Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0615 - Evaluating a Multi-Agent LLM Pipeline With Human-in-the-Loop for Drafting Patient Education Handouts From Eosinophilic Esophagitis Guidelines
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Andrew T. Sturgis, BS
University of Kentucky College of Medicine
Lexington, KY
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Andrew T. Sturgis, BS1, Marijeta Pekez, MD2, Tiffany B. Clark, BSN, RN2, Kimberly K. Bender, APRN2, Monika R. Potter, APP2, Balkeess Alhanaktah, MD3, Joseph E. Auer, MD2, Joel Richter, MD2, Ismail S. Bahaaeldeen, MD2
1University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington, KY; 2University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 3Faculty of Medicine, Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan
Introduction: Printed patient handouts are essential in clinical care but are often delayed following updates to society guidelines. Large language models (LLMs) may help accelerate this process. This study evaluates a multi-step agentic workflow, powered by Gemini 2.0 and guided by a human expert, to extract key information from the 2025 American College of Gastroenterology guidelines for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and generate patient-ready handouts.
Methods: The guidelines were processed using a multi-step agentic pipeline (Figure 1) with four AI agents handling extraction, simplification, and formatting. A board-certified gastroenterologist provided oversight at key points. The simplifying agent optimized content for patient readability based on the SMOG index. Python 3.7 automated the process. Eight handouts drafts were generated without manual editing, then evaluated by seven healthcare professionals—an esophagologist (45 years' experience), two attendings, one intern, two APPs, and one motility nurse. Each completed a 19-item Microsoft Form, rating six domains (1–5 Likert scale), plus overall satisfaction and comments.
Results: A total of 53 evaluations were submitted. As shown in Figure 2, average Likert scores across six categories ranged from 4.4 to 4.9; individual handout averages ranged from 4.5 to 4.8. Overall satisfaction was high: 60% very satisfied, 32% satisfied, and 8% neutral. For clinical readiness: 40% selected “ready now,” while 45% selected needing minor, moderate (13%), or major changes (2%). Average SMOG score was 12.4, exceeding the < 7 target. However, further simplification consistently led to loss of essential clinical content. Reviewers praised layout, tone, and clarity, while suggesting minor improvements in medical precision and depth.
Discussion: Prior LLM studies on handouts exist, but our approach adds unique strengths. Specialized agents reduced hallucinations and improved task fidelity. Restricting inputs to society guidelines minimized outdated content. A human-in-the-loop framework preserved oversight while AI handled the time-intensive drafting process. The model struggled to balance readability and information retention, but reviewers still found the materials clear and appropriate. Future work includes testing patient comprehension, feedback from non–healthcare providers, and adapting the workflow to other diseases. This tool shows strong promise for rapidly drafting high-quality patient materials requiring minimal modification across clinical contexts.
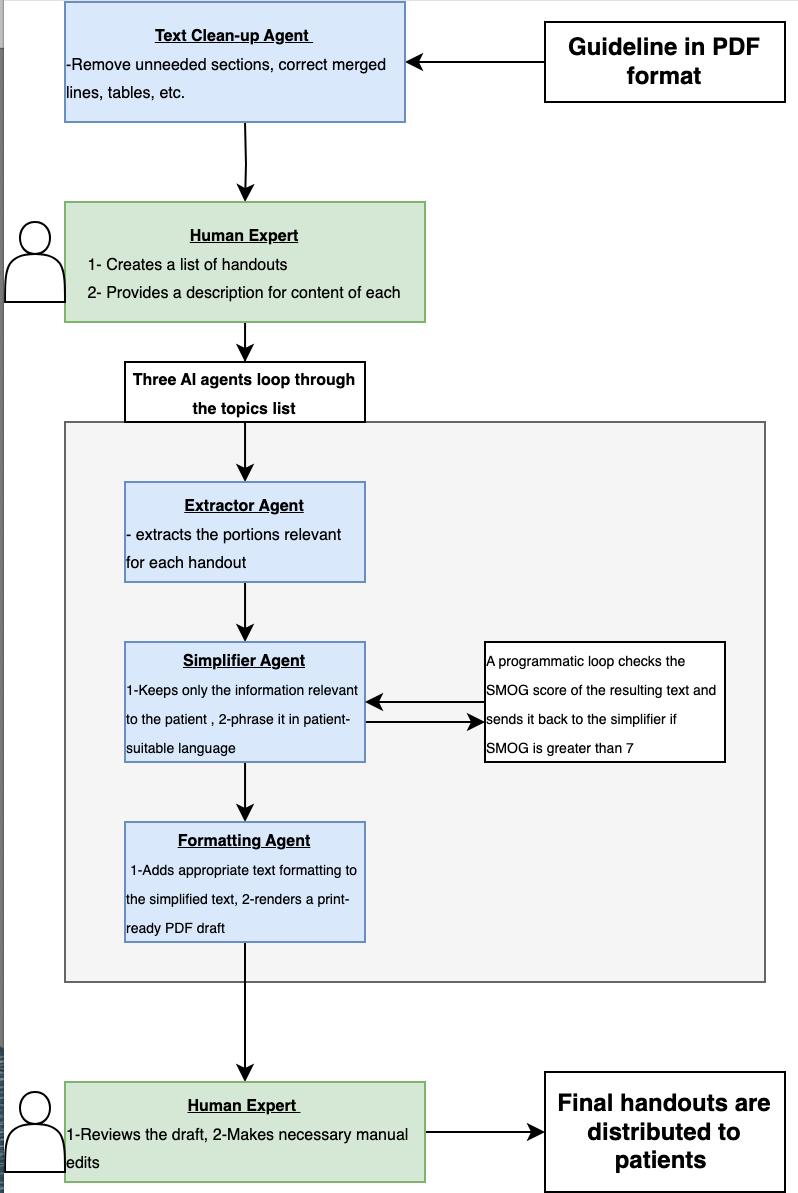
Figure: A diagrammatic representation illustrating the collaborative roles of the human expert and four specialized AI agents, each powered by large language models and equipped with tailored resources and task-specific instructions.
