Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0281 - Beyond Glycemic Control: Cardiovascular Outcomes of GLP-1/GIP Agonists in T2DM-IBD Patients

Muhammad Ali Ibrahim Kazi, MD
Anne Arundel Medical Center
Annapolis, MD
Presenting Author(s)
1Anne Arundel Medical Center, Annapolis, MD; 2University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH
Introduction:
Patients with coexisting Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) face an increased risk of cardiovascular complications due to shared pathways of chronic inflammation, metabolic dysregulation, and immune-mediated vascular injury. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists, such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, have demonstrated cardiometabolic benefits in diabetic populations. However, their impact on specific cardiac complications in patients with both T2DM and IBD remains understudied.
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX global federated health research network, focusing on adults (≥18 years) with concurrent diagnoses of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. After matching, both cohorts consisted of 12,331 patients.
Cohort 1 (n=12,331): Patients with T2DM and IBD who were treated with semaglutide or tirzepatide
Cohort 2 (n=12,331): Patients with T2DM and IBD who did not receive these agents
Propensity score matching was performed 1:1 on 51 covariates, including demographics, comorbidities (e.g., chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, liver disease), relevant procedures, and concomitant medications.
Results:
GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist therapy was associated with significantly reduced risks for all analyzed cardiac outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and inflammatory bowel disease. The following relative risks (RR) and p-values were observed in the matched cohorts:
Myocardial Infarction: RR 0.50, p < 0.001
Heart Failure: RR 0.58, p < 0.001
Atrial Fibrillation: RR 0.60, p < 0.001
Ventricular Fibrillation: RR 0.45, p < 0.001
Pericarditis: RR 0.36, p < 0.001
AV Block (First Degree): RR 0.67, p < 0.001
AV Block (Second Degree): RR 0.51, p < 0.001
Complete AV Block: RR 0.49, p < 0.001
Sudden Cardiac Death (proxy for cardiomyopathy): RR 0.52, p < 0.001
Discussion:
GLP-1 and dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists are associated with substantial reductions in cardiovascular risk among patients with T2DM and IBD. These findings underscore the potential benefit of these agents in cardiometabolic and inflammatory comorbidity management, supporting their broader use in high-risk populations.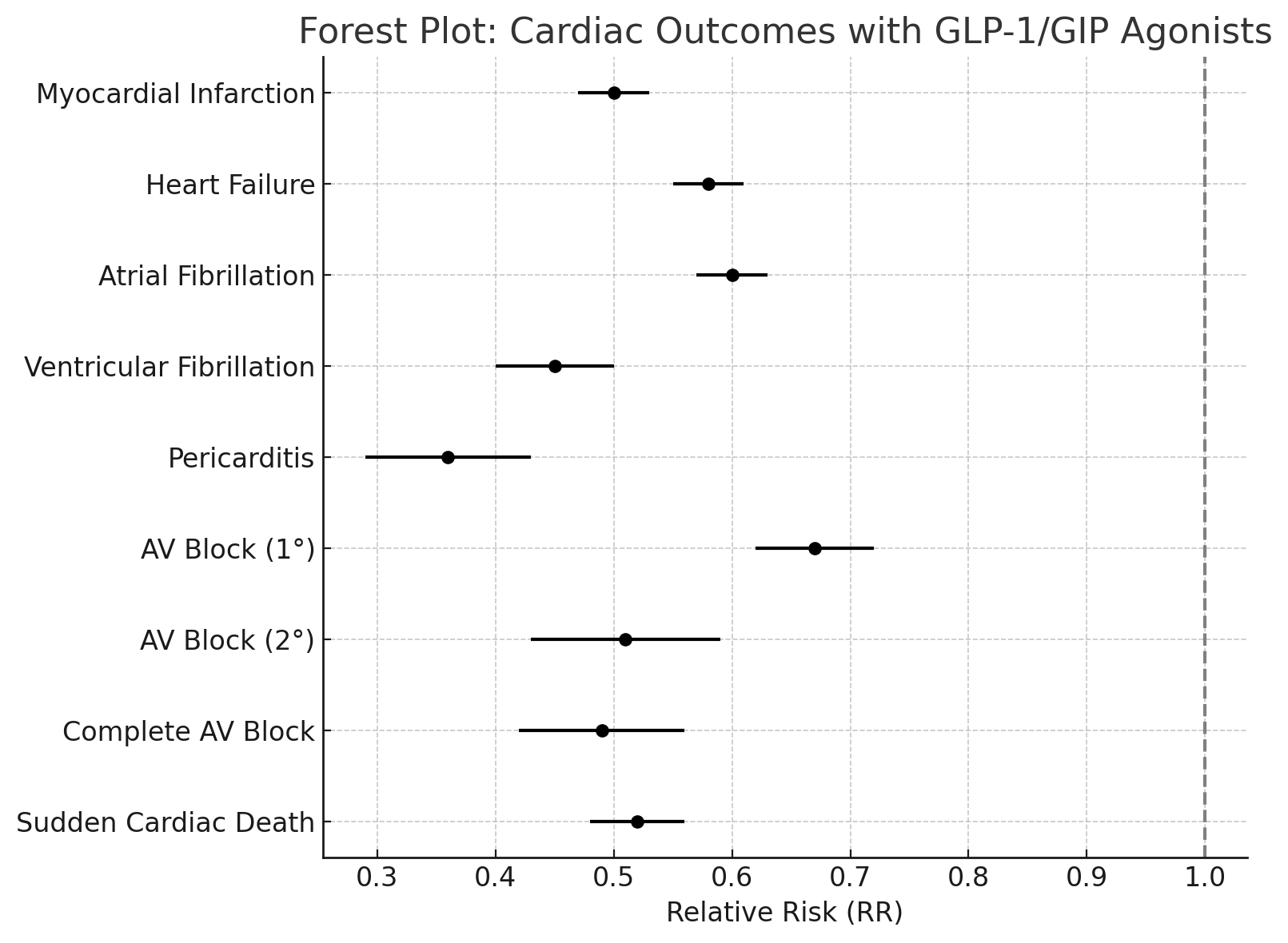
Figure: Figure: Forest Plot of Cardiac Outcomes Associated with GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonist Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Disclosures:
Muhammad Ali Ibrahim Kazi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akshay Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nirav Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patel Manthanbhai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanmeet Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Ali Ibrahim Kazi, MD1, Akshay Sharma, MD1, Nirav Agrawal, MD1, Patel Manthanbhai, MD2, Sanmeet Singh, MD1. P0281 - Beyond Glycemic Control: Cardiovascular Outcomes of GLP-1/GIP Agonists in T2DM-IBD Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
