Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3581 - Innovative Endoscopic Closure of Gastrocutaneous Fistula Using Polyloop and Hemostatic Clips in a Patient With Persistent PEG Tube Leakage
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Yazan Omari, MD (he/him/his)
Ascension Providence Hospital
Southfield, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Yazan Omari, MD, Saif Affas, MD, Roberto Gamarra, MD, FACG
Ascension Providence Hospital, Southfield, MI
Introduction: Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes are commonly used for enteral nutrition but may be complicated by leakage, infection, or, rarely, gastrocutaneous fistulas—especially challenging in patients with comorbidities. While surgery has been the traditional approach, it carries risks like delayed healing and prolonged hospitalization. Endoscopic methods provide a safer, less invasive alternative with faster recovery. Advanced tools such as over-the-scope clips, hemostatic clips, and polyloops now allow effective closure of fistulas that once required surgery.
Case Description/
Methods: A 69-year-old woman with a history of oral cancer and PEG tube placement presented with persistent peristomal leakage and erythema. CT of the abdomen showed a PEG tube in satisfactory position within the inferior gastric body. Initial esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) revealed a non-intact gastrostomy tract with a leaking tube. The PEG was removed endoscopically and replaced with an externally removable T-fastener PEG. Despite replacement, leakage continued, and conservative management failed. Repeat EGD identified an 8 mm gastrocutaneous fistula. Argon plasma coagulation (APC) was used to ablate the fistula edges to facilitate tissue adhesion. An OTSC could not be used due to radiation induced stricture. Four hemostatic clips were subsequently applied to approximate the tissue edges, followed by placement of a polyloop around the clips to reinforce the closure. The repair was successful with no bleeding or adverse events, and the site remained intact on follow-up.
Discussion: This case demonstrates the successful use of a hybrid endoscopic closure strategy combining APC, hemostatic clips, and polyloop deployment to manage a complex gastrocutaneous fistula. Although OTSCs are often effective in tissue apposition, they may be insufficient for larger or fibrotic defects. Hemostatic clips allow for incremental approximation, and polyloops offer circumferential tension to secure closure, effectively simulating a purse-string suture. This combination enhances mechanical strength, and provides durable closure even in challenging clinical scenarios.
For patients with significant comorbidities or cancer-related immunosuppression, this technique provides a safe and effective alternative to surgical repair. Compared to surgery, endoscopic techniques reduce anesthesia exposure, length of stay, postoperative pain, and recovery time. They also allow for immediate evaluation and treatment of the mucosa in a single session.
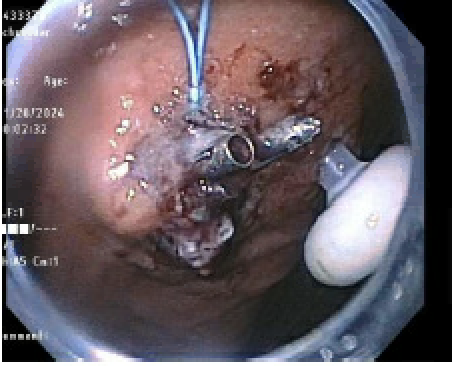
Figure: Fig1: APC ablation promoting granulation tissue formation and enhancing closure efficacy with the polyloop device.
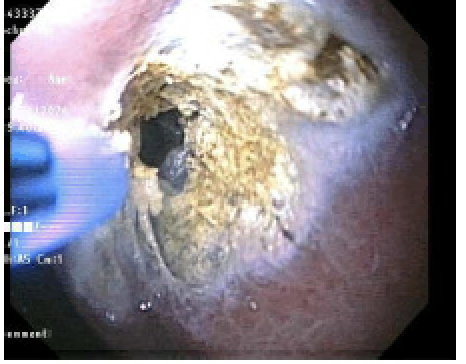
Figure: Fig2: Approximated fistula with polyloop device and clips intact
Disclosures:
Yazan Omari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saif Affas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Roberto Gamarra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Omari, MD, Saif Affas, MD, Roberto Gamarra, MD, FACG. P3581 - Innovative Endoscopic Closure of Gastrocutaneous Fistula Using Polyloop and Hemostatic Clips in a Patient With Persistent PEG Tube Leakage, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Ascension Providence Hospital, Southfield, MI
Introduction: Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes are commonly used for enteral nutrition but may be complicated by leakage, infection, or, rarely, gastrocutaneous fistulas—especially challenging in patients with comorbidities. While surgery has been the traditional approach, it carries risks like delayed healing and prolonged hospitalization. Endoscopic methods provide a safer, less invasive alternative with faster recovery. Advanced tools such as over-the-scope clips, hemostatic clips, and polyloops now allow effective closure of fistulas that once required surgery.
Case Description/
Methods: A 69-year-old woman with a history of oral cancer and PEG tube placement presented with persistent peristomal leakage and erythema. CT of the abdomen showed a PEG tube in satisfactory position within the inferior gastric body. Initial esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) revealed a non-intact gastrostomy tract with a leaking tube. The PEG was removed endoscopically and replaced with an externally removable T-fastener PEG. Despite replacement, leakage continued, and conservative management failed. Repeat EGD identified an 8 mm gastrocutaneous fistula. Argon plasma coagulation (APC) was used to ablate the fistula edges to facilitate tissue adhesion. An OTSC could not be used due to radiation induced stricture. Four hemostatic clips were subsequently applied to approximate the tissue edges, followed by placement of a polyloop around the clips to reinforce the closure. The repair was successful with no bleeding or adverse events, and the site remained intact on follow-up.
Discussion: This case demonstrates the successful use of a hybrid endoscopic closure strategy combining APC, hemostatic clips, and polyloop deployment to manage a complex gastrocutaneous fistula. Although OTSCs are often effective in tissue apposition, they may be insufficient for larger or fibrotic defects. Hemostatic clips allow for incremental approximation, and polyloops offer circumferential tension to secure closure, effectively simulating a purse-string suture. This combination enhances mechanical strength, and provides durable closure even in challenging clinical scenarios.
For patients with significant comorbidities or cancer-related immunosuppression, this technique provides a safe and effective alternative to surgical repair. Compared to surgery, endoscopic techniques reduce anesthesia exposure, length of stay, postoperative pain, and recovery time. They also allow for immediate evaluation and treatment of the mucosa in a single session.

Figure: Fig1: APC ablation promoting granulation tissue formation and enhancing closure efficacy with the polyloop device.

Figure: Fig2: Approximated fistula with polyloop device and clips intact
Disclosures:
Yazan Omari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saif Affas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Roberto Gamarra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Omari, MD, Saif Affas, MD, Roberto Gamarra, MD, FACG. P3581 - Innovative Endoscopic Closure of Gastrocutaneous Fistula Using Polyloop and Hemostatic Clips in a Patient With Persistent PEG Tube Leakage, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
