Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Plenary Session 4B: IBD
69 - Clinical and Endoscopic Improvements With Risankizumab Treatment in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease Who Previously Failed Ustekinumab
Wednesday, October 29, 2025
9:10 AM - 9:20 AM PDT
Location: North Ballroom 120BC

Jessica R. Allegretti, MD, MPH, FACG (she/her/hers)
Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Governors Award for Excellence in Clinical Research
Jessica R. Allegretti, MD, MPH, FACG1, Javier Zambrano, MD2, Daniel O'Brien, PhD2, Jameson Crowley, PhD3, Fernando Aponte, MD2, Yafei Zhang, PhD2, Jeanie K.. Meckes, PhD2, Christian Maaser, MD4
1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL; 3AbbVie inc., North Chicago, IL; 43Ambulanzzentrum Gastroenterologie, Klinikum Lüneburg, Lüneburg, Hamburg, Germany
Introduction: Risankizumab (RZB), an interleukin (IL)-23 p19 inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (CD), including refractory patients who previously failed ≥2 biologics.1-3 This post-hoc analysis reports the efficacy of RZB in patients with refractory CD previously exposed to ustekinumab (UST) from the phase 3 ADVANCE (NCT03105128) and MOTIVATE (NCT03104413) trials.
Methods: This analysis included patients with moderate-to-severe CD and intolerance/inadequate response to ≥1 biologic (both studies) and/or conventional therapy (ADVANCE) who received 12 weeks of intravenous (IV) RZB 600 mg induction or placebo (PBO); clinical responders to 12 weeks of RZB induction were rerandomized in the FORTIFY (NCT03105102) maintenance trial to receive 52 weeks of subcutaneous (SC) RZB (180 mg or 360 mg) or PBO (withdrawal). Clinical remission (per CD Activity Index [CDAI] and stool frequency/abdominal pain [SP/APS]) and endoscopic response were evaluated in a subgroup of patients with prior UST exposure.
Results: A total of 62 patients (ADVANCE) and 76 patients (MOTIVATE) with prior UST exposure were included in this analysis; most of whom had previously failed ≥3 biologics. Over 90% of them had previously failed anti-TNF and/or vedolizumab. At induction week 12, more patients treated with IV RZB 600 mg vs PBO achieved clinical remission per CDAI (ADVANCE: 37.2% vs 15.8%; MOTVIATE: 36.1% vs 10.0%) and SF/APS (ADVANCE: 25.6% vs 10.5%; MOTVIATE: 19.4% vs 10.0%) and endoscopic response (ADVANCE: 22.3% vs 5.4%; MOTIVATE: 19.5% vs 5.0%). At maintenance week 52, more patients treated with SC RZB 180 mg or 360 mg vs PBO (withdrawal) achieved clinical remission per CDAI (33.3% or 51.4% vs 20.0%) and SF/APS (33.3% or 48.6% vs 20.0%) and endoscopic response (33.3% or 29.4% vs 20.0%).
Discussion: Although RZB and UST have similar mechanisms of action (IL-23 inhibition), patients with refractory CD previously exposed to UST showed clinical and endoscopic improvements with RZB treatment. These findings were consistent with RZB’s efficacy rates observed in patients who failed ≥2 biologics as well as real-world evidence of RZB’s efficacy in patients with prior UST failure in CD.3-5
