Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0121 - All Strictures Point to IgG4: A Rare Case of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Tevan Luong, MD (he/him/his)
UCI School of Medicine
Orange, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Steve Huy D. Phan, BS1, Tevan Luong, MD2, Kevin Chow, MD2
1UCI School of Medicine, Westminster, CA; 2UCI School of Medicine, Orange, CA
Introduction: Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is an uncommon cholangiopathy that frequently coexists with autoimmune pancreatitis but can also present with isolated biliary involvement. Differentiating IgG4-SC from other cholangiopathies is essential, as treatment approaches differ significantly. We present a case of IgG4-SC with associated aortitis and pancreatitis.
Case Description/
Methods: A 74-year-old Vietnamese male with a history of renal cell carcinoma status post-nephrectomy in 2023, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypertension presented with a three-week history of jaundice, decreased appetite, and diffuse rash. Abdominal and pelvic computed tomography (CT) showed gallbladder and common bile duct (CBD) dilatation. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) further revealed intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilation, inflammatory aortic changes suggestive of aortitis, and low-density lesions in the renal cortex of his solitary kidney. Endoscopic ultrasound demonstrated a full-appearing pancreas; fine needle aspiration revealed no malignancy. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) identified a severe distal CBD stricture without evidence of choledocholithiasis, and a biliary stent was placed. CA 19-9 was normal at 2 U/mL, and serum IgG4 was elevated at 597 mg/dL. Based on the 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism (ACR/EULAR) classification criteria, the patient met diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease. He started a prednisone taper and was placed on rituximab for long-term immunosuppression.
Discussion: IgG4-related disease is a rare cause of sclerosing cholangitis seen predominantly in older Asian males. Often, performing MRCP before ERCP for suspected choledocholithiasis is inadvisable due to high unnecessary costs and delays to definitive care. However, in this case, MRCP provided early useful information of aortitis and possible renal involvement for the diagnosis of IgG4-SC, as CT with contrast was contraindicated due to the patient's solitary kidney and bile acid nephropathy. Therefore, in patients with worsening creatinine function and solitary kidney, MRCP before ERCP can be considered for further management of disease. Furthermore, obstructive cholangitis may be due to many different etiologies, with cholangiocarcinoma, being the deadliest. Therefore, early diagnosis through MRCP can be crucial to finding a definitive treatment.
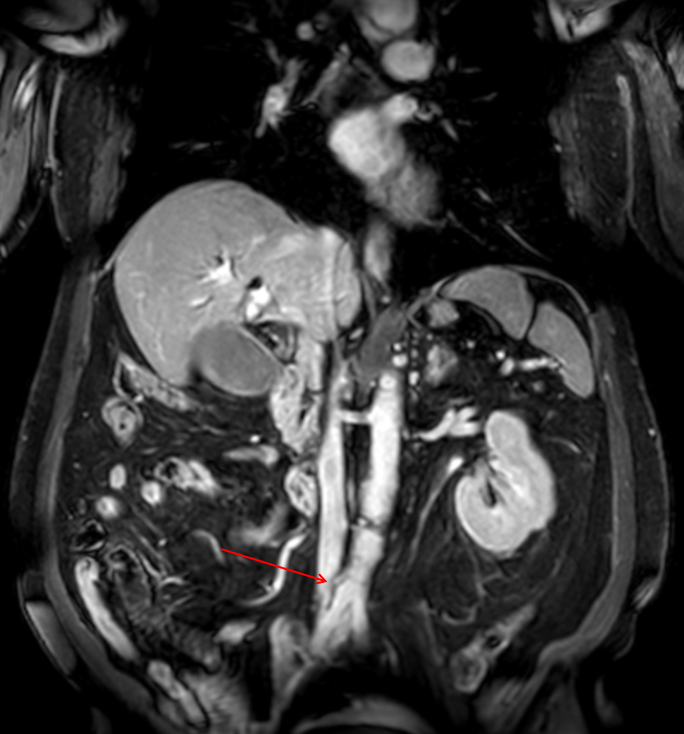
Figure: Image 1. MRCP showing enhancing soft tissue around the proximal right common iliac artery, suggesting aortitis.
Disclosures:
Steve Huy Phan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tevan Luong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Chow indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steve Huy D. Phan, BS1, Tevan Luong, MD2, Kevin Chow, MD2. P0121 - All Strictures Point to IgG4: A Rare Case of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UCI School of Medicine, Westminster, CA; 2UCI School of Medicine, Orange, CA
Introduction: Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is an uncommon cholangiopathy that frequently coexists with autoimmune pancreatitis but can also present with isolated biliary involvement. Differentiating IgG4-SC from other cholangiopathies is essential, as treatment approaches differ significantly. We present a case of IgG4-SC with associated aortitis and pancreatitis.
Case Description/
Methods: A 74-year-old Vietnamese male with a history of renal cell carcinoma status post-nephrectomy in 2023, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypertension presented with a three-week history of jaundice, decreased appetite, and diffuse rash. Abdominal and pelvic computed tomography (CT) showed gallbladder and common bile duct (CBD) dilatation. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) further revealed intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary dilation, inflammatory aortic changes suggestive of aortitis, and low-density lesions in the renal cortex of his solitary kidney. Endoscopic ultrasound demonstrated a full-appearing pancreas; fine needle aspiration revealed no malignancy. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) identified a severe distal CBD stricture without evidence of choledocholithiasis, and a biliary stent was placed. CA 19-9 was normal at 2 U/mL, and serum IgG4 was elevated at 597 mg/dL. Based on the 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism (ACR/EULAR) classification criteria, the patient met diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease. He started a prednisone taper and was placed on rituximab for long-term immunosuppression.
Discussion: IgG4-related disease is a rare cause of sclerosing cholangitis seen predominantly in older Asian males. Often, performing MRCP before ERCP for suspected choledocholithiasis is inadvisable due to high unnecessary costs and delays to definitive care. However, in this case, MRCP provided early useful information of aortitis and possible renal involvement for the diagnosis of IgG4-SC, as CT with contrast was contraindicated due to the patient's solitary kidney and bile acid nephropathy. Therefore, in patients with worsening creatinine function and solitary kidney, MRCP before ERCP can be considered for further management of disease. Furthermore, obstructive cholangitis may be due to many different etiologies, with cholangiocarcinoma, being the deadliest. Therefore, early diagnosis through MRCP can be crucial to finding a definitive treatment.

Figure: Image 1. MRCP showing enhancing soft tissue around the proximal right common iliac artery, suggesting aortitis.
Disclosures:
Steve Huy Phan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tevan Luong indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Chow indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steve Huy D. Phan, BS1, Tevan Luong, MD2, Kevin Chow, MD2. P0121 - All Strictures Point to IgG4: A Rare Case of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