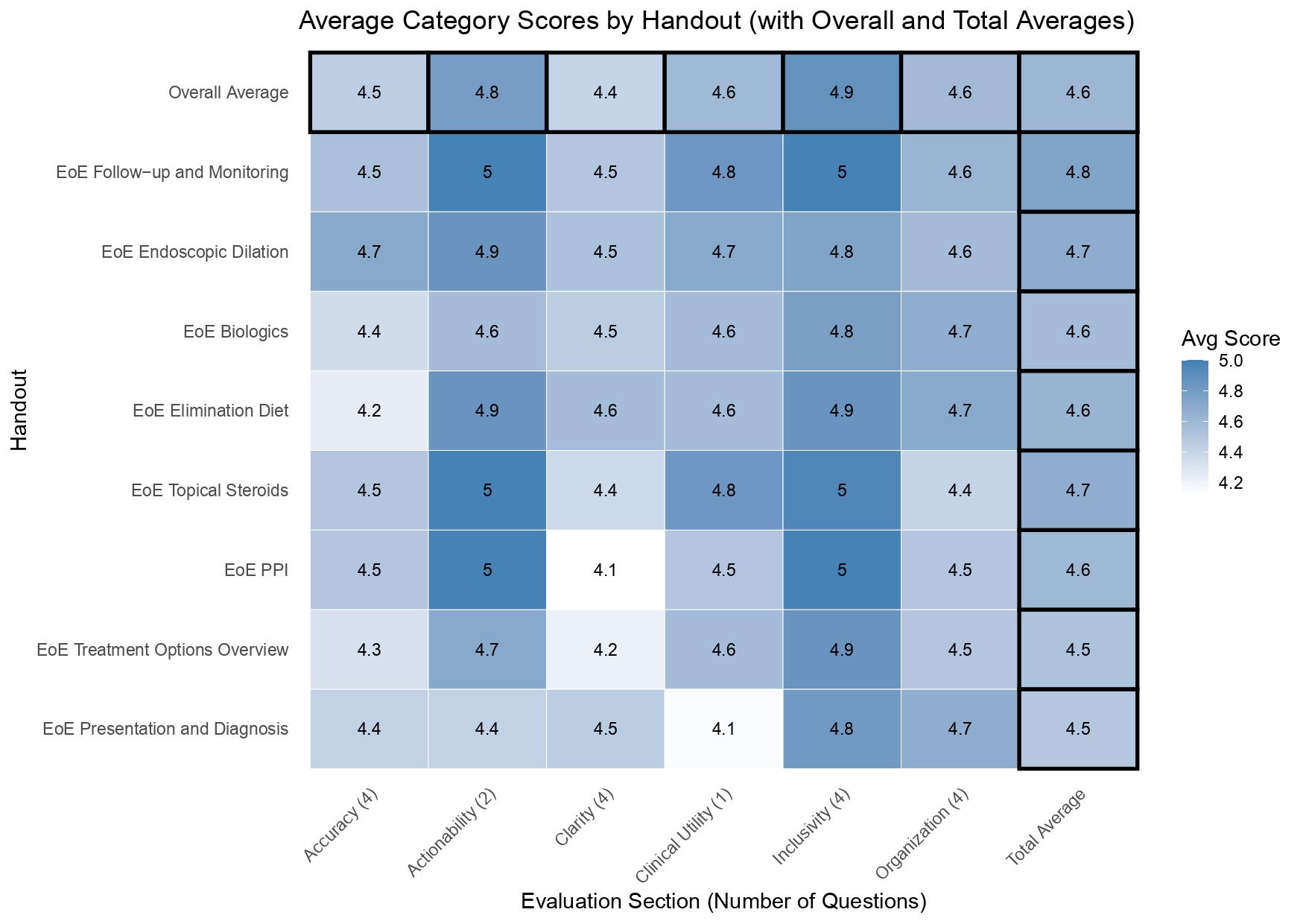
Figure: A heatmap displaying the average Likert scale scores (higher = more favorable) across evaluation categories for each individual handout, including a top summary row representing the overall average.
