Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0102 - When Youth Offers No Shield: A Case of Pancreatic Cancer in a Young Adult With Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Bilind S. Ismail, MD (he/him/his)
Willis Knighton Health
Shreveport, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Bilind Ismail, MD1, Ishita Ray, MD2, Shriya Vudari, MD3, Hassan Khanani, MS4, Aaron Burgin, MD1, Gazi Zibari, MD1
1Willis Knighton Health, Shreveport, LA; 2Mahatma Gandhi Medical College , Indore , India, Shreveport, LA; 3Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 4Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) are rare neoplasm, accounting for less than 2% of all pancreatic tumors. While pancreatic cancer is generally uncommon in younger individuals, its occurrence in this age group is not unheard of. PNETs can present in different ways. It can be functional or non functional. This case report highlights a young patient who is a 26-year-old male diagnosed with non functional PNET with a history of Neurofibromatosis type 1(NF1).
Case Description/
Methods: A 26-year-old male with neurofibromatosis type 1(NF1), a history of right below-knee amputation, and childhood Kawasaki disease presented with constant epigastric pain following Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and fine needle aspiration (FNA) of a pancreatic mass seen on CT, prompted by a palpable abdominal mass. The initial CT revealed a 3.9 × 4.6 × 3.2 cm soft tissue mass inseparable from the pancreatic head and the second portion of the duodenum. EUS demonstrated a hypoechoic pancreatic head mass with a 6 mm dilated main pancreatic duct with vascular involvement as superior mesenteric artery (SMA) encasement, and portal vein abutment. Labs showed total bilirubin 1.8 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 153 U/L, AST 25 U/L, ALT 13 U/L, and lipase 99 U/L. EUS findings raised concern for a main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) (T2N1Mx), but cytology confirmed a well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (PNET). DOTATATE PET/CT showed a 4.5 cm largely calcified mass with low uptake (SUV max 4.3) and no metastasis. He underwent Whipple procedure with cholecystectomy and biliary and pancreatic stent placements. At his 2-month follow-up, he remained asymptomatic and without complications.
Discussion: Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a genetic neurocutaneous disorder associated with various tumours, especially of the nervous system. While tumours like neurofibromas and optic gliomas are common in NF1, pancreatic tumors are rare and pose a diagnostic challenge. Pancreatic involvement in NF1 is diverse. Though uncommon, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) have been reported in NF1, sometimes with atypical presentations, like cystic appearances. The pathogenesis of pancreatic tumors in NF1 remains insufficiently understood. This case report adds to the growing body of literature on the association between NF1 and pancreatic tumors, emphasizing the importance of incorporating pancreatic evaluation studies in the surveillance and management protocols for patients with NF1.
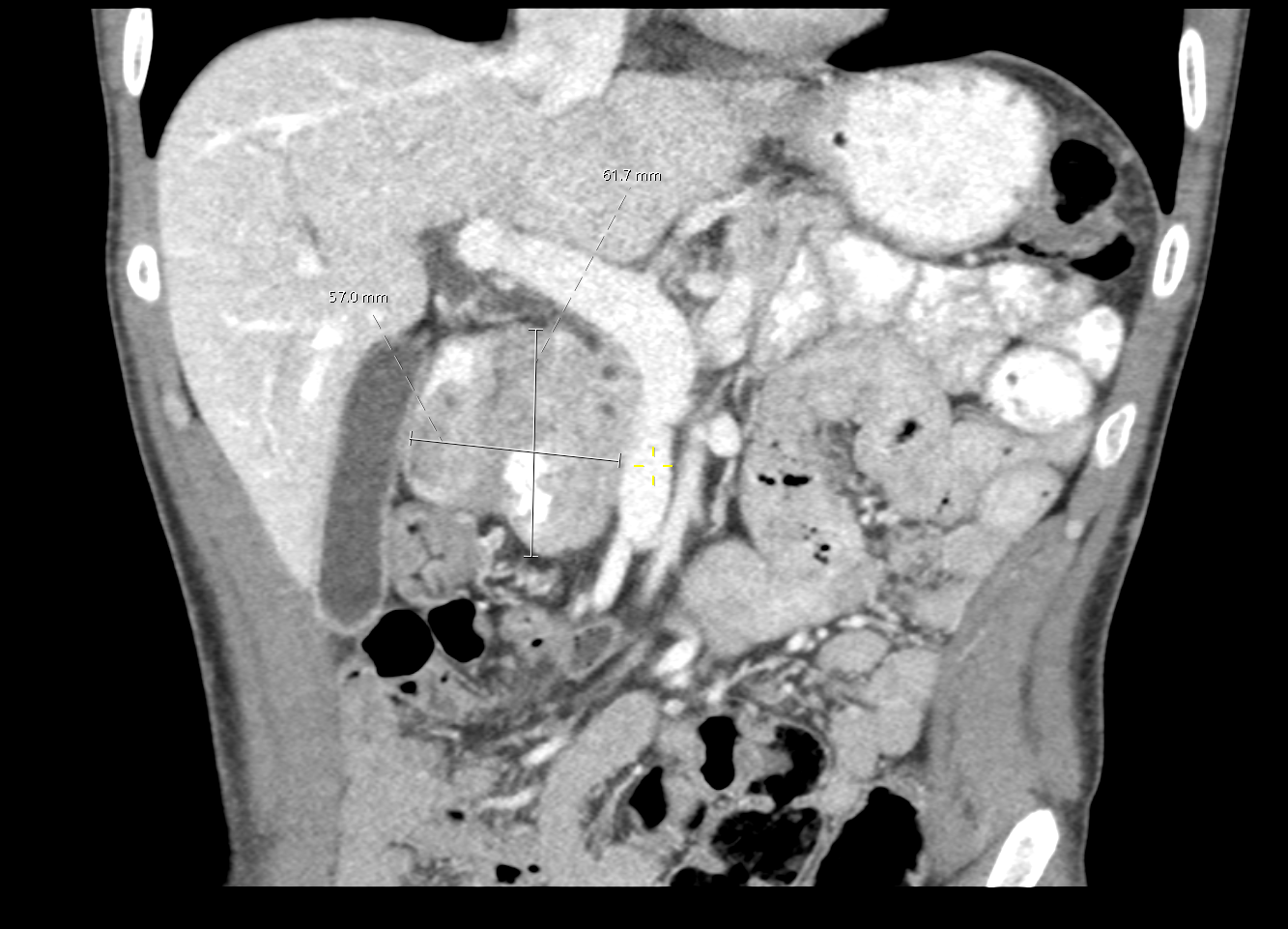
Figure: CT Abdomen coronal view shows a 6.1 × 5.7 cm soft tissue mass in the pancreatic head.
Disclosures:
