, Uniiversity of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville, Greenville, SC
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have revolutionized care for patients suffering from a variety of oncologic conditions. Their use has significantly increased since ipilimumab was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma. With widespread use has come increasingly recognized toxicities, most of which affect the GI tract and skin. Rarely, toxicity can manifest as hepatobiliary disease. We present a case of immune-mediated cholangitis (IMC) induced by ICI.
Case Description/
Methods: An 80-year-old female with metastatic endometrial cancer presented to the emergency department with encephalopathy due to hydrocodone-acetaminophen taken for cancer-related pain. She took a 1-week course of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) and completed pembrolizumab cycle 19 3 weeks prior to presentation. She was afebrile with normal vital signs. Physical exam noted no abdominal tenderness, asterixis, or jaundice. Labs showed markedly elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) to 1,881 IU/L (ULN 104), total bilirubin 1.2mg/dL (ULN 1.2), AST 396 IU/L (ULN 35), ALT 234 IU/L (ULN 35), and GGT 695 IU/L (ULN 36); liver enzymes were normal 1 month prior. INR 2.8 (ULN 1.2). WBC 13.4 (ULN 10.8). Acetaminophen level 38mcg/mL (ULN 30). MRI/MRCP showed a 7mm common bile duct with enhancement and thickening of the intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts without filling defect. Acute viral and autoimmune antibodies were unremarkable including AMA, IgG4, ASMA titer 1:20. N-acetylcysteine and antibiotics were prescribed on admission. INR normalized on day 2. Methylprednisolone 1mg/kg/day started on day 2 and ALP decreased by 50% by day 5, though remained elevated (462 IU/L) after 4 months with pembrolizumab discontinued. Follow up imaging at 4 months also showed resolution of biliary findings.
Discussion: IMC is a rare but increasingly reported complication of ICI therapy. While exposed to TMP-SMX 3 weeks prior, her laboratory pattern, imaging, and pembrolizumab exposure were more consistent with case series describing IMC. The rapid improvement following glucocorticoid therapy obviated the need for biopsy. Her transient coagulopathy was potentially due to concomitant acetaminophen toxicity. Glucocorticoids and discontinuation of the offending agent are the mainstays of therapy for IMC, though complete normalization of liver enzymes is rare. There are some data to suggest ursodiol may provide added benefit. Further research is necessary to provide diagnostic and management guidance.
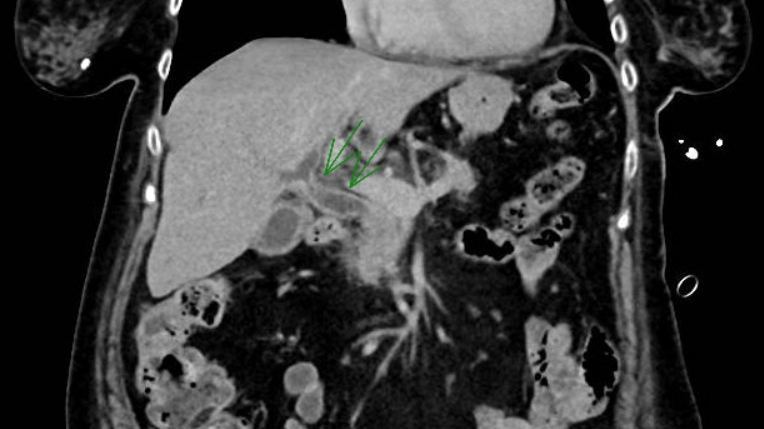
Figure: CT with contrast demonstrating bile duct thickening
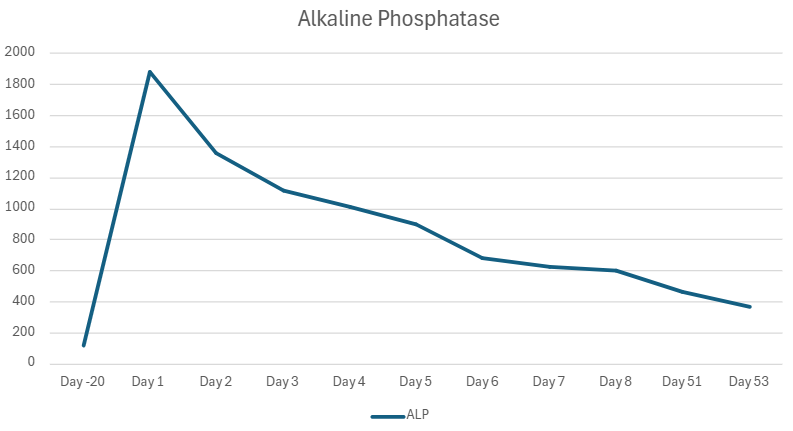
Figure: ALP trend following initiation of glucocorticoids on Day 2
Disclosures:
Scott Farley indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aayush Purohit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Baber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Scott Farley, MD1, Aayush Purohit, BS1, Joseph R. Baber, DO2. P0251 - A Rare Manifestation of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicity, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Prisma Health, University of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville, SC; 2Prisma Health, Uniiversity of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville, Greenville, SC
