Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0689 - The Tissue Systems Pathology Test (TSP-9) Informs Management of Patients That Are Indefinite for Dysplasia to Predict Missed Prevalent Neoplasia
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- RA
Ronen Arai, MD
Gastro Health
Coral Springs, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Ronen Arai, MD1, Elwood Martin, MD2
1Gastro Health, Coral Springs, FL; 2OhioHealth, Mansfield, OH
Introduction: Histological criteria for grading dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus (BE) can be complicated by inflammation, as reactive atypia is difficult to distinguish from dysplasia in BE. This leads to calls of indefinite for dysplasia (IND), for which guidelines recommend high-dose proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to resolve inflammation and enable a definitive diagnosis at repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) in 3-6 months. These patients remain at an increased risk of neoplastic progression and can benefit from objective risk stratification. The tissue systems pathology test (TissueCypher; TSP-9) detects molecular changes in BE tissue that precede visible histopathological changes. TSP-9 has been clinically validated to predict the 5-year risk of progression to high-grade dysplasia (HGD) or esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). The cases discussed here demonstrate how TSP-9 was used to guide risk-aligned management of two patients with IND.
Case Description/
Methods: Patient A (Table 1) presented with suspected BE, but EGD exam and targeted biopsies were significantly limited by concurrent severe esophagitis. Initial histopathology revealed IND, though TSP-9 yielded a high-risk score of 9.8 (62% probability of progression to HGD/EAC). Per guidelines, PPI therapy was initiated with follow-up EGD after resolution of the esophagitis. Due to the high-risk TSP-9 score, follow-up EGD was performed with enhanced imaging (Narrow Band Imaging, NBI) and intensive surveillance biopsies every 1cm, which revealed HGD, prompting EET.
Upon initial EGD, biopsies from Patient B (Table 1) were classified as IND, and TSP-9 testing was ordered (Figure 1). A high-risk score of 8.4 (34% probability of progression to HGD/EAC) informed a rapid referral for a follow-up EGD (< 2 months) with NBI. C3M5 was noted, and the patient received a confirmed diagnosis of HGD and intramucosal cancer. The TSP-9 results directly influenced the duration of esophageal mapping and an aggressive approach to endoscopic mucosal resection. The patient is now scheduled for a surveillance EGD and further ablation.
