Oral Paper Presentation
Annual Scientific Meeting
Session: Plenary Session 4B: IBD
67 - Relationship Between Clinical and Histologic Findings With Tulisokibart Induction at Week 12 and Maintenance Dosing at Week 50 in the Phase 2 Randomized Controlled ARTEMIS-UC Study in Participants With Ulcerative Colitis
Wednesday, October 29, 2025
8:50 AM - 9:00 AM PDT
Location: North Ballroom 120BC

Brigid S. Boland, MD
Altman Clinical Translational Research Institute, University of California, San Diego
San Diego, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Brigid S.. Boland, MD1, Christopher Ma, MD, MPH2, Rupert W.. Leong, MD3, Jaroslaw Leszczyszyn, MD4, Xavier Hébuterne, MD5, Jin Xu, 6, Wen Zhou, 6, Mark Yen, 6
1Altman Clinical Translational Research Institute, University of California, San Diego, San Diego, CA; 2University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada; 3Macquarie University, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia; 4Department of Gastroenterology, Melita Medical, Wroclaw, Dolnoslaskie, Poland; 5Department of Gastroenterology and Clinical Nutrition, CHU of Nice, University Cote d'Azur, Nice, Provence-Alpes-Cote d'Azur, France; 6Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ
Introduction: Although histologic remission has been associated with improved long-term outcomes in ulcerative colitis (UC), histology is inconsistently performed and heterogeneously evaluated in routine clinical care as an assessment of remission depth.
Methods: We evaluated the correlation between changes in clinical/biomarker/endoscopic and histologic endpoints following tulisokibart treatment over 50 weeks. ARTEMIS-UC enrolled 2 cohorts based on a genetic diagnostic test (Dx) for anti-TL1A treatment response: Cohort 1 (participants regardless of Dx results) and Cohort 2 (only Dx positive participants). We examined 15 relationships between 5 clinical/endoscopic/biomarker endpoints and 3 histologic endpoints at Week 12 (W12) after induction (Cohort 1) and Week 50 (W50) (Cohorts 1 and 2) among induction responders continuing maintenance tulisokibart. Histologic endpoints included histologic improvement, histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement (HEMI), and mucosal healing assessed in the Histology Analysis Set (HAS). Clinical/endoscopic/biomarker endpoints included Modified Mayo Score for clinical remission/clinical response/endoscopic improvement/normalization of fecal calprotectin and hsCRP normalization. The Phi correlation coefficient assessed pairwise correlations between clinical/endoscopic/biomarker and histologic endpoints.
Results: There were 65 and 34 tulisokibart participants included in the HAS population for the W12 and W50 analyses, respectively. The strongest correlations were the following: endoscopic improvement:HEMI, endoscopic improvement:mucosal healing, clinical remission:HEMI, and clinical remission:mucosal healing, all >0.8 at W12 (post-induction in Cohort 1) and >0.9 at W50 (post-maintenance dosing in Cohorts 1 and 2). Normalization of fecal calprotectin also demonstrated a strong correlation with histologic endpoints ( >0.7) at W50 (Table).
Discussion: Strong correlations exist between clinical/endoscopic and histologic endpoints after 12 weeks of induction therapy with tulisokibart, followed by 38 weeks of maintenance therapy in induction responders. These findings underscore the potential for clinical remission to reflect endoscopic and histologic healing in patients with UC, which may enhance patient management strategies and a more comprehensive understanding of treatment efficacy. Moreover, these findings indicate the potential of tulisokibart in achieving deep remission1 in patients with UC.