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have revolutionized care for patients suffering from a variety of oncologic conditions. Their use has significantly increased since ipilimumab was approved in 2011 for metastatic melanoma. With widespread use has come increasingly recognized toxicities, most of which affect the GI tract and skin. Rarely, toxicity can manifest as hepatobiliary disease. We present a case of immune-mediated cholangitis (IMC) induced by ICI.
Case Description/
Methods: An 80-year-old female with metastatic endometrial cancer presented to the emergency department with encephalopathy due to hydrocodone-acetaminophen taken for cancer-related pain. She took a 1-week course of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) and completed pembrolizumab cycle 19 3 weeks prior to presentation. She was afebrile with normal vital signs. Physical exam noted no abdominal tenderness, asterixis, or jaundice. Labs showed markedly elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) to 1,881 IU/L (ULN 104), total bilirubin 1.2mg/dL (ULN 1.2), AST 396 IU/L (ULN 35), ALT 234 IU/L (ULN 35), and GGT 695 IU/L (ULN 36); liver enzymes were normal 1 month prior. INR 2.8 (ULN 1.2). WBC 13.4 (ULN 10.8). Acetaminophen level 38mcg/mL (ULN 30). MRI/MRCP showed a 7mm common bile duct with enhancement and thickening of the intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts without filling defect. Acute viral and autoimmune antibodies were unremarkable including AMA, IgG4, ASMA titer 1:20. N-acetylcysteine and antibiotics were prescribed on admission. INR normalized on day 2. Methylprednisolone 1mg/kg/day started on day 2 and ALP decreased by 50% by day 5, though remained elevated (462 IU/L) after 4 months with pembrolizumab discontinued. Follow up imaging at 4 months also showed resolution of biliary findings.
Discussion: IMC is a rare but increasingly reported complication of ICI therapy. While exposed to TMP-SMX 3 weeks prior, her laboratory pattern, imaging, and pembrolizumab exposure were more consistent with case series describing IMC. The rapid improvement following glucocorticoid therapy obviated the need for biopsy. Her transient coagulopathy was potentially due to concomitant acetaminophen toxicity. Glucocorticoids and discontinuation of the offending agent are the mainstays of therapy for IMC, though complete normalization of liver enzymes is rare. There are some data to suggest ursodiol may provide added benefit. Further research is necessary to provide diagnostic and management guidance.

Figure: CT with contrast demonstrating bile duct thickening

Figure: ALP trend following initiation of glucocorticoids on Day 2
Disclosures:
Scott Farley indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aayush Purohit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Baber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Scott Farley, MD1, Aayush Purohit, BS1, Joseph R. Baber, DO2. P0251 - A Rare Manifestation of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicity, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