Discussion: These cases illustrate the utility of TSP-9 in managing IND cases, as a high-risk score can prompt the use of adjunctive endoscopic tools and ensure high-quality examination and intervention. The test predicted that these patients were at a high risk of progression and informed care that enabled the detection of neoplasia and use of EET to reduce the risk of mortality from EAC.
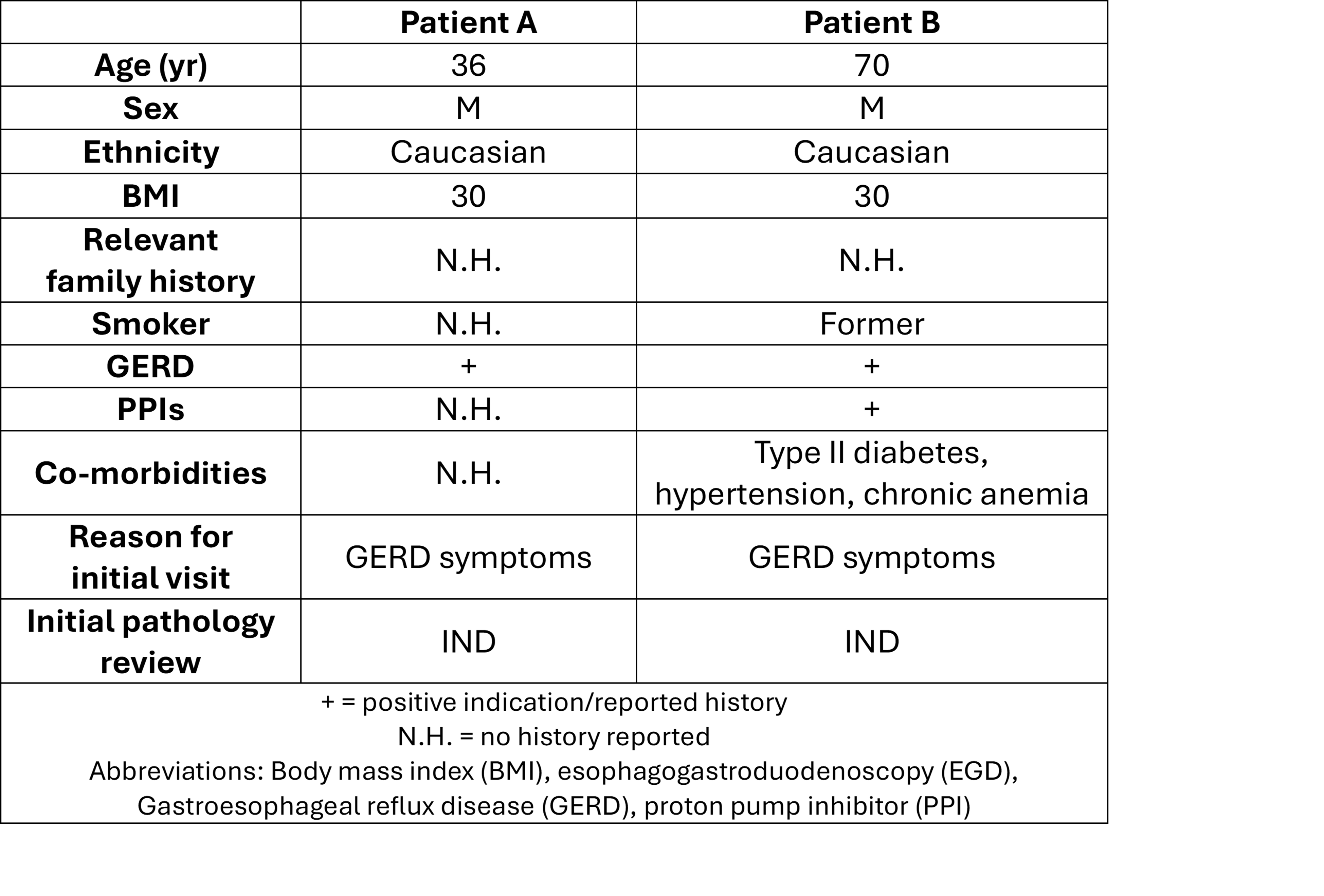
Figure: Table 1. Patient characteristics and clinical risk factor assessment
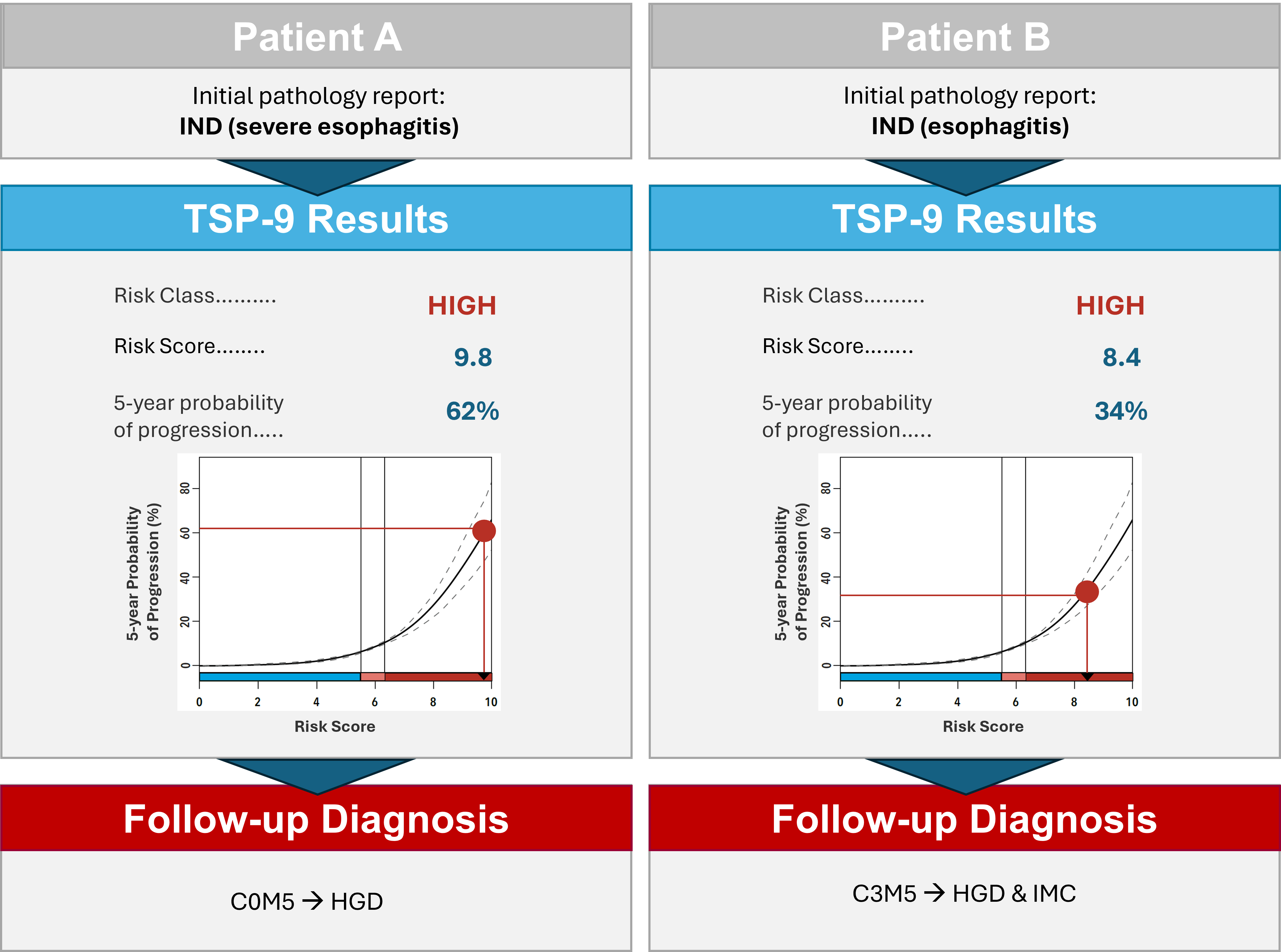
Figure: Figure 1. Initial pathology assessment, TSP-9 test results, and follow-up diagnosis
Disclosures:
Ronen Arai: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. Castle Biosciences – Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly – Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Speakers Bureau. Phathom – Speakers Bureau.
Elwood Martin: Castle Biosciences – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant.
Ronen Arai, MD1, Elwood Martin, MD2. P0689 - The Tissue Systems Pathology Test (TSP-9) Informs Management of Patients That Are Indefinite for Dysplasia to Predict Missed Prevalent Neoplasia, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Gastro Health, Coral Springs, FL; 2OhioHealth, Mansfield, OH
Introduction: Histological criteria for grading dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus (BE) can be complicated by inflammation, as reactive atypia is difficult to distinguish from dysplasia in BE. This leads to calls of indefinite for dysplasia (IND), for which guidelines recommend high-dose proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to resolve inflammation and enable a definitive diagnosis at repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) in 3-6 months. These patients remain at an increased risk of neoplastic progression and can benefit from objective risk stratification. The tissue systems pathology test (TissueCypher; TSP-9) detects molecular changes in BE tissue that precede visible histopathological changes. TSP-9 has been clinically validated to predict the 5-year risk of progression to high-grade dysplasia (HGD) or esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). The cases discussed here demonstrate how TSP-9 was used to guide risk-aligned management of two patients with IND.