References:
1. Lobatón T et al. United European Gastroenterol J. 2018;6:765─772.
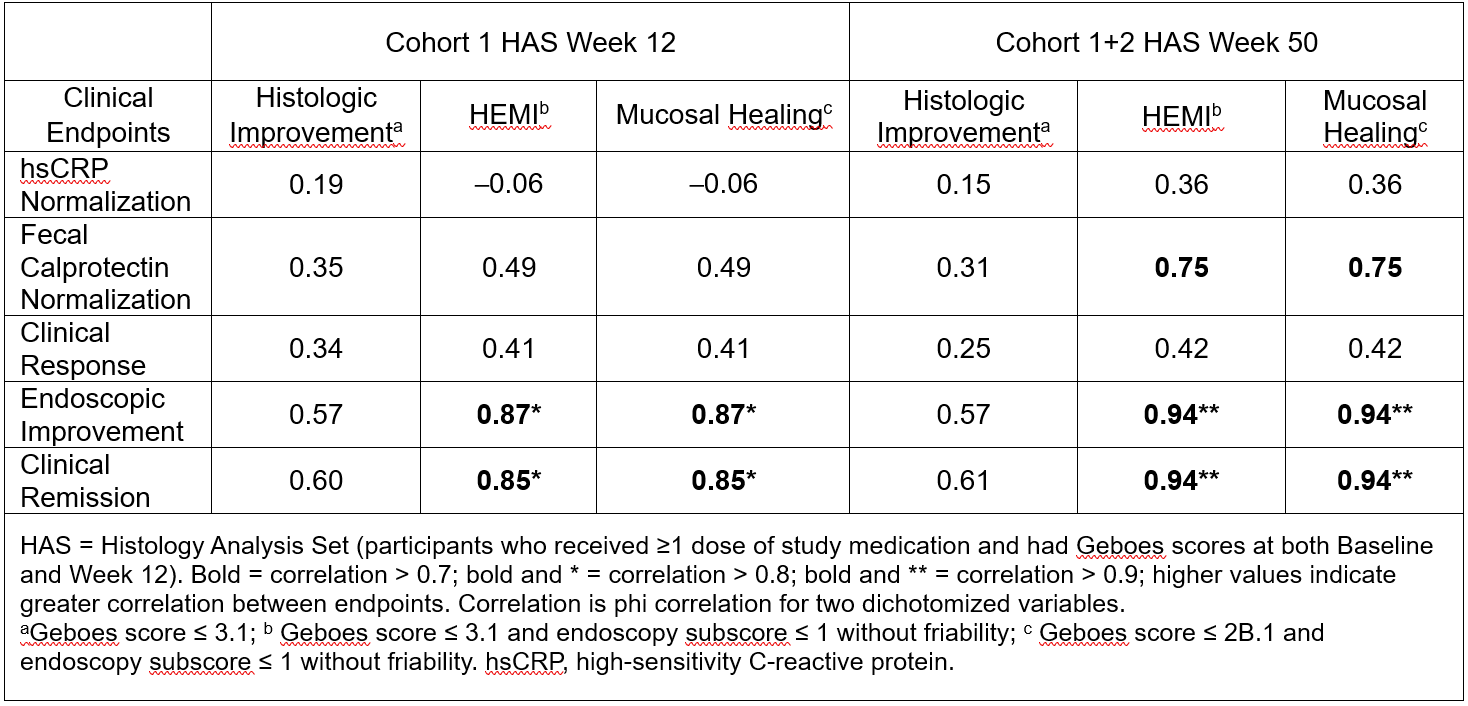
Figure: Table: Correlation between Clinical and Histologic Endpoints
Disclosures:
Brigid Boland: Celltrion – Consultant. Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation – leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group. Gilead Biosciences – Grant/Research Support. Mirador – Grant/Research Support. MSD – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. PLEXUS – leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group. Sanofi – Consultant.
Christopher Ma: Abbvie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker's fee. Alimentiv – Consultant, speaker's fee. Amgen – Consultant, speaker's fee. AVIR Pharma Inc. – Consultant, speaker's fee. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, speaker's fee. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker's fee. Ferring – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker's fee. Forte Biosciences – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant, speaker's fee. Gilead – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant, speaker's fee. McKesson – Consultant. Merck – Speaker's fee. Mirador Therapeutics – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant. Organon – speaker's fee. Pendopharm – Consultant, speaker's fee. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker's fee. Prometheus Biosciences Inc. – Consultant. Roche – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant, speaker's fee. Springer Publishing – Royalties. Takeda – Consultant, speaker's fee. Tillotts Pharma – Consultant, speaker's fee.
