Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0058 - Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics of TH 104, Buccal Nalmefene, in Healthy Subjects and Patients With Cholestatic Liver Disease
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- NB
Nir Barak, MD (he/him/his)
Tharimmune Inc
Bridgewater, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Nir Barak, MD, Randy Milby, PharmD, Sireesh Appajosyula, PharmD
Tharimmune Inc, Bridgewater, NJ
Introduction: TH104 is a buccal Nalmefene film developed for the treatment of pruritus in primary biliary cholangitis (PBC). Buccal administration avoids the liver first drug metabolism and therefore may be more suitable for use in patients with liver disease. Previous report (Frye 1997) found that liver disease increases the Area Under the Curve (AUC) when Nalmefene is administered intravenously. We herein report, a comparison of Nalmefene pharmacokinetics (PK) between healthy subjects and patients with cholestatic liver disease using TH104.
Methods: Data for this analysis was collected from 2 clinical studies. Both studies were approved by the local ethical and regulatory bodies. Study TH105 was a single-dose, single-center, open-label, randomized, 2-way crossover study of TH104 with the comparator (nalmefene injection), involving 20 normal healthy volunteers. After an overnight fast, subjects received a single dose of either TH104 (16 mg) or intravenous dose of nalmefene injection (1 mg) in a crossover design. Study AV106 enrolled 12 patients with cholestatic liver disease (Child Pough class A and B) and a known history of persistent generalized pruritus. After an overnight fasting of 10 hours, subjects received one dose of 2 mg of TH104. In order to standardize the PK analysis, results were corrected according to the dose administered. D'Agostino-Pearson test for normal distribution was used to compare between the groups. MedCalac software version 23.2.1 was used for calculations.
Results: For healthy subjects, the Cmax and Tmax were 0.66 ng/mL (SD 0.18) and 2.23 hours (SD 0.92). For patients with cholestatic liver disease, the Cmax and Tmax were 0.73 ng/mL (SD 0.37) and 2.16 hours (SD 0.83). For healthy subjects, the mean AUC was 7.16 ng*hour/mL (SD 2.15 ) with 95% CI of 6.15 to 8.16. For patients with cholestatic liver disease the mean AUC was 10.02 ng*hour/mL (SD 6.77) with 95% CI of 5.71 to 14.32. The difference between the groups was calculated to be 2.86 ng*hour/mL with 95% CI of difference -0.4519 to 6.1765. The two-tailed probability showed a value of P = 0.0879, and therefore D'Agostino-Pearson test accepted normality and determined that there is no statistical difference between the groups.
Discussion: The results of this study show, that Nalmefene PK does not statistically differ between healthy individuals and patients with mild to moderate cholestatic liver disease, when TH104 is used.
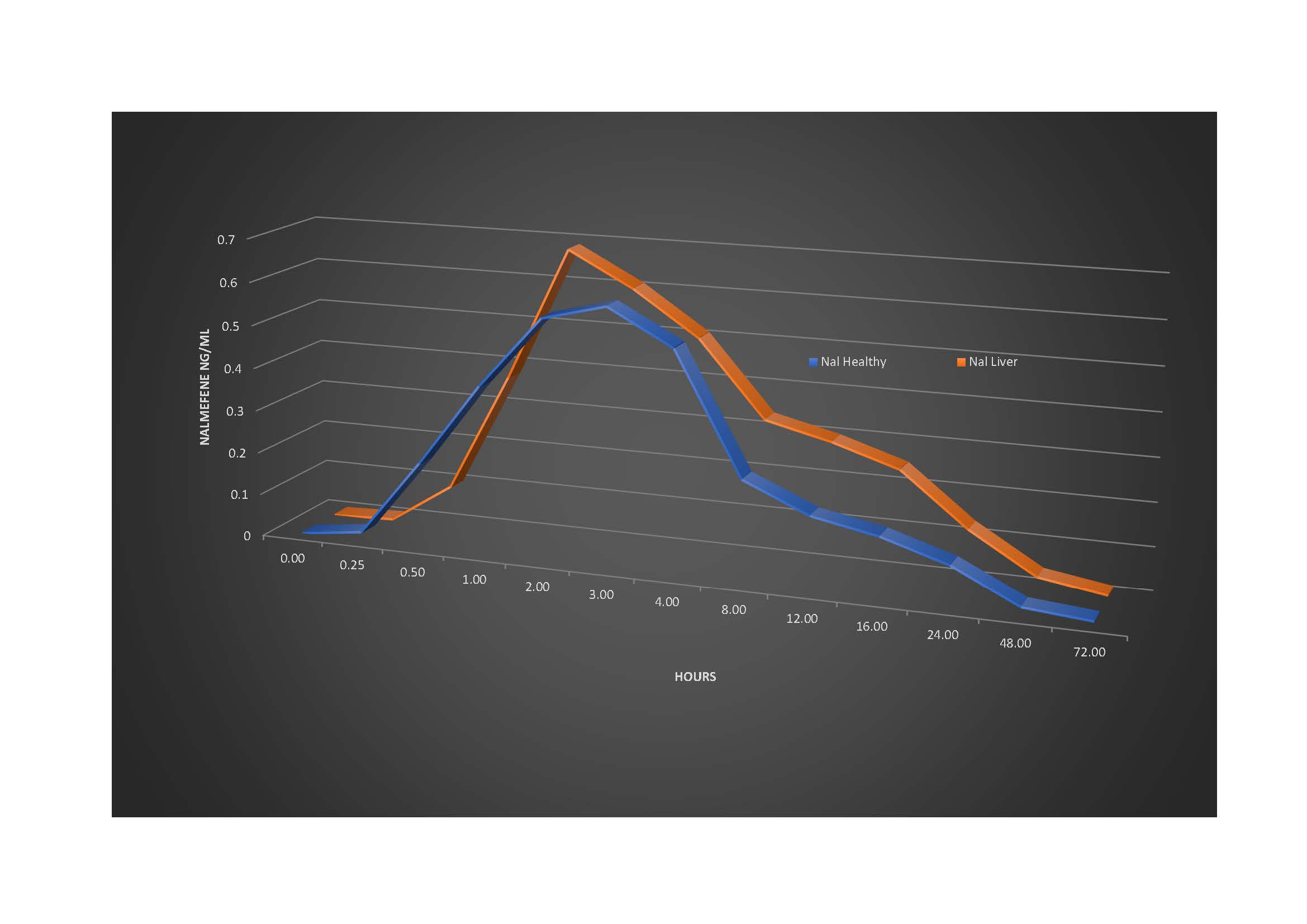
Figure: Nalmefene Concentration (nanoG/ml) versus Time (hours) plot. Nal Healthy denotes Nalmefene pK in healthy subjects; Nal Liver denotes Nalmefene pK in patients with cholestatic liver disease.
Disclosures:
Nir Barak: Tharimmune Inc – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Randy Milby: Tharimmune Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Employee, Owner/Ownership Interest, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Sireesh Appajosyula: Tharimmune Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Nir Barak, MD, Randy Milby, PharmD, Sireesh Appajosyula, PharmD. P0058 - Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics of TH 104, Buccal Nalmefene, in Healthy Subjects and Patients With Cholestatic Liver Disease, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Tharimmune Inc, Bridgewater, NJ
