Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0364 - Novel Molecular Testing Modalities Facilitate Diagnosis of Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Patient With Hidradenitis Suppurativa

Vanessa Avalone, MD
Boston Medical Center
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Vanessa Avalone, MD1, Felicia Lee, MD1, Marya Pulaski, MD1, John C. Lee, MD2, Horst C. Weber, MD3
1Boston Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2VA Boston Healthcare System, West Roxbury, MA; 3VA Boston Healthcare System, Jamaica Plain, MA
Introduction:
Anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC) is a rare malignancy with increasing incidence and mortality rates in the United States. The treatment of ASCC with chemoradiation remains standard of care. However, with next generation sequencing (NGS) and cell free methylated DNA (cfDNA; Galleri test), novel targeted therapies are being investigated. Risk factors for ASCC include human papillomavirus (HPV), tobacco use, and immunocompromised states. Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory skin condition that has been associated with cutaneous and mucosal SCC arising from HS lesions. Malignancy risk increases with HS severity, HPV presence, and duration and location in the ano-genital region. We present a case of ASCC in a HS patient whose diagnosis was aided by precision medicine tools.
Case Description/
Methods:
A 67-year-old non-smoker male with long-standing HS affecting his axilla and perineal area, presented to Primacy Care Clinic with several months of peri-anal discomfort and a swollen inguinal lymph node (LN). Biopsy of the LN showed HPV-associated, metastatic p16-positive SCC (Figure 1) without a known primary tumor. Subsequent cfDNA methylation screening predicted cancer signals originating from the head/neck and anus regions. Colonoscopy was performed, which revealed a mass at the dentate line (Figure 1) without involvement of the anal canal. NGS was performed on LN tissue with the molecular profile summarized in table 1, and PD-L1 tumor proportion score was highly positive with 80% suggesting tentatively actionable targets of the PIK3K/AKT/MTOR pathways and immunotherapy. Initially, the patient received chemoradiation with 5FU/ Mitomycin and XRT with an excellent response.
Discussion: The screening for tumor specific methylated ctDNA (Galleri test) proved successful as a novel diagnostic tool, identifying cancer signals of anal origin even in the absence of lower GI tract symptoms. HPV infection is the principal molecular alteration found in both ASCC and in SCC arising in long-standing HS, especially in the anogenital region. However, the molecular signature of HS in general is distinct from that in ASCC including mutations of g-secretase complex genes suggesting no direct molecular relation between ASCC and HS. Mutations of the PIK3K/AKT/MTOR pathway are being tested in trials as therapeutic actionable targets and may offer possible options for recurrent disease.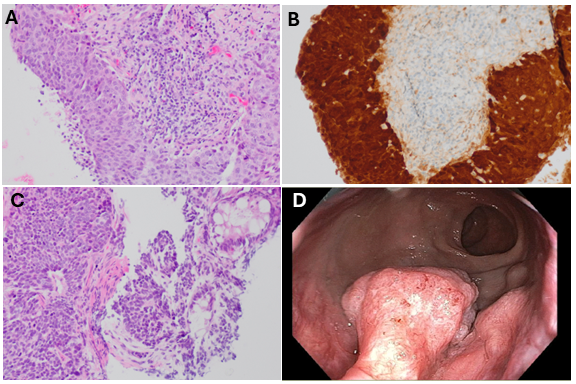
Figure: Figure 1: Tissue samples from lymph node biopsy (Panel A, left top: H&E at 200X, and Panel B, top right: p16 immunohistochemistry at 200X), rectum (Panel C, bottom left: H&E at 200X), and the endoscopic view of the anal mass lesion (Panel D, bottom right).
