Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0288 - The Impact of Concurrent Bevacizumab Therapy on Adverse Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Colonic Luminal Stenting for Malignant Obstruction: A Retrospective Multicenter US Comparative Cohort Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mostafa Eysha, MD
Texas Tech University Health Science Center El Paso
El Paso, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Mostafa Eysha, MD1, Mohanad Elchouemi, BS2, Seyma Bayram, MD3, Alan Jurado, MD2, Arsalan Asad, BS4, Ahmed Eysha, MD5, Mona A. Ali, MD6, Anas A. Elsaka, MD6, M. Ammar Kalas, MD7, Paul Estrada, MD2, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD7
1Texas Tech University Health Science Center El Paso, El Paso, TX; 2Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX; 3The Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, PA; 4John Sealy School of Medicine, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt; 6Mansoura University, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 7Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX
Introduction: Malignant colonic obstruction is a critical complication of advanced colorectal cancer, often managed with self-expandable metallic stents (SEMS). Bevacizumab (Avastin), an anti-angiogenic therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer, is associated with a risk of gastrointestinal (GI) perforation and other adverse events like peritonitis and sepsis. The concurrent use of SEMS and Bevacizumab has raised concerns regarding an increased risk of such complications, with existing literature presenting conflicting evidence and methodological limitations. The study aimed to assess the risk of adverse outcomes in patients undergoing colonic luminal stenting while receiving Bevacizumab therapy.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted using de-identified patient data from the TriNetX database. Adult patients (≥18 years old) who underwent colonic luminal stenting were identified using the ICD-10 codes. Patients were then stratified into two groups based on receiving or not receiving Bevacizumab. To minimize selection bias and hidden confounders, 1:1 propensity score matching was performed, adjusting for patient demographics and relevant comorbidities. Odds ratios (OR) for perforation, peritonitis, sepsis, septic shock, emergent exploratory laparotomy and all-cause mortality at one year were calculated to compare the matched cohorts.
Results: The initial cohorts consisted of 478 patients receiving Bevacizumab therapy and 2,036 patients not receiving Bevacizumab therapy. After propensity score matching, each group comprised 474 patients. At the one-year follow-up, patients receiving Bevacizumab therapy had significantly higher odds of perforation (OR 2.17, 95% CI 1.41-3.33), peritonitis (OR 1.79, 95% CI 1.24-2.59), and sepsis (OR 1.49, 95% CI 1.07-2.07) compared to the no Bevacizumab group. Conversely, the odds for all-cause mortality (OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.74-1.30), emergent exploratory laparotomy (OR 1.37, 95% CI 0.62-3.02), and septic shock requiring pressors (OR 1.04, 95% CI 0.57-1.90) were not significantly different between the two groups (Table 1).
Discussion: In this large real-world cohort study, colonic luminal stenting was associated with a higher risk of perforation in patients receiving Bevacizumab compared to the control group. These findings underscore the importance of a careful risk-benefit assessment and heightened vigilance for specific adverse events when considering luminal stenting in this patient population.
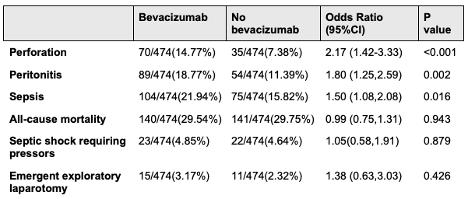
Figure: Table 1. Adverse outcomes after colon luminal stenting in patients receiving Bevacizumab therapy versus those not receiving Bevacizumab
Disclosures:
Mostafa Eysha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohanad Elchouemi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Seyma Bayram indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alan Jurado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arsalan Asad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Eysha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Elsaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
M. Ammar Kalas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Estrada indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sherif Elhanafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mostafa Eysha, MD1, Mohanad Elchouemi, BS2, Seyma Bayram, MD3, Alan Jurado, MD2, Arsalan Asad, BS4, Ahmed Eysha, MD5, Mona A. Ali, MD6, Anas A. Elsaka, MD6, M. Ammar Kalas, MD7, Paul Estrada, MD2, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD7. P0288 - The Impact of Concurrent Bevacizumab Therapy on Adverse Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Colonic Luminal Stenting for Malignant Obstruction: A Retrospective Multicenter US Comparative Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Texas Tech University Health Science Center El Paso, El Paso, TX; 2Paul L. Foster School of Medicine, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX; 3The Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, PA; 4John Sealy School of Medicine, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX; 5Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt; 6Mansoura University, Mansoura, Ad Daqahliyah, Egypt; 7Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, TX
Introduction: Malignant colonic obstruction is a critical complication of advanced colorectal cancer, often managed with self-expandable metallic stents (SEMS). Bevacizumab (Avastin), an anti-angiogenic therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer, is associated with a risk of gastrointestinal (GI) perforation and other adverse events like peritonitis and sepsis. The concurrent use of SEMS and Bevacizumab has raised concerns regarding an increased risk of such complications, with existing literature presenting conflicting evidence and methodological limitations. The study aimed to assess the risk of adverse outcomes in patients undergoing colonic luminal stenting while receiving Bevacizumab therapy.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted using de-identified patient data from the TriNetX database. Adult patients (≥18 years old) who underwent colonic luminal stenting were identified using the ICD-10 codes. Patients were then stratified into two groups based on receiving or not receiving Bevacizumab. To minimize selection bias and hidden confounders, 1:1 propensity score matching was performed, adjusting for patient demographics and relevant comorbidities. Odds ratios (OR) for perforation, peritonitis, sepsis, septic shock, emergent exploratory laparotomy and all-cause mortality at one year were calculated to compare the matched cohorts.
Results: The initial cohorts consisted of 478 patients receiving Bevacizumab therapy and 2,036 patients not receiving Bevacizumab therapy. After propensity score matching, each group comprised 474 patients. At the one-year follow-up, patients receiving Bevacizumab therapy had significantly higher odds of perforation (OR 2.17, 95% CI 1.41-3.33), peritonitis (OR 1.79, 95% CI 1.24-2.59), and sepsis (OR 1.49, 95% CI 1.07-2.07) compared to the no Bevacizumab group. Conversely, the odds for all-cause mortality (OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.74-1.30), emergent exploratory laparotomy (OR 1.37, 95% CI 0.62-3.02), and septic shock requiring pressors (OR 1.04, 95% CI 0.57-1.90) were not significantly different between the two groups (Table 1).
Discussion: In this large real-world cohort study, colonic luminal stenting was associated with a higher risk of perforation in patients receiving Bevacizumab compared to the control group. These findings underscore the importance of a careful risk-benefit assessment and heightened vigilance for specific adverse events when considering luminal stenting in this patient population.

Figure: Table 1. Adverse outcomes after colon luminal stenting in patients receiving Bevacizumab therapy versus those not receiving Bevacizumab
Disclosures:
Mostafa Eysha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohanad Elchouemi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Seyma Bayram indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alan Jurado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Arsalan Asad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Eysha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mona Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Elsaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
M. Ammar Kalas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Estrada indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sherif Elhanafi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mostafa Eysha, MD1, Mohanad Elchouemi, BS2, Seyma Bayram, MD3, Alan Jurado, MD2, Arsalan Asad, BS4, Ahmed Eysha, MD5, Mona A. Ali, MD6, Anas A. Elsaka, MD6, M. Ammar Kalas, MD7, Paul Estrada, MD2, Sherif E. Elhanafi, MD7. P0288 - The Impact of Concurrent Bevacizumab Therapy on Adverse Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Colonic Luminal Stenting for Malignant Obstruction: A Retrospective Multicenter US Comparative Cohort Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
