Sunday Poster Session
Category: Diet, Nutrition, and Obesity
P0539 - Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists Reduce All-Cause Mortality and Healthcare Utilization in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AF
Andrew Ford, MD
Case Western Reserve University / MetroHealth
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Andrew Ford, MD1, Jack Loesch, BA2, Arjun Chatterjee, MD3, Sara Valencia, MD4, Keren Zhou, MD5, Anthony Lembo, MD, FACG4, Samita Garg, MD4
1Case Western Reserve University / MetroHealth, Cleveland, OH; 2Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH; 3Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 4Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 5Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are FDA approved for type 2 diabetes (T2D) and weight loss and are increasingly being used off-label for patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). We evaluated the risks and healthcare utilization among T1D patients receiving these medications up to 2 years.
Methods: We utilized the TriNetX database, a global federated network with data from numerous healthcare organizations. We identified patients with T1D using ICD-10 codes and excluded those with T2D diagnoses and SGLT-2i use. T1D patients were then divided into two cohorts based on whether or not they had received GLP-1RAs. We then performed 1:1 propensity matching for demographics (age, sex, and race), inflammatory bowel disease, BMI and HbA1c. Primary outcomes included ED visits, hospitalizations, DKA, hypoglycemia, prokinetic prescriptions, and all-cause mortality. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained for all outcomes except all-cause mortality, for which Cox regression analysis was performed to obtain hazard ratio (HR) at two years. Index event was defined as meeting inclusion criteria as well as at least six months of continuous GLP-1RA use for the respective cohort based on refill documentation.
