Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0166 - Biliary Obstruction Secondary to Lymphatic Metastasis From Invasive Breast Carcinoma: A Case Report
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Aziz Eshov, DO (he/him/his)
Skagit Regional Hospital
Arlington, AR
Presenting Author(s)
Aziz Eshov, DO1, Samit Datta, MD2
1Skagit Regional Hospital, Arlington, WA; 2Skagit Regional Hospital., Mount Vernon, WA
Introduction: Cowden syndrome (CS) is an AD disorder that elevates breast cancer risk by 25%. Metastatic involvement of the GI tract occurs in about 10% of breast cancer cases. This report details a rare instance of obstructive jaundice due to lymph node metastasis invading the biliary duct, originating from recurrent invasive lobular breast carcinoma.
Case Description/
Methods: We present a 39-year-old female who was initially diagnosed with invasive lobular breast cancer in 2021 and was found to have CS. Following her initial diagnosis, she underwent a mastectomy and completed courses of radiation and chemotherapy. As a prophylactic measure, she underwent a right radical mastectomy, hysterectomy, and bilateral salpingectomy.
In 2025, patient presented with complaints of jaundice and fatigue. She was found to have hyperbilirubinemia. CT abdomen revealed extensive metastatic disease involving the liver, pancreas, and bones, along with multifocal lymphadenopathy (Figure 1). EUS identified hypoechoic lesion measuring 1.7 cm causing cutoff of the CBD which was sampled with FNA (Figure 2). ERCP identified a non-dilated common bile duct with an obstruction suspected at the site of the lymph node. CBD stent could not be placed during ERCP due to the inability to advance the wire beyond the common bile duct. FNA biopsy of the lymph node confirmed breast origin. As biliary stent placement was not feasible, percutaneous biliary drainage (PTBD) was performed. Patient started chemotherapy but ultimately succumbed to fulminant liver failure.
