Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Plenary Session 1B: Pancreas
18 - High Performance of a Blood-Based Biomarker Test to Detect Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer in a High-Risk Population, Across Two Independent Clinical Validation Studies
Monday, October 27, 2025
2:45 PM - 2:55 PM PDT
Location: North Ballroom 120BC

Patricio M Polanco, MD
University of Texas Southwestern
Dallas, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Patricio M Polanco, MD1, Aimee Lucas, MD2, Randall Brand, MD3, Tamas Gonda, MD4, Erkut Borazanci, MD5, Jose Trevino, MD6, Evan Glazer, MD7, Salvatore Paiella, MD, PhD8, Rosalie Sears, PhD9, Eli M. Grindedal, PhD10, Raymond Wadlow, MD11, Bryson W. Katona, 12, George Zogopoulos, MD, PhD13, Daniel A. Sussman, MD14, Ora K. Gordon, MD15, Thomas King, MD, PhD16, George Dumuth, MS17, Lisa Ford, PhD18, Norma A. Palma, PhD18
1University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, TX; 2Mount Sinai West, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 3University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA; 4NYU Langone Health, New York, NY; 5HonorHealth Research Institute, Phoenix, AZ; 6Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine and Richmond VA Medical Center, Richmond, VA; 7University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 8University of Verona, Verona, Veneto, Italy; 9Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR; 10University of Oslo, Oslo, Oslo, Norway; 11Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, VA; 12University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; 13McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, PQ, Canada; 14University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, FL; 15St. John's Cancer Institute/Providence Health, Torrance, CA; 16Immunovia Inc, Durham, NC; 17Stat One LLC, Morrisville, NC; 18Immunovia, Durham, NC
Introduction: Early detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), has a significant impact on patient outcomes. Patients with known pathogenic genetic variants (PGV), family history predisposing them to PDAC, or presence of cystic neoplasms should undergo regular surveillance per clinical guidelines. Interval imaging, the current standard of care for these programs, can be costly, burdensome, and often with limited accuracy. We previously conducted two independent clinical validation (CV) studies (CLARITI, NCT06947382 and VERIFI, NCT06947395) where PancreaSure, a serum-based early detection test for PDAC, showed high accuracy in differentiating early-stage disease versus high-risk control patients. We set out to determine test performance across both studies overall and in key patient sub-populations.
Methods: Two multicenter, case-control, blinded studies were conducted (Figure 1) to investigate the performance of PancreaSure, a blood-based biomarker signature comprising a mathematical summation of ICAM-1, THSB1, CTSD, TIMP1, and CA19-9 values with a predefined cutoff to differentiate Stage I and Stage II PDAC from controls at high-risk due to PGV, family history, or other clinical factors. Performance of the test in key sub-populations across studies was also investigated.
Results: Across the two clinical validation studies, serum from 317 Stage I-II PDAC cases and 1134 high-risk controls were collected from 21 US and 2 European sites. PancreaSure sensitivity and specificity overall was 78% and 92%, respectively. The test had significantly better sensitivity than CA19-9 alone in the individual studies and across both studies (66%, p< 0.001). PancreaSure showed high performance in key sub-populations (genetic/familial high-risk, patients diagnosed with diabetes, and those harboring small pancreatic cysts) across the two studies (Table 1), with significantly higher sensitivity than CA19-9 overall (p< 0.05). Test performance in patients at high-risk for genetic/familial PDAC showed the highest specificity (94%).
Discussion: Across two independent clinical validation studies, PancreaSure showed high accuracy in differentiating Stage I and Stage II PDAC from high-risk controls in a large, pooled cohort. These results further support the robustness of the test’s performance and can serve as a tool for early-stage PDAC detection in patients of varying high-risk profiles.