Results: After propensity score matching, 4760 patients were identified in each group (Table). The matched cohorts were predominantly White (71.9% in GLP-1RA cohort, 71.8% in non-GLP-1RA cohort) and female (62.0% in both). Patients taking GLP-1RAs had lower ED visits (OR 0.46, 95% CI 0.39-0.55, p< 0.001), all-cause admission (OR 0.24, CI 0.17-0.33, p< .001), DKA (OR 0.58, 95% CI 0.36-0.93, p=0.02), prokinetic use (OR 0.73, CI 0.56-0.95, p=0.02), and all-cause mortality (HR 0.24, CI 0.16-0.34, p=0.005). There was no significant difference between groups for hypoglycemia (p=0.4).
Discussion: Patients with T1D receiving GLP-1RAs had significantly lower ED visits, inpatient admission, DKA, prokinetic prescriptions, and all-cause mortality with no significant effect on hypoglycemia. This data suggests that GLP-1RAs may not only be safe, but also beneficial for patients with T1D, though prospective data are necessary to confirm our conclusions.
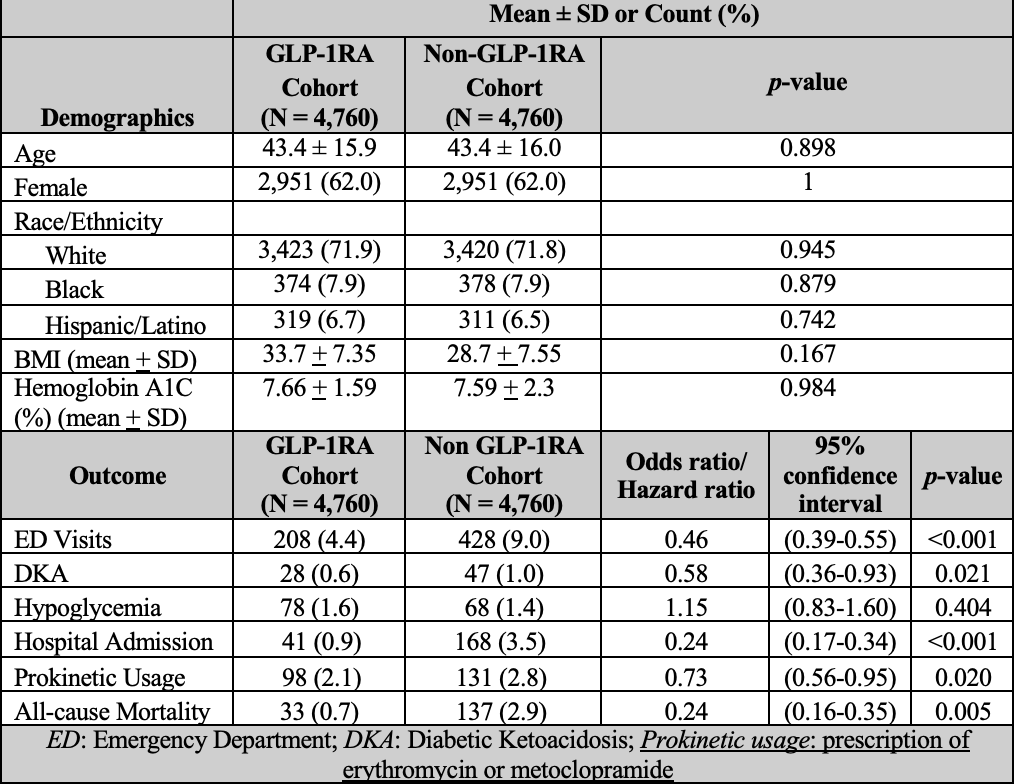
Figure: Table 1: Demographics, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of GLP-1RA and Non-GLP1-RA Cohorts After Propensity Score Matching
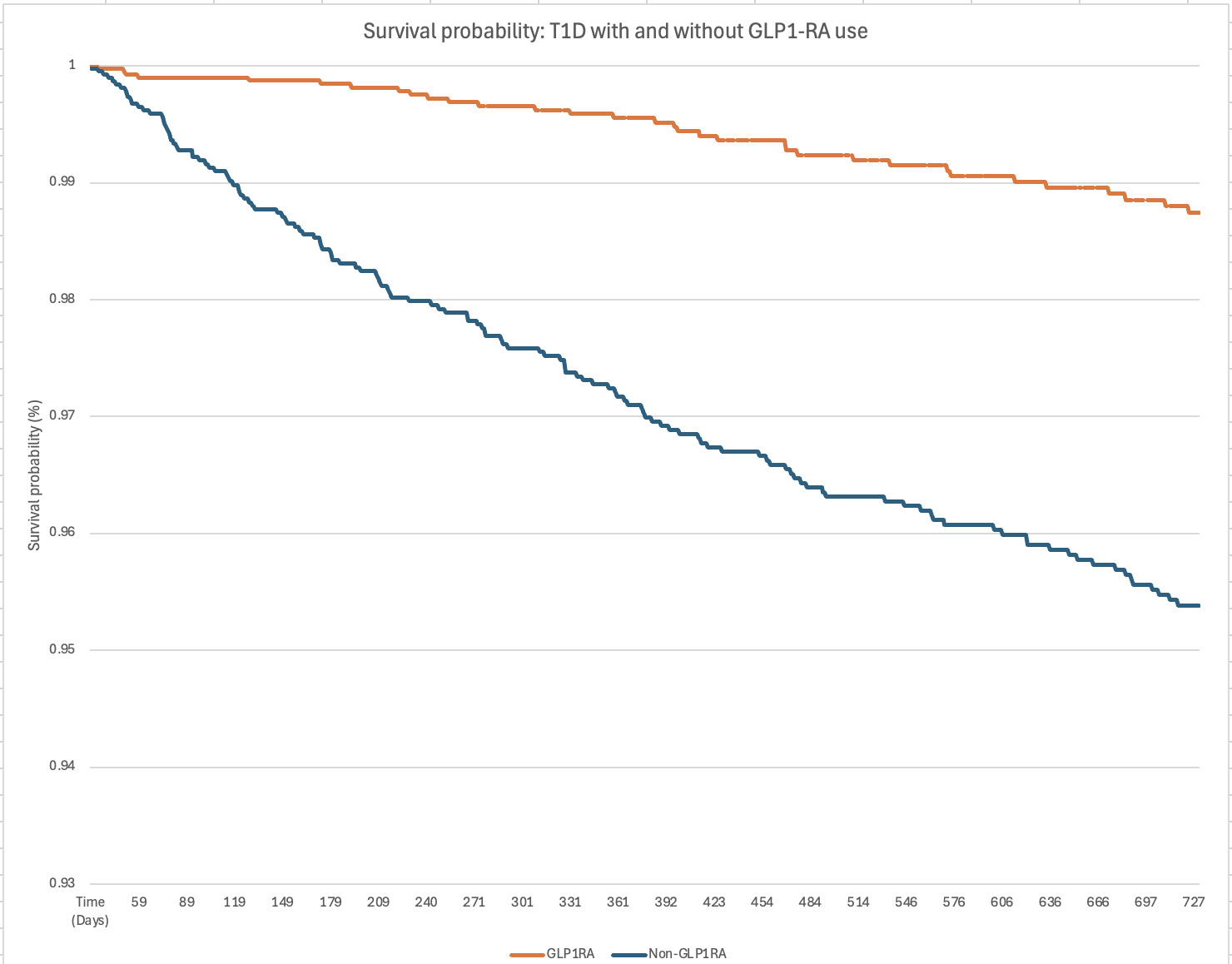
Figure: Figure 1: Survival Probability Comparison Between GLP1-RA and Non-GLP1-RA Patients With T1D
Disclosures:
Andrew Ford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jack Loesch: Eli Lilly and Company – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Arjun Chatterjee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Valencia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Keren Zhou: Corcept – Consultant. NeuroSolutions 100 – Grant/Research Support. Xeris – Speakers Bureau.