Discussion: Biliary duct obstruction resulting from invasive lymph node represents a rare complication of recurrent invasive lobular carcinoma. Typically, obstructive jaundice is managed with the placement of a biliary duct stent for decompression, thereby resolving hyperbilirubinemia. Failure to address hyperbilirubinemia can lead to delays in chemotherapy administration. For patients unable to undergo stent placement, PTBD serves as an alternative intervention. Nonetheless, PTBD is associated with risks of recurrent obstruction and infections. This case report exemplifies the rare occurrence of obstructive jaundice attributable to lymph node invasion from metastatic breast cancer, which has not been widely reported.
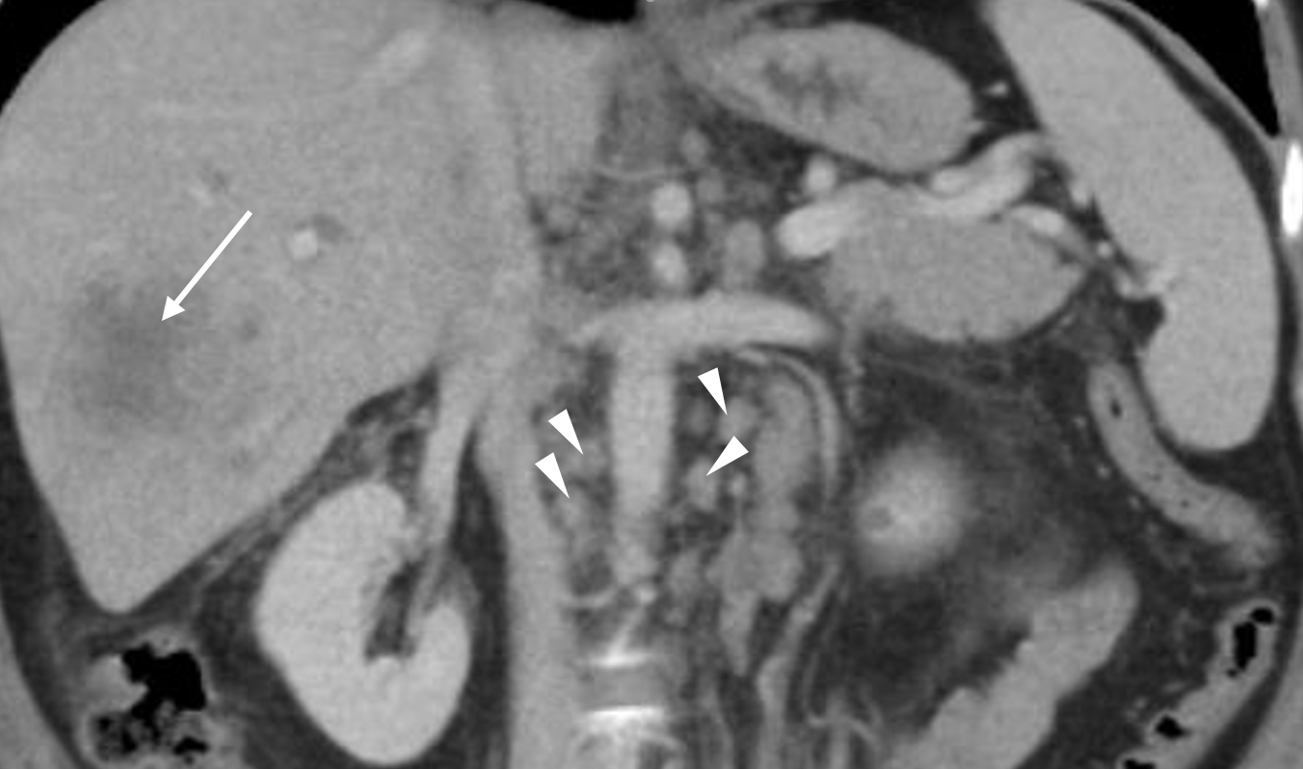
Figure: Figure 1
Liver metastasis (white arrow) and lymphadenopathies (white triangles)
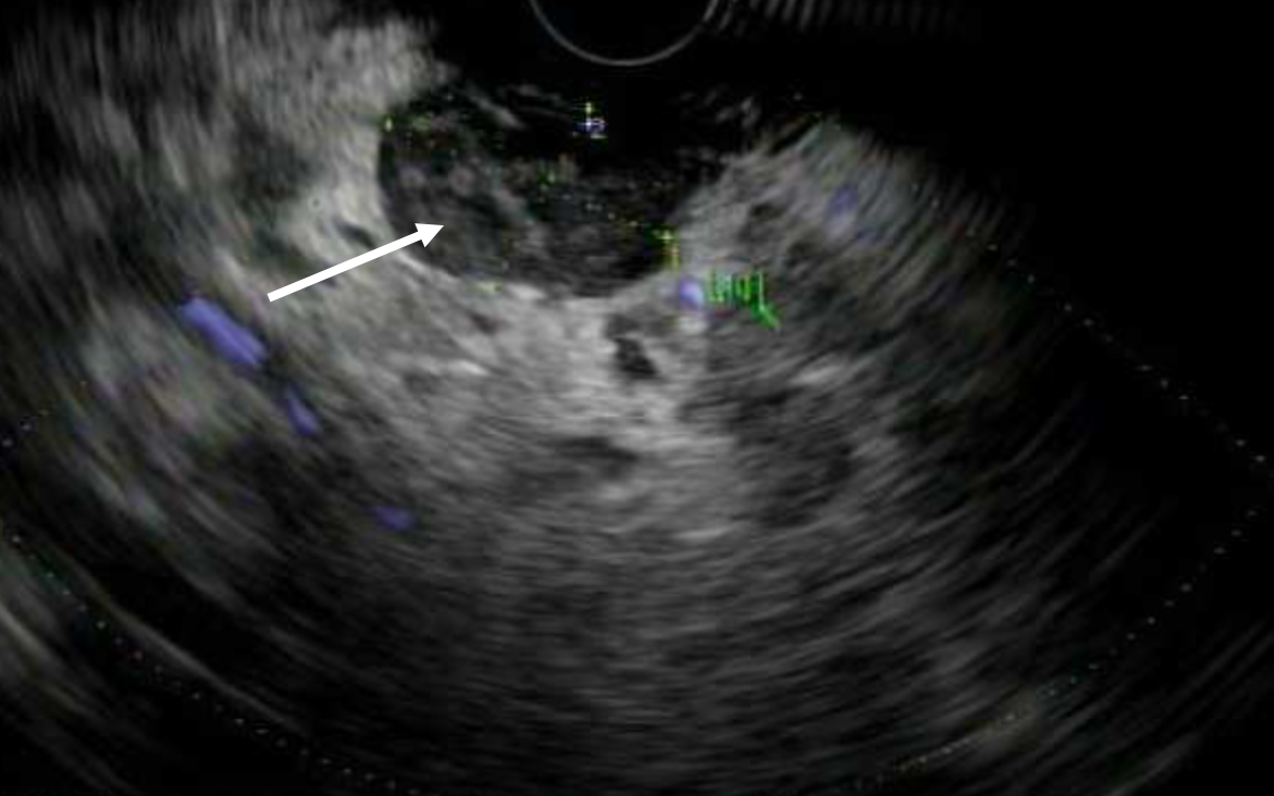
Figure: Figure 2
White arrow showing hypoechoic structure on the EUS.
Disclosures:
Aziz Eshov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samit Datta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aziz Eshov, DO1, Samit Datta, MD2. P0166 - Biliary Obstruction Secondary to Lymphatic Metastasis From Invasive Breast Carcinoma: A Case Report, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Skagit Regional Hospital, Arlington, WA; 2Skagit Regional Hospital., Mount Vernon, WA
Introduction: Cowden syndrome (CS) is an AD disorder that elevates breast cancer risk by 25%. Metastatic involvement of the GI tract occurs in about 10% of breast cancer cases. This report details a rare instance of obstructive jaundice due to lymph node metastasis invading the biliary duct, originating from recurrent invasive lobular breast carcinoma.
Case Description/
Methods: We present a 39-year-old female who was initially diagnosed with invasive lobular breast cancer in 2021 and was found to have CS. Following her initial diagnosis, she underwent a mastectomy and completed courses of radiation and chemotherapy. As a prophylactic measure, she underwent a right radical mastectomy, hysterectomy, and bilateral salpingectomy.