Introduction: TH104 is a buccal Nalmefene film developed for the treatment of pruritus in primary biliary cholangitis (PBC). Buccal administration avoids the liver first drug metabolism and therefore may be more suitable for use in patients with liver disease. Previous report (Frye 1997) found that liver disease increases the Area Under the Curve (AUC) when Nalmefene is administered intravenously. We herein report, a comparison of Nalmefene pharmacokinetics (PK) between healthy subjects and patients with cholestatic liver disease using TH104.
Methods: Data for this analysis was collected from 2 clinical studies. Both studies were approved by the local ethical and regulatory bodies. Study TH105 was a single-dose, single-center, open-label, randomized, 2-way crossover study of TH104 with the comparator (nalmefene injection), involving 20 normal healthy volunteers. After an overnight fast, subjects received a single dose of either TH104 (16 mg) or intravenous dose of nalmefene injection (1 mg) in a crossover design. Study AV106 enrolled 12 patients with cholestatic liver disease (Child Pough class A and B) and a known history of persistent generalized pruritus. After an overnight fasting of 10 hours, subjects received one dose of 2 mg of TH104. In order to standardize the PK analysis, results were corrected according to the dose administered. D'Agostino-Pearson test for normal distribution was used to compare between the groups. MedCalac software version 23.2.1 was used for calculations.
Results: For healthy subjects, the Cmax and Tmax were 0.66 ng/mL (SD 0.18) and 2.23 hours (SD 0.92). For patients with cholestatic liver disease, the Cmax and Tmax were 0.73 ng/mL (SD 0.37) and 2.16 hours (SD 0.83). For healthy subjects, the mean AUC was 7.16 ng*hour/mL (SD 2.15 ) with 95% CI of 6.15 to 8.16. For patients with cholestatic liver disease the mean AUC was 10.02 ng*hour/mL (SD 6.77) with 95% CI of 5.71 to 14.32. The difference between the groups was calculated to be 2.86 ng*hour/mL with 95% CI of difference -0.4519 to 6.1765. The two-tailed probability showed a value of P = 0.0879, and therefore D'Agostino-Pearson test accepted normality and determined that there is no statistical difference between the groups.
Discussion: The results of this study show, that Nalmefene PK does not statistically differ between healthy individuals and patients with mild to moderate cholestatic liver disease, when TH104 is used.

Figure: Nalmefene Concentration (nanoG/ml) versus Time (hours) plot. Nal Healthy denotes Nalmefene pK in healthy subjects; Nal Liver denotes Nalmefene pK in patients with cholestatic liver disease.
Disclosures:
Nir Barak: Tharimmune Inc – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Randy Milby: Tharimmune Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Employee, Owner/Ownership Interest, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Sireesh Appajosyula: Tharimmune Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Nir Barak, MD, Randy Milby, PharmD, Sireesh Appajosyula, PharmD. P0058 - Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics of TH 104, Buccal Nalmefene, in Healthy Subjects and Patients With Cholestatic Liver Disease, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
