Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P3532 - Redo Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Is Associated With Improvement in Symptoms and Regain of Clinical Success for Refractory Gastroparesis: A Single Center Experience
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- HA
Hashem N. Albunni, MD
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, IN
Presenting Author(s)
Hashem N. Albunni, MD, John Wo, MD, Nwal Hadaki, MD, Yervant Ichkhanian, MD, Sarah Stainko, NP, Akira Saito, MD, Robert Siwiec, MD, Thomas Nowak, MD, Jacque Peterman, BS, John M. DeWitt, MD, Mohammad Al-Haddad, MD
Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN
Introduction: Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) showed promising results in improving gastroparesis (GP) related symptoms and quality of life (QoL). Nevertheless, a proportion of patients fail to respond to G-POEM after initial improvement. Redo G-POEM has been proposed as a management option in this case, but data on safety, feasibility, and outcomes of G-POEM in this group remains scarce. We aimed to assess the safety and describe clinical and scintigraphy outcomes after redo G-POEM.
Methods: Prospectively enrolled patients who underwent an initial G-POEM followed by a redo G-POEM at a single institution from February 2018 to May 2025 were included. All redo G-POEM procedures were performed at least 6 months post the initial G-POEM. Evaluations were conducted at baseline and 6 months for the initial and redo G-POEMs. Validated tools were used to assess patient outcomes, including Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI), Patient Assessment of Gastrointestinal Disorders Symptom Severity Index (PAGI-SYM), and 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36). Additionally, 4-hour solid phase gastric emptying scan (GES) results were recorded. Clinical success of redo G-POEM was defined as improvement in GCSI scores by ≥ 1 point compared to baseline.
Results: 14 patients (92.9% female, mean age 48.4±14.2 years) were included in this study. 7 patients (50.0%) had idiopathic, 4 (28.6%) had diabetic, and 3 (21.4%) had post-surgical GP. The median (interquartile range) for the time between initial and redo G-POEMs was 12 (8-27) months. The mean total GCSI score markedly improved from a baseline prior to initial G-POEM of 3.5(±0.8) to 2.4(±1.5) at 6 months post-redo G-POEM (p=0.047; Table 1; Figure 1). The average PAGI-SYM total score significantly improved from a baseline prior to initial G-POEM of 3.2(±0.9) to 2.2(±1.3) at 6 months post-redo G-POEM (p=0.008). The mean SF 36 QOL total score and mean 4-hour gastric retention using GES showed improvement trends after redo G-POEM but did not reach statistical significance. Clinical success (using the post G-POEM failure GSCI score) was achieved in 50.0% of patients who underwent redo G-POEM. There were no reported adverse events.
Discussion: Redo G-POEM significantly improved symptom severity for patients with primary failures or those who experienced symptom recurrence post G-POEM with no associated adverse events. Additional research involving a larger cohort is required to determine which patients would derive the greatest benefit from redo G-POEM.
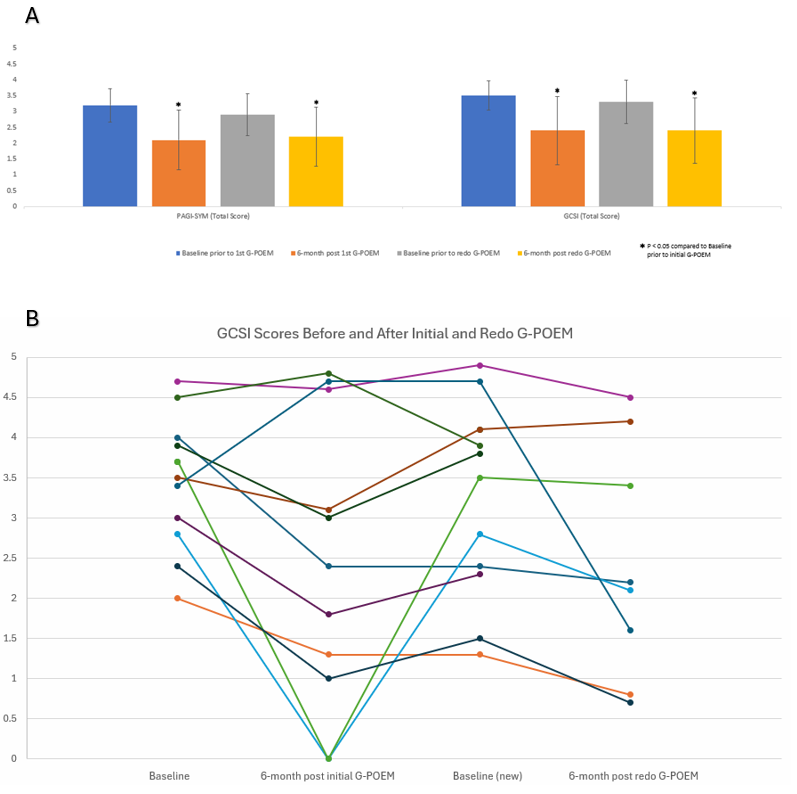
Figure: Figure 1. A. Patient Assessment of Gastrointestinal Disorders Symptom Severity Index (PAGI-SYM), and Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) [mean and 95% confidence intervals]. Statistically significant results compared to initial pre-G-POEM baseline scores are annotated with an asterisk. B. GCSI scores in patients undergoing repeat G-POEM demonstrating the initial decrease in scores followed by symptoms relapse and the effect of redo G-POEM on these scores.