In 2025, patient presented with complaints of jaundice and fatigue. She was found to have hyperbilirubinemia. CT abdomen revealed extensive metastatic disease involving the liver, pancreas, and bones, along with multifocal lymphadenopathy (Figure 1). EUS identified hypoechoic lesion measuring 1.7 cm causing cutoff of the CBD which was sampled with FNA (Figure 2). ERCP identified a non-dilated common bile duct with an obstruction suspected at the site of the lymph node. CBD stent could not be placed during ERCP due to the inability to advance the wire beyond the common bile duct. FNA biopsy of the lymph node confirmed breast origin. As biliary stent placement was not feasible, percutaneous biliary drainage (PTBD) was performed. Patient started chemotherapy but ultimately succumbed to fulminant liver failure.
Discussion: Biliary duct obstruction resulting from invasive lymph node represents a rare complication of recurrent invasive lobular carcinoma. Typically, obstructive jaundice is managed with the placement of a biliary duct stent for decompression, thereby resolving hyperbilirubinemia. Failure to address hyperbilirubinemia can lead to delays in chemotherapy administration. For patients unable to undergo stent placement, PTBD serves as an alternative intervention. Nonetheless, PTBD is associated with risks of recurrent obstruction and infections. This case report exemplifies the rare occurrence of obstructive jaundice attributable to lymph node invasion from metastatic breast cancer, which has not been widely reported.

Figure: Figure 1
Liver metastasis (white arrow) and lymphadenopathies (white triangles)

Figure: Figure 2
White arrow showing hypoechoic structure on the EUS.
Disclosures:
Aziz Eshov indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samit Datta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aziz Eshov, DO1, Samit Datta, MD2. P0166 - Biliary Obstruction Secondary to Lymphatic Metastasis From Invasive Breast Carcinoma: A Case Report, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