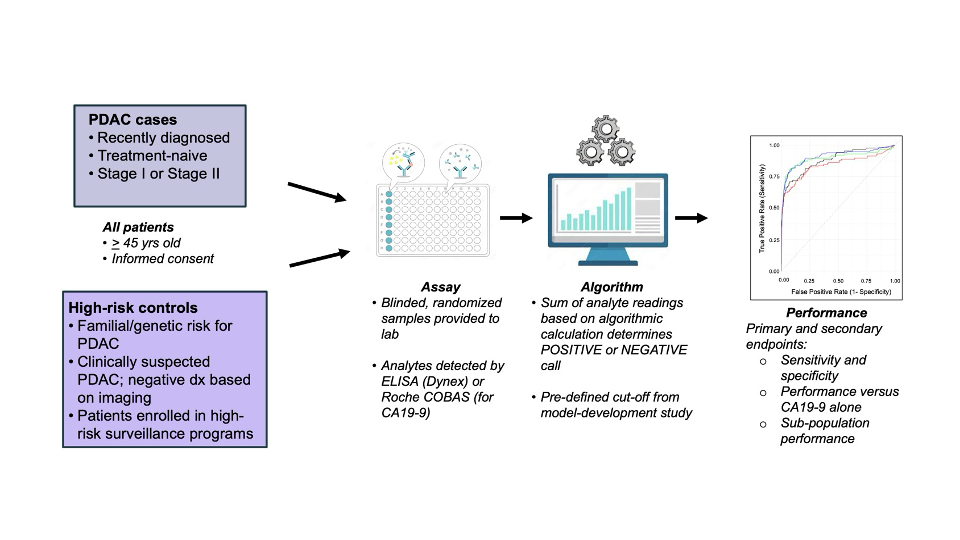
Figure: Study schema of clinical validation studies of PancreaSure to detect early-stage pancreatic cancer.
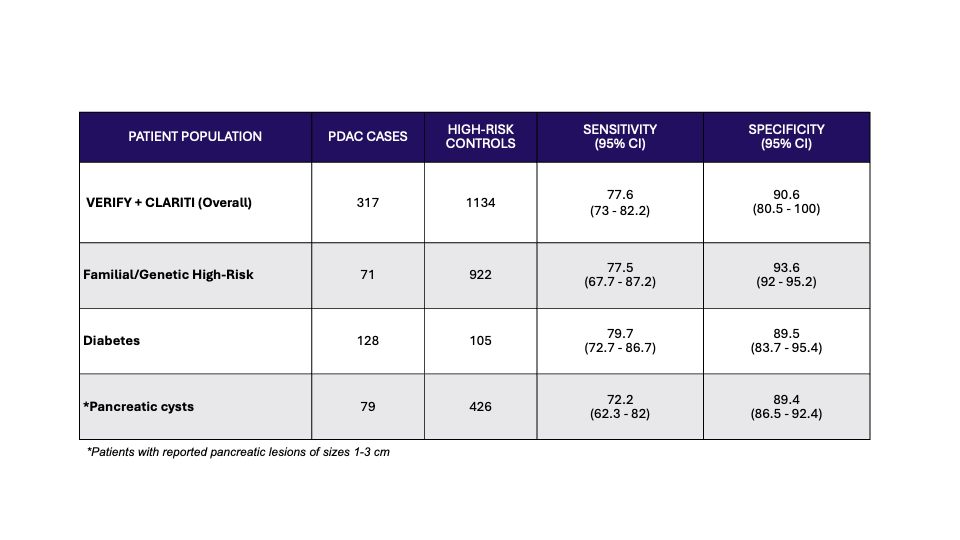
Figure: Test performance in the overall patient population and key sub-populations in combined validation studies of PancreaSure
Disclosures:
Patricio M Polanco indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aimee Lucas: Immunovia – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant.
Randall Brand: Immunovia – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Tamas Gonda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erkut Borazanci indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jose Trevino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Evan Glazer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salvatore Paiella indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rosalie Sears indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eli Grindedal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raymond Wadlow indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bryson Katona: Immunovia – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant.
George Zogopoulos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Sussman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ora Gordon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas King: Immunovia – Employee.
George Dumuth: Immunovia – Consultant.
Lisa Ford: Immunovia – Employee.
Norma Palma: Immunovia – Employee.