Abbreviations: G-POEM, gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy
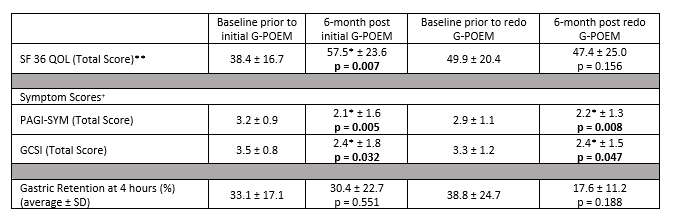
Figure: *p < 0.05 as compared to baseline prior to initial GPOEM. **Range from 0 to 100; +Range from 0 to 5
Table 1. Total scores of SF-36 QOL, PAGI-SYM, and GCSI (mean ± SD), and results of nuclear medicine gastric emptying 4-hour scan (GES) before and after initial G-POEM and redo G-POEM in patients with GP.
Disclosures:
Hashem Albunni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Wo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nwal Hadaki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yervant Ichkhanian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarah Stainko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akira Saito indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Robert Siwiec indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Nowak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacque Peterman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John DeWitt: Boston Scientific, Inc. – Consultant. Cook Medical – Consultant. Olympus America – Consultant.
Mohammad Al-Haddad: Amplified Sciences – Grant/Research Support. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Interpace diagnostics – Consultant.
Hashem N. Albunni, MD, John Wo, MD, Nwal Hadaki, MD, Yervant Ichkhanian, MD, Sarah Stainko, NP, Akira Saito, MD, Robert Siwiec, MD, Thomas Nowak, MD, Jacque Peterman, BS, John M. DeWitt, MD, Mohammad Al-Haddad, MD. P3532 - Redo Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Is Associated With Improvement in Symptoms and Regain of Clinical Success for Refractory Gastroparesis: A Single Center Experience, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN
Introduction: Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) showed promising results in improving gastroparesis (GP) related symptoms and quality of life (QoL). Nevertheless, a proportion of patients fail to respond to G-POEM after initial improvement. Redo G-POEM has been proposed as a management option in this case, but data on safety, feasibility, and outcomes of G-POEM in this group remains scarce. We aimed to assess the safety and describe clinical and scintigraphy outcomes after redo G-POEM.
Methods: Prospectively enrolled patients who underwent an initial G-POEM followed by a redo G-POEM at a single institution from February 2018 to May 2025 were included. All redo G-POEM procedures were performed at least 6 months post the initial G-POEM. Evaluations were conducted at baseline and 6 months for the initial and redo G-POEMs. Validated tools were used to assess patient outcomes, including Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI), Patient Assessment of Gastrointestinal Disorders Symptom Severity Index (PAGI-SYM), and 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36). Additionally, 4-hour solid phase gastric emptying scan (GES) results were recorded. Clinical success of redo G-POEM was defined as improvement in GCSI scores by ≥ 1 point compared to baseline.
Results: 14 patients (92.9% female, mean age 48.4±14.2 years) were included in this study. 7 patients (50.0%) had idiopathic, 4 (28.6%) had diabetic, and 3 (21.4%) had post-surgical GP. The median (interquartile range) for the time between initial and redo G-POEMs was 12 (8-27) months. The mean total GCSI score markedly improved from a baseline prior to initial G-POEM of 3.5(±0.8) to 2.4(±1.5) at 6 months post-redo G-POEM (p=0.047; Table 1; Figure 1). The average PAGI-SYM total score significantly improved from a baseline prior to initial G-POEM of 3.2(±0.9) to 2.2(±1.3) at 6 months post-redo G-POEM (p=0.008). The mean SF 36 QOL total score and mean 4-hour gastric retention using GES showed improvement trends after redo G-POEM but did not reach statistical significance. Clinical success (using the post G-POEM failure GSCI score) was achieved in 50.0% of patients who underwent redo G-POEM. There were no reported adverse events.
Discussion: Redo G-POEM significantly improved symptom severity for patients with primary failures or those who experienced symptom recurrence post G-POEM with no associated adverse events. Additional research involving a larger cohort is required to determine which patients would derive the greatest benefit from redo G-POEM.

Figure: Figure 1. A. Patient Assessment of Gastrointestinal Disorders Symptom Severity Index (PAGI-SYM), and Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) [mean and 95% confidence intervals]. Statistically significant results compared to initial pre-G-POEM baseline scores are annotated with an asterisk. B. GCSI scores in patients undergoing repeat G-POEM demonstrating the initial decrease in scores followed by symptoms relapse and the effect of redo G-POEM on these scores.
Abbreviations: G-POEM, gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy

Figure: *p < 0.05 as compared to baseline prior to initial GPOEM. **Range from 0 to 100; +Range from 0 to 5
Table 1. Total scores of SF-36 QOL, PAGI-SYM, and GCSI (mean ± SD), and results of nuclear medicine gastric emptying 4-hour scan (GES) before and after initial G-POEM and redo G-POEM in patients with GP.
Disclosures:
Hashem Albunni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Wo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nwal Hadaki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yervant Ichkhanian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarah Stainko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akira Saito indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Robert Siwiec indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Nowak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacque Peterman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John DeWitt: Boston Scientific, Inc. – Consultant. Cook Medical – Consultant. Olympus America – Consultant.
Mohammad Al-Haddad: Amplified Sciences – Grant/Research Support. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Interpace diagnostics – Consultant.
Hashem N. Albunni, MD, John Wo, MD, Nwal Hadaki, MD, Yervant Ichkhanian, MD, Sarah Stainko, NP, Akira Saito, MD, Robert Siwiec, MD, Thomas Nowak, MD, Jacque Peterman, BS, John M. DeWitt, MD, Mohammad Al-Haddad, MD. P3532 - Redo Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Is Associated With Improvement in Symptoms and Regain of Clinical Success for Refractory Gastroparesis: A Single Center Experience, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