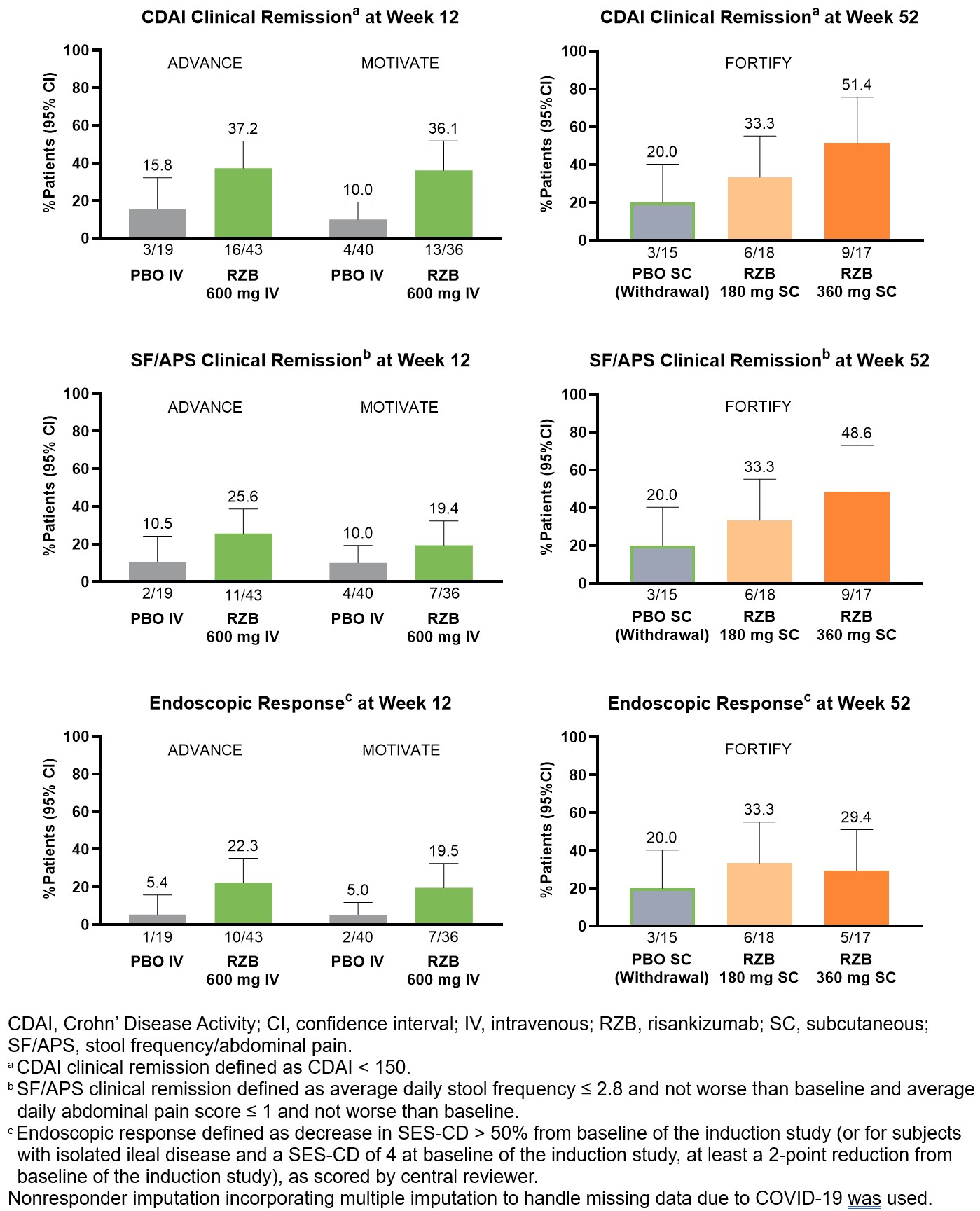
Figure: Clinical and Endoscopic Outcomes in Patients With Prior Ustekinumab Exposure
Disclosures:
Jessica Allegretti: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker, Speakers Bureau. Adiso – Consultant. Bristol Myer Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Finch – Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Iterative Scopes – Consultant. Janssen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker. Merck – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Roivant – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roivant Adiso – Consultant. Seres Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Shattuck Labs – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. TRXBio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Vedanta – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Javier Zambrano: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Daniel O'Brien: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Jameson Crowley: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Fernando Aponte: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Yafei Zhang: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Jeanie Meckes: AbbVie inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Christian Maaser: Abbvie, Alfasigma, Biogen, Dr Falk Pharma, Ferring Arzneimittel, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, MSD Sharp & Dhome, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung, Takeda Pharma, – Honoraria fees, Speakers Bureau.
Jessica R. Allegretti, MD, MPH, FACG1, Javier Zambrano, MD2, Daniel O'Brien, PhD2, Jameson Crowley, PhD3, Fernando Aponte, MD2, Yafei Zhang, PhD2, Jeanie K.. Meckes, PhD2, Christian Maaser, MD4, 69, Clinical and Endoscopic Improvements With Risankizumab Treatment in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease Who Previously Failed Ustekinumab, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Jessica R. Allegretti, MD, MPH, FACG1, Javier Zambrano, MD2, Daniel O'Brien, PhD2, Jameson Crowley, PhD3, Fernando Aponte, MD2, Yafei Zhang, PhD2, Jeanie K.. Meckes, PhD2, Christian Maaser, MD4
1Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Endoscopy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL; 3AbbVie inc., North Chicago, IL; 43Ambulanzzentrum Gastroenterologie, Klinikum Lüneburg, Lüneburg, Hamburg, Germany
Introduction: Risankizumab (RZB), an interleukin (IL)-23 p19 inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (CD), including refractory patients who previously failed ≥2 biologics.1-3 This post-hoc analysis reports the efficacy of RZB in patients with refractory CD previously exposed to ustekinumab (UST) from the phase 3 ADVANCE (NCT03105128) and MOTIVATE (NCT03104413) trials.
