Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0198 - When Malignancy Mimics the Benign: A Delayed Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Rishika Trivedi, MD
DHR Health
McAllen, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Rishika Trivedi, MD1, Prince Shah-Riar, MD2, Mahmoud Barbarawi, MD1, Asif Zamir, MD, FACG3
1DHR Health, McAllen, TX; 2DHR Health, Edinburg, Tx, McAllen, TX; 3DHR Health Gastroenterology, Edinburg, TX
Introduction: Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare but lethal malignancy that frequently evades early diagnosis due to its insidious onset. When imaging and tissue sampling repeatedly return inconclusive results, clinicians face diagnostic uncertainty. We present a case where cholangiocarcinoma was diagnosed only after multiple nondiagnostic interventions and eventual cholangioscopy-guided biopsy.
Case Description/
Methods: A 54-year-old male presented with 2 weeks of nausea, abdominal pain, pale stools, tea-colored urine, and 20 lb weight loss. Labs showed AST 249, ALT 566, ALP 348, and total bilirubin 3.9. A CT of the abdomen revealed a 1.8x1.6 cm hypodense lesion in the pancreatic head with biliary dilatation. EUS FNA and ERCP with brushings were non-diagnostic, and a plastic stent was placed. A second ERCP revealed a distal CBD stricture due to persistent cholestasis, prompting the placement of a fully covered metal stent. However, liver enzymes continued to rise following the procedure. Liver biopsy revealed no malignancy, and MRI with liver protocol failed to identify an obstructive lesion. Labs worsened to AST 74, ALT 82, ALP 300, GGT 197, total bilirubin 16.2, direct bilirubin 8.3, and albumin 3.3. A third ERCP with cholangioscopy showed uneven areas in the tissue ( Figure 1), and a specific biopsy found unusual glandular cells. Immunohistochemistry was positive for CK7, CK20, mesothelin, SMAD4, and Ki-67, confirming cholangiocarcinoma.
Discussion: This case illustrates the diagnostic complexity of cholangiocarcinoma. Despite imaging and multiple benign biopsies, the diagnosis remained uncertain. MRI and liver biopsy were unrevealing. Only cholangioscopy-enabled biopsy confirmed malignancy. Cholangioscopy should be considered early when standard evaluation is nondiagnostic. This case highlights the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion and utilizing advanced diagnostics in patients with unexplained, progressive cholestasis.
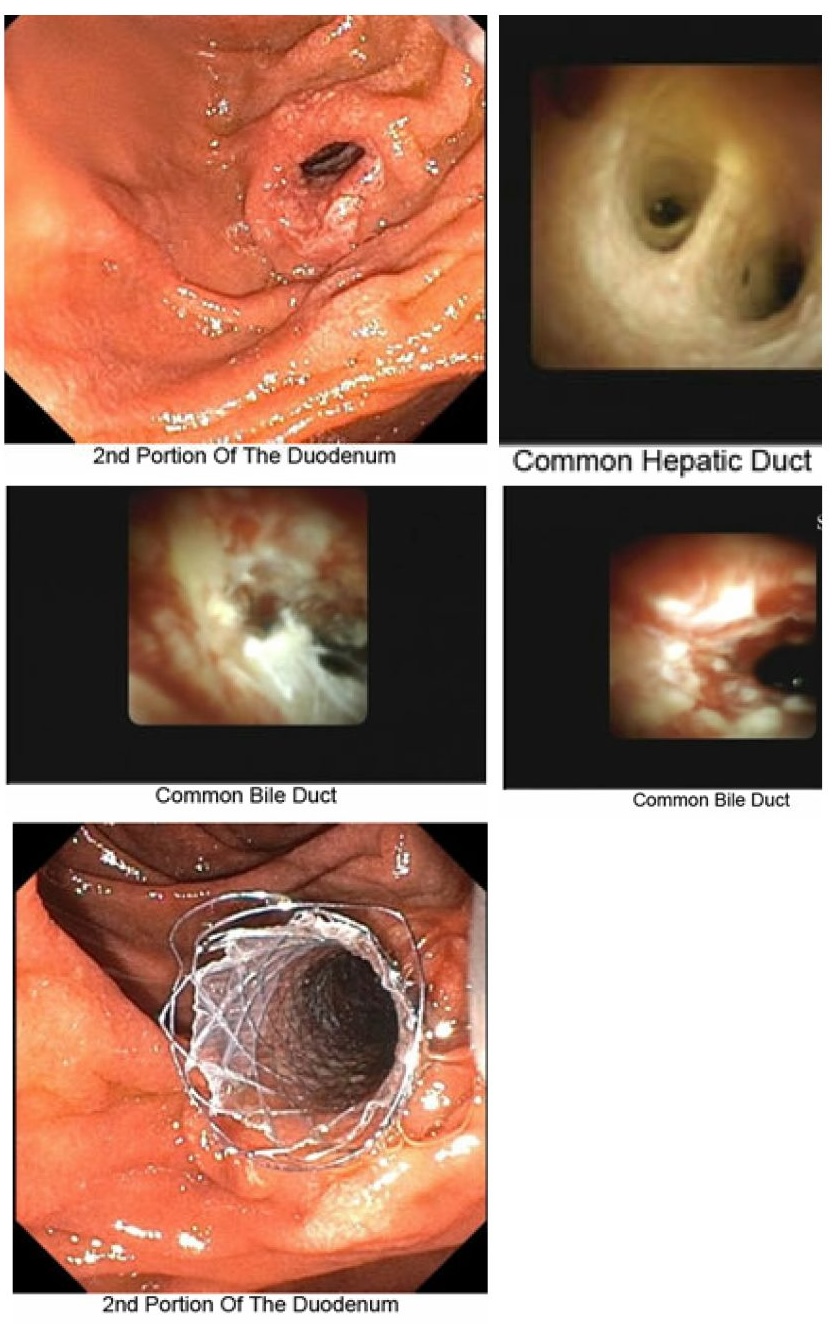
Figure: Figure 1: Endoscopic findings and interventions in the common bile duct: Erythema and irregularity noted in the lower third of the common bile duct, with abnormal mucosa. One stent covered metal stent was placed; biopsy was performed in the affected region.
Disclosures:
