Sunday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P0787 - Reduction in Gastrointestinal Visits and Portal Messaging Following Tenapanor (IBSRELA) Initiation for Community Gastrointestinal Patients
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- AF
Alan Fossa, PhD
Arbor Research Collaborative for Health
Ann Arbor, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Alan Fossa, PhD1, Luisa Scott, PhD2, Asma Khapra, MD3, Lavanya Viswanathan, MD, MS, FACG4, Kyle Staller, MD, MPH5
1Arbor Research Collaborative for Health, Ann Arbor, MI; 2Ardelyx, Inc., Waltham, MA; 3Gastro Health, Fairfax, VA; 4UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 5Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) is a chronic disorder of gut-brain interaction (DGBI) associated with high healthcare resource utilization (HCRU). Tenapanor (TEN [IBSRELA]) is a first-in-class, minimally absorbed inhibitor of intestinal sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 3 approved for the treatment of IBS-C in adults. An electronic health records (EHR) study is ongoing to understand the real-world use and outcomes of IBS-C medications in community gastrointestinal (GI) practices. Here, we report findings for within-patient changes in GI-related HCRU following TEN initiation for the treatment of IBS‑C.
Methods: This observational study used EHR data from patients treated at a large medical group of approximately 350 gastroenterology providers serving over 6 million patients across 7 states. Eligible patients were aged ≥18 years, had a diagnosis of IBS, had ≥1 visit within the 365 days before initiating TEN, and initiated TEN ≥365 days prior to the EHR data pull. The within-patient change in clinical encounters and portal message activity was calculated by comparing utilization in the 365 days before versus after TEN initiation. Within-patient change in HCRU was stratified by tertile of pre-TEN HCRU.
Results: The study included 712 patients, of whom 86% were female, 44% were Medicare eligible, and the average age was 48 years. Overall, the median within-patient change in GI visits after TEN initiation was −1 (quartile [Q]1: −2, Q3: 0) for regular visits and 0 (Q1: −3, Q3: 1) for labs. High utilizers (≥4 pre-TEN clinical encounters) had substantial reductions in regular visits (median change: −3, Q1: −4, Q3: −2) and labs (median change: −4, Q1: −7; Q3: −3) after TEN (Figure). Portal message activity also decreased in high utilizers (≥10 portal messages or ≥606 message words): number of messages (median change: −6, Q1: −19, Q3: 2) and words in messages (median change: −531, Q1: −1059, Q3: 54)) (Figure). Changes in clinical encounters and portal message activity after TEN were limited among low and moderate utilizers (Figure).
Discussion: These preliminary findings indicate that GI-related clinical encounters and patient portal message activity substantially decreased after TEN initiation among patients with high pre-TEN HCRU in each category. This suggests that TEN may reduce burden on the healthcare system and patients by reducing high HCRU, potentially leading to cost savings.