Case Description/
Methods: Patient A (Table 1) presented with suspected BE, but EGD exam and targeted biopsies were significantly limited by concurrent severe esophagitis. Initial histopathology revealed IND, though TSP-9 yielded a high-risk score of 9.8 (62% probability of progression to HGD/EAC). Per guidelines, PPI therapy was initiated with follow-up EGD after resolution of the esophagitis. Due to the high-risk TSP-9 score, follow-up EGD was performed with enhanced imaging (Narrow Band Imaging, NBI) and intensive surveillance biopsies every 1cm, which revealed HGD, prompting EET.
Upon initial EGD, biopsies from Patient B (Table 1) were classified as IND, and TSP-9 testing was ordered (Figure 1). A high-risk score of 8.4 (34% probability of progression to HGD/EAC) informed a rapid referral for a follow-up EGD (< 2 months) with NBI. C3M5 was noted, and the patient received a confirmed diagnosis of HGD and intramucosal cancer. The TSP-9 results directly influenced the duration of esophageal mapping and an aggressive approach to endoscopic mucosal resection. The patient is now scheduled for a surveillance EGD and further ablation.
Discussion: These cases illustrate the utility of TSP-9 in managing IND cases, as a high-risk score can prompt the use of adjunctive endoscopic tools and ensure high-quality examination and intervention. The test predicted that these patients were at a high risk of progression and informed care that enabled the detection of neoplasia and use of EET to reduce the risk of mortality from EAC.

Figure: Table 1. Patient characteristics and clinical risk factor assessment

Figure: Figure 1. Initial pathology assessment, TSP-9 test results, and follow-up diagnosis
Disclosures:
Ronen Arai: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. Castle Biosciences – Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly – Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Speakers Bureau. Phathom – Speakers Bureau.
Elwood Martin: Castle Biosciences – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant.
Ronen Arai, MD1, Elwood Martin, MD2. P0689 - The Tissue Systems Pathology Test (TSP-9) Informs Management of Patients That Are Indefinite for Dysplasia to Predict Missed Prevalent Neoplasia, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