Bilind Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishita Ray indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shriya Vudari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassan Khanani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron Burgin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gazi Zibari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bilind Ismail, MD1, Ishita Ray, MD2, Shriya Vudari, MD3, Hassan Khanani, MS4, Aaron Burgin, MD1, Gazi Zibari, MD1. P0102 - When Youth Offers No Shield: A Case of Pancreatic Cancer in a Young Adult With Neurofibromatosis Type 1, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Willis Knighton Health, Shreveport, LA; 2Mahatma Gandhi Medical College , Indore , India, Shreveport, LA; 3Louisiana State University, Shreveport, LA; 4Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) are rare neoplasm, accounting for less than 2% of all pancreatic tumors. While pancreatic cancer is generally uncommon in younger individuals, its occurrence in this age group is not unheard of. PNETs can present in different ways. It can be functional or non functional. This case report highlights a young patient who is a 26-year-old male diagnosed with non functional PNET with a history of Neurofibromatosis type 1(NF1).
Case Description/
Methods: A 26-year-old male with neurofibromatosis type 1(NF1), a history of right below-knee amputation, and childhood Kawasaki disease presented with constant epigastric pain following Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and fine needle aspiration (FNA) of a pancreatic mass seen on CT, prompted by a palpable abdominal mass. The initial CT revealed a 3.9 × 4.6 × 3.2 cm soft tissue mass inseparable from the pancreatic head and the second portion of the duodenum. EUS demonstrated a hypoechoic pancreatic head mass with a 6 mm dilated main pancreatic duct with vascular involvement as superior mesenteric artery (SMA) encasement, and portal vein abutment. Labs showed total bilirubin 1.8 mg/dL, alkaline phosphatase 153 U/L, AST 25 U/L, ALT 13 U/L, and lipase 99 U/L. EUS findings raised concern for a main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) (T2N1Mx), but cytology confirmed a well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (PNET). DOTATATE PET/CT showed a 4.5 cm largely calcified mass with low uptake (SUV max 4.3) and no metastasis. He underwent Whipple procedure with cholecystectomy and biliary and pancreatic stent placements. At his 2-month follow-up, he remained asymptomatic and without complications.
Discussion: Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a genetic neurocutaneous disorder associated with various tumours, especially of the nervous system. While tumours like neurofibromas and optic gliomas are common in NF1, pancreatic tumors are rare and pose a diagnostic challenge. Pancreatic involvement in NF1 is diverse. Though uncommon, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) have been reported in NF1, sometimes with atypical presentations, like cystic appearances. The pathogenesis of pancreatic tumors in NF1 remains insufficiently understood. This case report adds to the growing body of literature on the association between NF1 and pancreatic tumors, emphasizing the importance of incorporating pancreatic evaluation studies in the surveillance and management protocols for patients with NF1.

Figure: CT Abdomen coronal view shows a 6.1 × 5.7 cm soft tissue mass in the pancreatic head.
Disclosures:
Bilind Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishita Ray indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shriya Vudari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassan Khanani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aaron Burgin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gazi Zibari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bilind Ismail, MD1, Ishita Ray, MD2, Shriya Vudari, MD3, Hassan Khanani, MS4, Aaron Burgin, MD1, Gazi Zibari, MD1. P0102 - When Youth Offers No Shield: A Case of Pancreatic Cancer in a Young Adult With Neurofibromatosis Type 1, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