Rishika Trivedi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Shah-Riar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Barbarawi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asif Zamir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rishika Trivedi, MD1, Prince Shah-Riar, MD2, Mahmoud Barbarawi, MD1, Asif Zamir, MD, FACG3. P0198 - When Malignancy Mimics the Benign: A Delayed Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1DHR Health, McAllen, TX; 2DHR Health, Edinburg, Tx, McAllen, TX; 3DHR Health Gastroenterology, Edinburg, TX
Introduction: Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare but lethal malignancy that frequently evades early diagnosis due to its insidious onset. When imaging and tissue sampling repeatedly return inconclusive results, clinicians face diagnostic uncertainty. We present a case where cholangiocarcinoma was diagnosed only after multiple nondiagnostic interventions and eventual cholangioscopy-guided biopsy.
Case Description/
Methods: A 54-year-old male presented with 2 weeks of nausea, abdominal pain, pale stools, tea-colored urine, and 20 lb weight loss. Labs showed AST 249, ALT 566, ALP 348, and total bilirubin 3.9. A CT of the abdomen revealed a 1.8x1.6 cm hypodense lesion in the pancreatic head with biliary dilatation. EUS FNA and ERCP with brushings were non-diagnostic, and a plastic stent was placed. A second ERCP revealed a distal CBD stricture due to persistent cholestasis, prompting the placement of a fully covered metal stent. However, liver enzymes continued to rise following the procedure. Liver biopsy revealed no malignancy, and MRI with liver protocol failed to identify an obstructive lesion. Labs worsened to AST 74, ALT 82, ALP 300, GGT 197, total bilirubin 16.2, direct bilirubin 8.3, and albumin 3.3. A third ERCP with cholangioscopy showed uneven areas in the tissue ( Figure 1), and a specific biopsy found unusual glandular cells. Immunohistochemistry was positive for CK7, CK20, mesothelin, SMAD4, and Ki-67, confirming cholangiocarcinoma.
Discussion: This case illustrates the diagnostic complexity of cholangiocarcinoma. Despite imaging and multiple benign biopsies, the diagnosis remained uncertain. MRI and liver biopsy were unrevealing. Only cholangioscopy-enabled biopsy confirmed malignancy. Cholangioscopy should be considered early when standard evaluation is nondiagnostic. This case highlights the importance of maintaining a high index of suspicion and utilizing advanced diagnostics in patients with unexplained, progressive cholestasis.

Figure: Figure 1: Endoscopic findings and interventions in the common bile duct: Erythema and irregularity noted in the lower third of the common bile duct, with abnormal mucosa. One stent covered metal stent was placed; biopsy was performed in the affected region.
Disclosures:
Rishika Trivedi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Shah-Riar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Barbarawi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asif Zamir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rishika Trivedi, MD1, Prince Shah-Riar, MD2, Mahmoud Barbarawi, MD1, Asif Zamir, MD, FACG3. P0198 - When Malignancy Mimics the Benign: A Delayed Diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
