Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0083 - Predictors of Biliary Malignancy Among GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Users
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH
Yale New Haven Health
Bridgeport, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH1, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH2, Yussif Issaka, MBChB3, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD4, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil5, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD6, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS7, Joseph A. Atarere, MBChB, MPH8, Eunice Omeludike, MD9, Lewis Roberts, MBChB, PhD10
1Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 2VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University, West Haven, CT; 3Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 4Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 5Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY; 6Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 7Yale University, New Haven, CT; 8MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Baltimore, MD; 9Piedmont Athens Regional Medical Centre, Athens, GA; 10Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Biliary malignancies, including gallbladder and bile duct cancers, are rare but aggressive tumors often diagnosed at advanced stages. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are widely used for obesity and type 2 DM; however, their link with biliary neoplasia remains unclear. While early safety concerns raised questions about hepatobiliary risks, emerging evidence suggests potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic benefits. This study assessed the association between GLP-1 RA use and biliary malignancy, identifying independent predictors among users, using data from a large US cohort.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort analysis using the All of Us Research Program, which integrates electronic health records (EHR), surveys, and biomarkers to support precision medicine. Adults with obesity or type 2 DM (2016–2022) were included; those with pancreatitis, CKD stage 3–5, prior biliary cancer or a personal/family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia were excluded. Biliary malignancy was defined by EHR diagnoses of gallbladder and intrahepatic/extrahepatic bile duct cancers. A 1:1 nearest-neighbor propensity score matching compared GLP-1 RA users and non-users. Multivariable logistic regression adjusted for demographics, comorbidities (smoking, MASLD, gallstones, autoimmune disease, HIV), personal/ family history of cancers and medications (statins, insulin, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, metformin, sulfonylureas, TZD). A secondary model examined predictors among GLP-1 RA users.
Results: Of 219,416 eligible individuals, 17,190 (7.8%) were GLP-1 RA users. Across the cohort, biliary malignancy occurred in 276 individuals (0.126%). Among 34,380 matched participants, there was no significant association between GLP-1 RA use and biliary cancers [adjusted OR (aOR): 1.14; 95% CI: 0.39–3.35; p = 0.814]. Within GLP-1 users, gallstones (aOR: 7.42; 95% CI: 2.59–21.28; p < 0.001) and HIV infection (aOR: 7.35; 95% CI: 1.60–33.84; p = 0.011) were strong independent predictors. SGLT2 inhibitor use showed a suggestive protective trend (aOR: 0.16; 95% CI: 0.02–1.21; p = 0.075).
Discussion: GLP-1 RA use was not associated with increased biliary malignancy risk, but gallstones and HIV strongly predicted risk among users. The protective signal from SGLT2 inhibitors, though non-significant, prompts the need for further research. These findings support targeted surveillance in high-risk GLP-1 RA users and suggest SGLT2 inhibitors as promising candidates for future prevention studies.
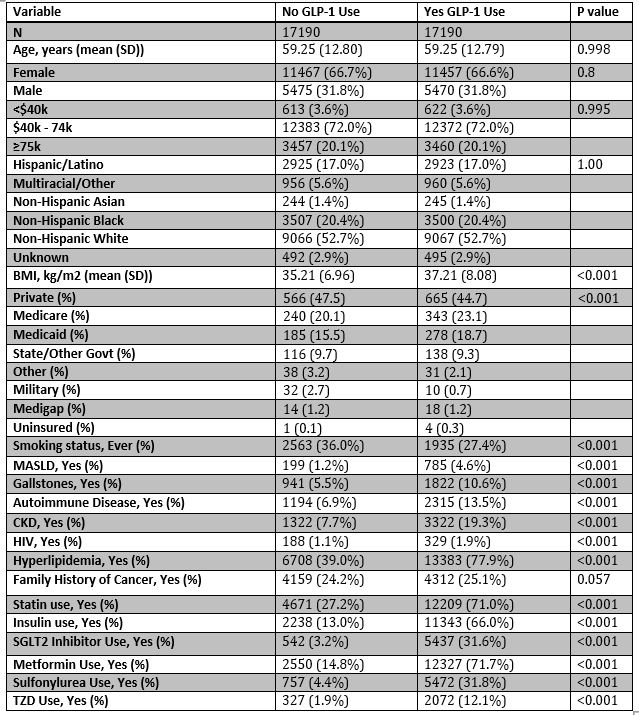
Figure: Table 1: Characteristics of Participants After Propensity Score Matching on Demographic Characteristics.
GLP-1 RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; BMI: Body Mass Index; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TZD: Thiazolidinedione.
Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables and percentages for categorical variables.
P-values are derived from t-tests (continuous) or chi-square tests (categorical).