Rupert Leong: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Aspen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Chiesi – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Ferring – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Gastroenterological Society of Australia – Grant/Research Support. Glutagen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Gutsy Group – Grant/Research Support. Hospira – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Joanna Tiddy grant – Grant/Research Support. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member. McCusker Charitable Foundation – Grant/Research Support. Medical Research Future Fund – Grant/Research Support. MSD – Advisory Committee/Board Member. NHMRC – Grant/Research Support. Novartis – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Shire – Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support.
Jaroslaw Leszczyszyn: Janssen Research & Development – Consultant. MSD – Grant/Research Support.
Xavier Hébuterne: Abbvie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Abivax – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Alphasigma – Grant/Research Support. Amgen – lecture fees. Arena – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Cellogen – Grant/Research Support. Eli Lilly – Grant/Research Support. Enterome – Grant/Research Support. Fresenius Kabi – lecture fees. Galapagos – Consultant, lecture fees. Gilead – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. InDex Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. MSD – Grant/Research Support. Mylan – lecture fees. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Roche – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Salix – Grant/Research Support. Sangamo – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Theravance – Grant/Research Support. Viatris – Consultant.
Jin Xu: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. – Employee, Stock Options.
Wen Zhou: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. – Employee, Stock Options.
Mark Yen: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. – Employee, Stock Options.
Brigid S.. Boland, MD1, Christopher Ma, MD, MPH2, Rupert W.. Leong, MD3, Jaroslaw Leszczyszyn, MD4, Xavier Hébuterne, MD5, Jin Xu, 6, Wen Zhou, 6, Mark Yen, 6, 67, Relationship Between Clinical and Histologic Findings With Tulisokibart Induction at Week 12 and Maintenance Dosing at Week 50 in the Phase 2 Randomized Controlled ARTEMIS-UC Study in Participants With Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Altman Clinical Translational Research Institute, University of California, San Diego, San Diego, CA; 2University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada; 3Macquarie University, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia; 4Department of Gastroenterology, Melita Medical, Wroclaw, Dolnoslaskie, Poland; 5Department of Gastroenterology and Clinical Nutrition, CHU of Nice, University Cote d'Azur, Nice, Provence-Alpes-Cote d'Azur, France; 6Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ
Introduction: Although histologic remission has been associated with improved long-term outcomes in ulcerative colitis (UC), histology is inconsistently performed and heterogeneously evaluated in routine clinical care as an assessment of remission depth.
Methods: We evaluated the correlation between changes in clinical/biomarker/endoscopic and histologic endpoints following tulisokibart treatment over 50 weeks. ARTEMIS-UC enrolled 2 cohorts based on a genetic diagnostic test (Dx) for anti-TL1A treatment response: Cohort 1 (participants regardless of Dx results) and Cohort 2 (only Dx positive participants). We examined 15 relationships between 5 clinical/endoscopic/biomarker endpoints and 3 histologic endpoints at Week 12 (W12) after induction (Cohort 1) and Week 50 (W50) (Cohorts 1 and 2) among induction responders continuing maintenance tulisokibart. Histologic endpoints included histologic improvement, histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement (HEMI), and mucosal healing assessed in the Histology Analysis Set (HAS). Clinical/endoscopic/biomarker endpoints included Modified Mayo Score for clinical remission/clinical response/endoscopic improvement/normalization of fecal calprotectin and hsCRP normalization. The Phi correlation coefficient assessed pairwise correlations between clinical/endoscopic/biomarker and histologic endpoints.