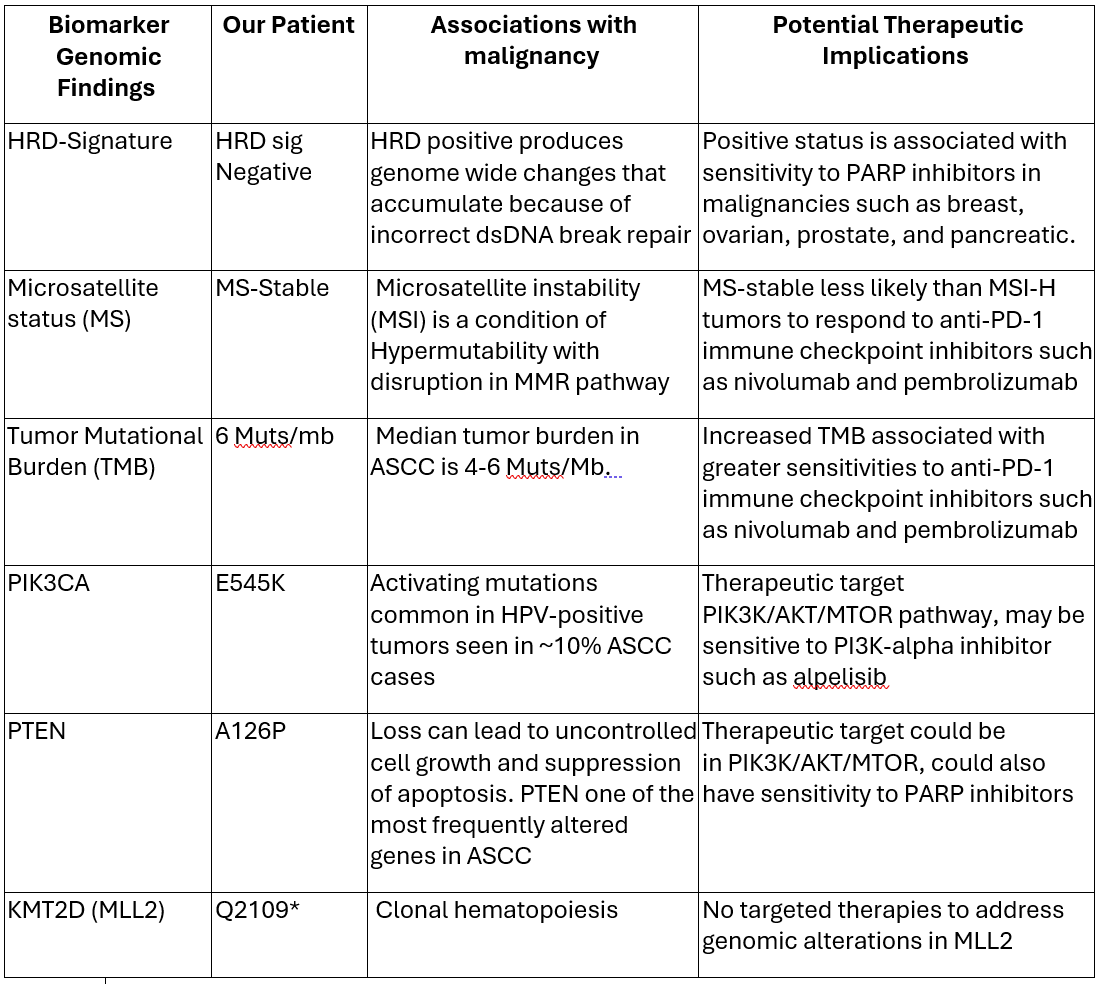
Figure: Table 1. Molecular profile of this patient with ASCC using FoundationMedicineR testing with NGS and PD-L1 immunohistochemistry on tissue from lymphnode metastasis. PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) was highly positive with 80%.
Disclosures:
Vanessa Avalone indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Felicia Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marya Pulaski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Horst Weber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vanessa Avalone, MD1, Felicia Lee, MD1, Marya Pulaski, MD1, John C. Lee, MD2, Horst C. Weber, MD3. P0364 - Novel Molecular Testing Modalities Facilitate Diagnosis of Anal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Patient With Hidradenitis Suppurativa, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.