Methods: This analysis included patients with moderate-to-severe CD and intolerance/inadequate response to ≥1 biologic (both studies) and/or conventional therapy (ADVANCE) who received 12 weeks of intravenous (IV) RZB 600 mg induction or placebo (PBO); clinical responders to 12 weeks of RZB induction were rerandomized in the FORTIFY (NCT03105102) maintenance trial to receive 52 weeks of subcutaneous (SC) RZB (180 mg or 360 mg) or PBO (withdrawal). Clinical remission (per CD Activity Index [CDAI] and stool frequency/abdominal pain [SP/APS]) and endoscopic response were evaluated in a subgroup of patients with prior UST exposure.
Results: A total of 62 patients (ADVANCE) and 76 patients (MOTIVATE) with prior UST exposure were included in this analysis; most of whom had previously failed ≥3 biologics. Over 90% of them had previously failed anti-TNF and/or vedolizumab. At induction week 12, more patients treated with IV RZB 600 mg vs PBO achieved clinical remission per CDAI (ADVANCE: 37.2% vs 15.8%; MOTVIATE: 36.1% vs 10.0%) and SF/APS (ADVANCE: 25.6% vs 10.5%; MOTVIATE: 19.4% vs 10.0%) and endoscopic response (ADVANCE: 22.3% vs 5.4%; MOTIVATE: 19.5% vs 5.0%). At maintenance week 52, more patients treated with SC RZB 180 mg or 360 mg vs PBO (withdrawal) achieved clinical remission per CDAI (33.3% or 51.4% vs 20.0%) and SF/APS (33.3% or 48.6% vs 20.0%) and endoscopic response (33.3% or 29.4% vs 20.0%).
Discussion: Although RZB and UST have similar mechanisms of action (IL-23 inhibition), patients with refractory CD previously exposed to UST showed clinical and endoscopic improvements with RZB treatment. These findings were consistent with RZB’s efficacy rates observed in patients who failed ≥2 biologics as well as real-world evidence of RZB’s efficacy in patients with prior UST failure in CD.3-5
- D'Haens G, et al. Lancet 399.10340 (2022):2015-2030.
- Ferrante M, et al. Lancet 399.10340 (2022):2031-2046.
- Ferrante M, et al. Am J Gastroenterol 117.10 (2022):S498-S499.
- Zinger A, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 22.6 (2024):1336-1338.
- Fumery M, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 22.12 (2024):2451-2458.

Figure: Clinical and Endoscopic Outcomes in Patients With Prior Ustekinumab Exposure
Disclosures:
Jessica Allegretti: Abbvie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker, Speakers Bureau. Adiso – Consultant. Bristol Myer Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Finch – Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Iterative Scopes – Consultant. Janssen – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker. Merck – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Roivant – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roivant Adiso – Consultant. Seres Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Shattuck Labs – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. TRXBio – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Vedanta – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Javier Zambrano: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Daniel O'Brien: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Jameson Crowley: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Fernando Aponte: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Yafei Zhang: AbbVie Inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Jeanie Meckes: AbbVie inc. – Employee, Stock Options.
Christian Maaser: Abbvie, Alfasigma, Biogen, Dr Falk Pharma, Ferring Arzneimittel, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, MSD Sharp & Dhome, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung, Takeda Pharma, – Honoraria fees, Speakers Bureau.
Jessica R. Allegretti, MD, MPH, FACG1, Javier Zambrano, MD2, Daniel O'Brien, PhD2, Jameson Crowley, PhD3, Fernando Aponte, MD2, Yafei Zhang, PhD2, Jeanie K.. Meckes, PhD2, Christian Maaser, MD4, 69, Clinical and Endoscopic Improvements With Risankizumab Treatment in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease Who Previously Failed Ustekinumab, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.