Results: There were 65 and 34 tulisokibart participants included in the HAS population for the W12 and W50 analyses, respectively. The strongest correlations were the following: endoscopic improvement:HEMI, endoscopic improvement:mucosal healing, clinical remission:HEMI, and clinical remission:mucosal healing, all >0.8 at W12 (post-induction in Cohort 1) and >0.9 at W50 (post-maintenance dosing in Cohorts 1 and 2). Normalization of fecal calprotectin also demonstrated a strong correlation with histologic endpoints ( >0.7) at W50 (Table).
Discussion: Strong correlations exist between clinical/endoscopic and histologic endpoints after 12 weeks of induction therapy with tulisokibart, followed by 38 weeks of maintenance therapy in induction responders. These findings underscore the potential for clinical remission to reflect endoscopic and histologic healing in patients with UC, which may enhance patient management strategies and a more comprehensive understanding of treatment efficacy. Moreover, these findings indicate the potential of tulisokibart in achieving deep remission1 in patients with UC.
References:
1. Lobatón T et al. United European Gastroenterol J. 2018;6:765─772.

Figure: Table: Correlation between Clinical and Histologic Endpoints
Disclosures:
Brigid Boland: Celltrion – Consultant. Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation – leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group. Gilead Biosciences – Grant/Research Support. Mirador – Grant/Research Support. MSD – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. PLEXUS – leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group. Sanofi – Consultant.
Christopher Ma: Abbvie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker's fee. Alimentiv – Consultant, speaker's fee. Amgen – Consultant, speaker's fee. AVIR Pharma Inc. – Consultant, speaker's fee. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, speaker's fee. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker's fee. Ferring – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker's fee. Forte Biosciences – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant, speaker's fee. Gilead – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant, speaker's fee. McKesson – Consultant. Merck – Speaker's fee. Mirador Therapeutics – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant. Organon – speaker's fee. Pendopharm – Consultant, speaker's fee. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker's fee. Prometheus Biosciences Inc. – Consultant. Roche – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant, speaker's fee. Springer Publishing – Royalties. Takeda – Consultant, speaker's fee. Tillotts Pharma – Consultant, speaker's fee.
Rupert Leong: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Aspen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Chiesi – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Ferring – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Gastroenterological Society of Australia – Grant/Research Support. Glutagen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Gutsy Group – Grant/Research Support. Hospira – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Joanna Tiddy grant – Grant/Research Support. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member. McCusker Charitable Foundation – Grant/Research Support. Medical Research Future Fund – Grant/Research Support. MSD – Advisory Committee/Board Member. NHMRC – Grant/Research Support. Novartis – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Shire – Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support.
Jaroslaw Leszczyszyn: Janssen Research & Development – Consultant. MSD – Grant/Research Support.
Xavier Hébuterne: Abbvie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Abivax – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Alphasigma – Grant/Research Support. Amgen – lecture fees. Arena – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Cellogen – Grant/Research Support. Eli Lilly – Grant/Research Support. Enterome – Grant/Research Support. Fresenius Kabi – lecture fees. Galapagos – Consultant, lecture fees. Gilead – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. InDex Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. MSD – Grant/Research Support. Mylan – lecture fees. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Roche – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Salix – Grant/Research Support. Sangamo – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Theravance – Grant/Research Support. Viatris – Consultant.
Jin Xu: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. – Employee, Stock Options.
Wen Zhou: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. – Employee, Stock Options.
Mark Yen: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. – Employee, Stock Options.
Brigid S.. Boland, MD1, Christopher Ma, MD, MPH2, Rupert W.. Leong, MD3, Jaroslaw Leszczyszyn, MD4, Xavier Hébuterne, MD5, Jin Xu, 6, Wen Zhou, 6, Mark Yen, 6, 67, Relationship Between Clinical and Histologic Findings With Tulisokibart Induction at Week 12 and Maintenance Dosing at Week 50 in the Phase 2 Randomized Controlled ARTEMIS-UC Study in Participants With Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