Anthony Lembo: Allurion – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Ardeylx – Consultant. Atmo – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bristol Myer Squibb – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). GSK – Consultant. Ironwood – DSMB. J&J – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Salix – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Vibrant – Consultant.
Samita Garg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Ford, MD1, Jack Loesch, BA2, Arjun Chatterjee, MD3, Sara Valencia, MD4, Keren Zhou, MD5, Anthony Lembo, MD, FACG4, Samita Garg, MD4. P0539 - Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists Reduce All-Cause Mortality and Healthcare Utilization in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Andrew Ford, MD1, Jack Loesch, BA2, Arjun Chatterjee, MD3, Sara Valencia, MD4, Keren Zhou, MD5, Anthony Lembo, MD, FACG4, Samita Garg, MD4
1Case Western Reserve University / MetroHealth, Cleveland, OH; 2Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH; 3Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 4Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 5Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are FDA approved for type 2 diabetes (T2D) and weight loss and are increasingly being used off-label for patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). We evaluated the risks and healthcare utilization among T1D patients receiving these medications up to 2 years.
Methods: We utilized the TriNetX database, a global federated network with data from numerous healthcare organizations. We identified patients with T1D using ICD-10 codes and excluded those with T2D diagnoses and SGLT-2i use. T1D patients were then divided into two cohorts based on whether or not they had received GLP-1RAs. We then performed 1:1 propensity matching for demographics (age, sex, and race), inflammatory bowel disease, BMI and HbA1c. Primary outcomes included ED visits, hospitalizations, DKA, hypoglycemia, prokinetic prescriptions, and all-cause mortality. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained for all outcomes except all-cause mortality, for which Cox regression analysis was performed to obtain hazard ratio (HR) at two years. Index event was defined as meeting inclusion criteria as well as at least six months of continuous GLP-1RA use for the respective cohort based on refill documentation.
Results: After propensity score matching, 4760 patients were identified in each group (Table). The matched cohorts were predominantly White (71.9% in GLP-1RA cohort, 71.8% in non-GLP-1RA cohort) and female (62.0% in both). Patients taking GLP-1RAs had lower ED visits (OR 0.46, 95% CI 0.39-0.55, p< 0.001), all-cause admission (OR 0.24, CI 0.17-0.33, p< .001), DKA (OR 0.58, 95% CI 0.36-0.93, p=0.02), prokinetic use (OR 0.73, CI 0.56-0.95, p=0.02), and all-cause mortality (HR 0.24, CI 0.16-0.34, p=0.005). There was no significant difference between groups for hypoglycemia (p=0.4).
Discussion: Patients with T1D receiving GLP-1RAs had significantly lower ED visits, inpatient admission, DKA, prokinetic prescriptions, and all-cause mortality with no significant effect on hypoglycemia. This data suggests that GLP-1RAs may not only be safe, but also beneficial for patients with T1D, though prospective data are necessary to confirm our conclusions.

Figure: Table 1: Demographics, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of GLP-1RA and Non-GLP1-RA Cohorts After Propensity Score Matching

Figure: Figure 1: Survival Probability Comparison Between GLP1-RA and Non-GLP1-RA Patients With T1D
Disclosures:
Andrew Ford indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jack Loesch: Eli Lilly and Company – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Arjun Chatterjee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sara Valencia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Keren Zhou: Corcept – Consultant. NeuroSolutions 100 – Grant/Research Support. Xeris – Speakers Bureau.
Anthony Lembo: Allurion – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Ardeylx – Consultant. Atmo – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bristol Myer Squibb – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). GSK – Consultant. Ironwood – DSMB. J&J – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Salix – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Vibrant – Consultant.
Samita Garg indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Ford, MD1, Jack Loesch, BA2, Arjun Chatterjee, MD3, Sara Valencia, MD4, Keren Zhou, MD5, Anthony Lembo, MD, FACG4, Samita Garg, MD4. P0539 - Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists Reduce All-Cause Mortality and Healthcare Utilization in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