Patricio M Polanco, MD1, Aimee Lucas, MD2, Randall Brand, MD3, Tamas Gonda, MD4, Erkut Borazanci, MD5, Jose Trevino, MD6, Evan Glazer, MD7, Salvatore Paiella, MD, PhD8, Rosalie Sears, PhD9, Eli M. Grindedal, PhD10, Raymond Wadlow, MD11, Bryson W. Katona, 12, George Zogopoulos, MD, PhD13, Daniel A. Sussman, MD14, Ora K. Gordon, MD15, Thomas King, MD, PhD16, George Dumuth, MS17, Lisa Ford, PhD18, Norma A. Palma, PhD18, 18, High Performance of a Blood-Based Biomarker Test to Detect Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer in a High-Risk Population, Across Two Independent Clinical Validation Studies, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, TX; 2Mount Sinai West, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 3University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA; 4NYU Langone Health, New York, NY; 5HonorHealth Research Institute, Phoenix, AZ; 6Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine and Richmond VA Medical Center, Richmond, VA; 7University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 8University of Verona, Verona, Veneto, Italy; 9Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR; 10University of Oslo, Oslo, Oslo, Norway; 11Inova Schar Cancer Institute, Fairfax, VA; 12University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; 13McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, PQ, Canada; 14University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, FL; 15St. John's Cancer Institute/Providence Health, Torrance, CA; 16Immunovia Inc, Durham, NC; 17Stat One LLC, Morrisville, NC; 18Immunovia, Durham, NC
Introduction: Early detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), has a significant impact on patient outcomes. Patients with known pathogenic genetic variants (PGV), family history predisposing them to PDAC, or presence of cystic neoplasms should undergo regular surveillance per clinical guidelines. Interval imaging, the current standard of care for these programs, can be costly, burdensome, and often with limited accuracy. We previously conducted two independent clinical validation (CV) studies (CLARITI, NCT06947382 and VERIFI, NCT06947395) where PancreaSure, a serum-based early detection test for PDAC, showed high accuracy in differentiating early-stage disease versus high-risk control patients. We set out to determine test performance across both studies overall and in key patient sub-populations.
Methods: Two multicenter, case-control, blinded studies were conducted (Figure 1) to investigate the performance of PancreaSure, a blood-based biomarker signature comprising a mathematical summation of ICAM-1, THSB1, CTSD, TIMP1, and CA19-9 values with a predefined cutoff to differentiate Stage I and Stage II PDAC from controls at high-risk due to PGV, family history, or other clinical factors. Performance of the test in key sub-populations across studies was also investigated.
Results: Across the two clinical validation studies, serum from 317 Stage I-II PDAC cases and 1134 high-risk controls were collected from 21 US and 2 European sites. PancreaSure sensitivity and specificity overall was 78% and 92%, respectively. The test had significantly better sensitivity than CA19-9 alone in the individual studies and across both studies (66%, p< 0.001). PancreaSure showed high performance in key sub-populations (genetic/familial high-risk, patients diagnosed with diabetes, and those harboring small pancreatic cysts) across the two studies (Table 1), with significantly higher sensitivity than CA19-9 overall (p< 0.05). Test performance in patients at high-risk for genetic/familial PDAC showed the highest specificity (94%).
Discussion: Across two independent clinical validation studies, PancreaSure showed high accuracy in differentiating Stage I and Stage II PDAC from high-risk controls in a large, pooled cohort. These results further support the robustness of the test’s performance and can serve as a tool for early-stage PDAC detection in patients of varying high-risk profiles.

Figure: Study schema of clinical validation studies of PancreaSure to detect early-stage pancreatic cancer.

Figure: Test performance in the overall patient population and key sub-populations in combined validation studies of PancreaSure
Disclosures:
Patricio M Polanco indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aimee Lucas: Immunovia – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant.
Randall Brand: Immunovia – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Tamas Gonda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erkut Borazanci indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jose Trevino indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Evan Glazer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salvatore Paiella indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rosalie Sears indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eli Grindedal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raymond Wadlow indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bryson Katona: Immunovia – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant.
George Zogopoulos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daniel Sussman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ora Gordon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas King: Immunovia – Employee.
George Dumuth: Immunovia – Consultant.
Lisa Ford: Immunovia – Employee.
Norma Palma: Immunovia – Employee.
Patricio M Polanco, MD1, Aimee Lucas, MD2, Randall Brand, MD3, Tamas Gonda, MD4, Erkut Borazanci, MD5, Jose Trevino, MD6, Evan Glazer, MD7, Salvatore Paiella, MD, PhD8, Rosalie Sears, PhD9, Eli M. Grindedal, PhD10, Raymond Wadlow, MD11, Bryson W. Katona, 12, George Zogopoulos, MD, PhD13, Daniel A. Sussman, MD14, Ora K. Gordon, MD15, Thomas King, MD, PhD16, George Dumuth, MS17, Lisa Ford, PhD18, Norma A. Palma, PhD18, 18, High Performance of a Blood-Based Biomarker Test to Detect Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer in a High-Risk Population, Across Two Independent Clinical Validation Studies, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.