Disclosures:
Andrew Sturgis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marijeta Pekez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tiffany Clark indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kimberly Bender indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monika Potter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Balkeess Alhanaktah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Auer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joel Richter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ismail Bahaaeldeen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew T. Sturgis, BS1, Marijeta Pekez, MD2, Tiffany B. Clark, BSN, RN2, Kimberly K. Bender, APRN2, Monika R. Potter, APP2, Balkeess Alhanaktah, MD3, Joseph E. Auer, MD2, Joel Richter, MD2, Ismail S. Bahaaeldeen, MD2. P0615 - Evaluating a Multi-Agent LLM Pipeline With Human-in-the-Loop for Drafting Patient Education Handouts From Eosinophilic Esophagitis Guidelines, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Andrew T. Sturgis, BS1, Marijeta Pekez, MD2, Tiffany B. Clark, BSN, RN2, Kimberly K. Bender, APRN2, Monika R. Potter, APP2, Balkeess Alhanaktah, MD3, Joseph E. Auer, MD2, Joel Richter, MD2, Ismail S. Bahaaeldeen, MD2
1University of Kentucky College of Medicine, Lexington, KY; 2University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 3Faculty of Medicine, Hashemite University, Zarqa, Az Zarqa', Jordan
Introduction: Printed patient handouts are essential in clinical care but are often delayed following updates to society guidelines. Large language models (LLMs) may help accelerate this process. This study evaluates a multi-step agentic workflow, powered by Gemini 2.0 and guided by a human expert, to extract key information from the 2025 American College of Gastroenterology guidelines for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and generate patient-ready handouts.
Methods: The guidelines were processed using a multi-step agentic pipeline (Figure 1) with four AI agents handling extraction, simplification, and formatting. A board-certified gastroenterologist provided oversight at key points. The simplifying agent optimized content for patient readability based on the SMOG index. Python 3.7 automated the process. Eight handouts drafts were generated without manual editing, then evaluated by seven healthcare professionals—an esophagologist (45 years' experience), two attendings, one intern, two APPs, and one motility nurse. Each completed a 19-item Microsoft Form, rating six domains (1–5 Likert scale), plus overall satisfaction and comments.
Results: A total of 53 evaluations were submitted. As shown in Figure 2, average Likert scores across six categories ranged from 4.4 to 4.9; individual handout averages ranged from 4.5 to 4.8. Overall satisfaction was high: 60% very satisfied, 32% satisfied, and 8% neutral. For clinical readiness: 40% selected “ready now,” while 45% selected needing minor, moderate (13%), or major changes (2%). Average SMOG score was 12.4, exceeding the < 7 target. However, further simplification consistently led to loss of essential clinical content. Reviewers praised layout, tone, and clarity, while suggesting minor improvements in medical precision and depth.
Discussion: Prior LLM studies on handouts exist, but our approach adds unique strengths. Specialized agents reduced hallucinations and improved task fidelity. Restricting inputs to society guidelines minimized outdated content. A human-in-the-loop framework preserved oversight while AI handled the time-intensive drafting process. The model struggled to balance readability and information retention, but reviewers still found the materials clear and appropriate. Future work includes testing patient comprehension, feedback from non–healthcare providers, and adapting the workflow to other diseases. This tool shows strong promise for rapidly drafting high-quality patient materials requiring minimal modification across clinical contexts.

Figure: A diagrammatic representation illustrating the collaborative roles of the human expert and four specialized AI agents, each powered by large language models and equipped with tailored resources and task-specific instructions.

Figure: A heatmap displaying the average Likert scale scores (higher = more favorable) across evaluation categories for each individual handout, including a top summary row representing the overall average.
Disclosures:
Andrew Sturgis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marijeta Pekez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tiffany Clark indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kimberly Bender indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monika Potter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Balkeess Alhanaktah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Auer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joel Richter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ismail Bahaaeldeen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew T. Sturgis, BS1, Marijeta Pekez, MD2, Tiffany B. Clark, BSN, RN2, Kimberly K. Bender, APRN2, Monika R. Potter, APP2, Balkeess Alhanaktah, MD3, Joseph E. Auer, MD2, Joel Richter, MD2, Ismail S. Bahaaeldeen, MD2. P0615 - Evaluating a Multi-Agent LLM Pipeline With Human-in-the-Loop for Drafting Patient Education Handouts From Eosinophilic Esophagitis Guidelines, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.