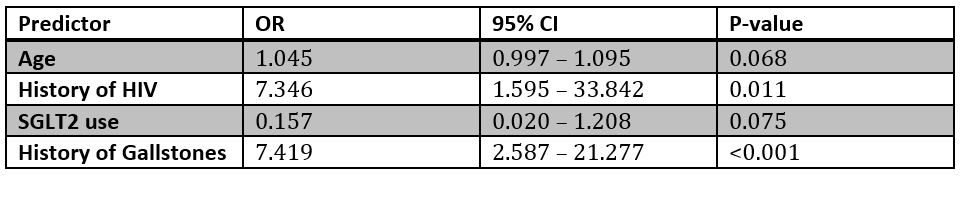
Figure: Odds Ratios (ORs) are derived from a multivariable logistic regression model restricted to patients on GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Predictors were selected using bidirectional stepwise regression.
OR: Odds Ratio; CI: Confidence Interval.
The adjusted model includes demographic factors, clinical characteristics, medication use, smoking status, and family history.
Disclosures:
Sarpong Boateng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basile Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yussif Issaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Al Ajlouni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Ameyaw indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ikechukwu Eze indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Atarere indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eunice Omeludike indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lewis Roberts indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH1, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH2, Yussif Issaka, MBChB3, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD4, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil5, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD6, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS7, Joseph A. Atarere, MBChB, MPH8, Eunice Omeludike, MD9, Lewis Roberts, MBChB, PhD10. P0083 - Predictors of Biliary Malignancy Among GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Users, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport, CT; 2VA Connecticut Healthcare System and Yale University, West Haven, CT; 3Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 4Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Odessa, TX; 5Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY; 6Yale New Haven Health, Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT; 7Yale University, New Haven, CT; 8MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Baltimore, MD; 9Piedmont Athens Regional Medical Centre, Athens, GA; 10Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
Introduction: Biliary malignancies, including gallbladder and bile duct cancers, are rare but aggressive tumors often diagnosed at advanced stages. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are widely used for obesity and type 2 DM; however, their link with biliary neoplasia remains unclear. While early safety concerns raised questions about hepatobiliary risks, emerging evidence suggests potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic benefits. This study assessed the association between GLP-1 RA use and biliary malignancy, identifying independent predictors among users, using data from a large US cohort.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort analysis using the All of Us Research Program, which integrates electronic health records (EHR), surveys, and biomarkers to support precision medicine. Adults with obesity or type 2 DM (2016–2022) were included; those with pancreatitis, CKD stage 3–5, prior biliary cancer or a personal/family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia were excluded. Biliary malignancy was defined by EHR diagnoses of gallbladder and intrahepatic/extrahepatic bile duct cancers. A 1:1 nearest-neighbor propensity score matching compared GLP-1 RA users and non-users. Multivariable logistic regression adjusted for demographics, comorbidities (smoking, MASLD, gallstones, autoimmune disease, HIV), personal/ family history of cancers and medications (statins, insulin, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, metformin, sulfonylureas, TZD). A secondary model examined predictors among GLP-1 RA users.
Results: Of 219,416 eligible individuals, 17,190 (7.8%) were GLP-1 RA users. Across the cohort, biliary malignancy occurred in 276 individuals (0.126%). Among 34,380 matched participants, there was no significant association between GLP-1 RA use and biliary cancers [adjusted OR (aOR): 1.14; 95% CI: 0.39–3.35; p = 0.814]. Within GLP-1 users, gallstones (aOR: 7.42; 95% CI: 2.59–21.28; p < 0.001) and HIV infection (aOR: 7.35; 95% CI: 1.60–33.84; p = 0.011) were strong independent predictors. SGLT2 inhibitor use showed a suggestive protective trend (aOR: 0.16; 95% CI: 0.02–1.21; p = 0.075).
Discussion: GLP-1 RA use was not associated with increased biliary malignancy risk, but gallstones and HIV strongly predicted risk among users. The protective signal from SGLT2 inhibitors, though non-significant, prompts the need for further research. These findings support targeted surveillance in high-risk GLP-1 RA users and suggest SGLT2 inhibitors as promising candidates for future prevention studies.

Figure: Table 1: Characteristics of Participants After Propensity Score Matching on Demographic Characteristics.
GLP-1 RA: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; BMI: Body Mass Index; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TZD: Thiazolidinedione.
Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables and percentages for categorical variables.
P-values are derived from t-tests (continuous) or chi-square tests (categorical).

Figure: Odds Ratios (ORs) are derived from a multivariable logistic regression model restricted to patients on GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Predictors were selected using bidirectional stepwise regression.
OR: Odds Ratio; CI: Confidence Interval.
The adjusted model includes demographic factors, clinical characteristics, medication use, smoking status, and family history.
Disclosures:
Sarpong Boateng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Basile Njei indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yussif Issaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Al Ajlouni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prince Ameyaw indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ikechukwu Eze indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Atarere indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eunice Omeludike indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lewis Roberts indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarpong Boateng, MD, MPH1, Basile Njei, MD, PhD, MPH2, Yussif Issaka, MBChB3, Guy Loic Nguefang Tchoukeu, MD4, Yazan Al Ajlouni, MD, Mphil5, Prince A. Ameyaw, MD6, Ikechukwu Elvis. Eze, MBBS7, Joseph A. Atarere, MBChB, MPH8, Eunice Omeludike, MD9, Lewis Roberts, MBChB, PhD10. P0083 - Predictors of Biliary Malignancy Among GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Users, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