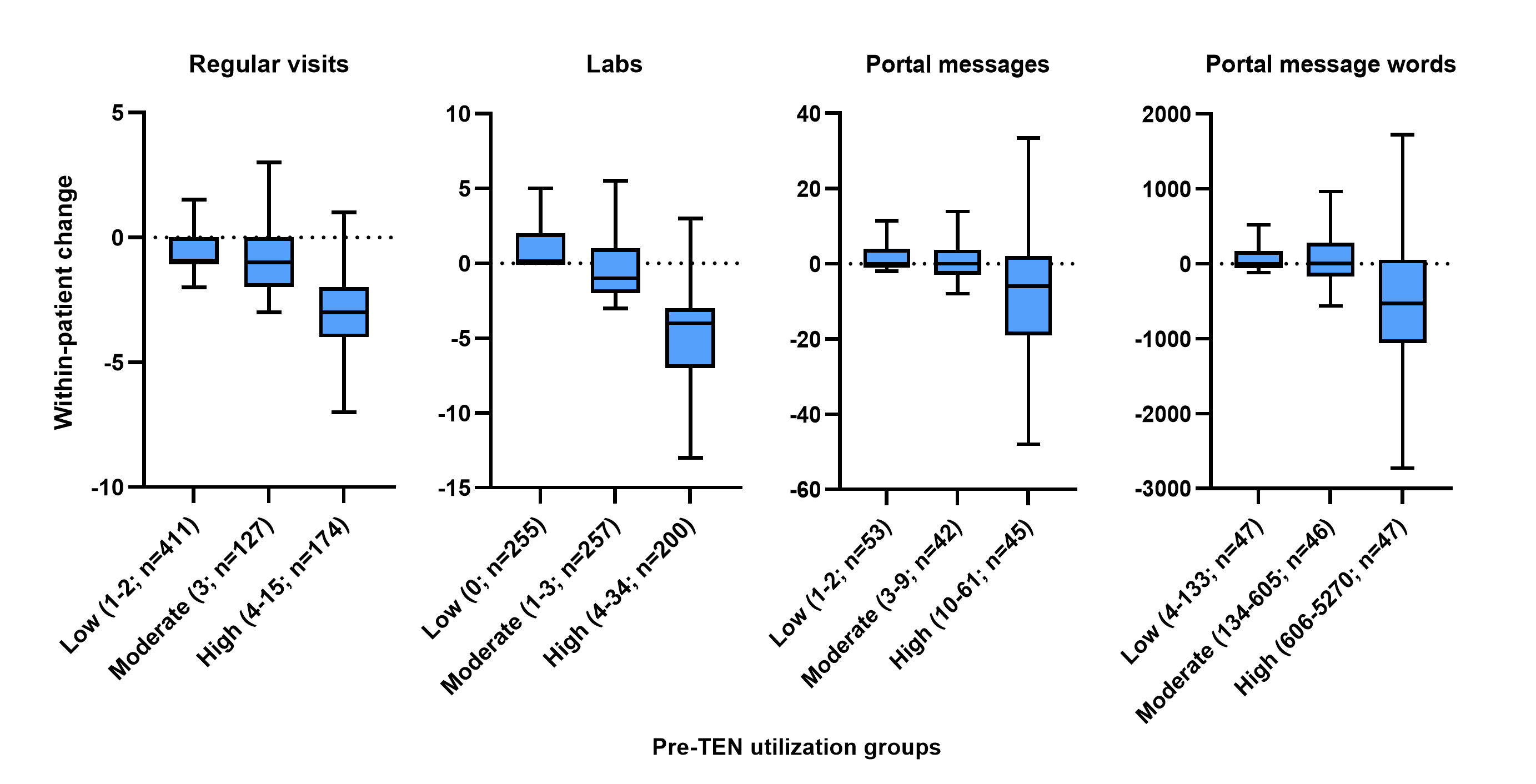
Figure: Figure: Within-Patient Change in HCRU Before and After TEN Initiation by Tertiles of Utilization Over the 365 Days Before TEN
Disclosures:
Alan Fossa: Arbor Research Collaborative for Health – Grant/Research Support.
Luisa Scott: Ardelyx, Inc. – Employee.
Asma Khapra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lavanya Viswanathan: Ardelyx, Inc. – Advisor or Review Panel Member, The above are unpaid., Speakers Bureau.
Kyle Staller: Ardelyx – Grant/Research Support. Gemelli – Consultant. Laborie – Consultant. Mahana – Consultant. Salix – Consultant. Takeda – Expert witness.
Alan Fossa, PhD1, Luisa Scott, PhD2, Asma Khapra, MD3, Lavanya Viswanathan, MD, MS, FACG4, Kyle Staller, MD, MPH5. P0787 - Reduction in Gastrointestinal Visits and Portal Messaging Following Tenapanor (IBSRELA) Initiation for Community Gastrointestinal Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Arbor Research Collaborative for Health, Ann Arbor, MI; 2Ardelyx, Inc., Waltham, MA; 3Gastro Health, Fairfax, VA; 4UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 5Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) is a chronic disorder of gut-brain interaction (DGBI) associated with high healthcare resource utilization (HCRU). Tenapanor (TEN [IBSRELA]) is a first-in-class, minimally absorbed inhibitor of intestinal sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 3 approved for the treatment of IBS-C in adults. An electronic health records (EHR) study is ongoing to understand the real-world use and outcomes of IBS-C medications in community gastrointestinal (GI) practices. Here, we report findings for within-patient changes in GI-related HCRU following TEN initiation for the treatment of IBS‑C.
Methods: This observational study used EHR data from patients treated at a large medical group of approximately 350 gastroenterology providers serving over 6 million patients across 7 states. Eligible patients were aged ≥18 years, had a diagnosis of IBS, had ≥1 visit within the 365 days before initiating TEN, and initiated TEN ≥365 days prior to the EHR data pull. The within-patient change in clinical encounters and portal message activity was calculated by comparing utilization in the 365 days before versus after TEN initiation. Within-patient change in HCRU was stratified by tertile of pre-TEN HCRU.
Results: The study included 712 patients, of whom 86% were female, 44% were Medicare eligible, and the average age was 48 years. Overall, the median within-patient change in GI visits after TEN initiation was −1 (quartile [Q]1: −2, Q3: 0) for regular visits and 0 (Q1: −3, Q3: 1) for labs. High utilizers (≥4 pre-TEN clinical encounters) had substantial reductions in regular visits (median change: −3, Q1: −4, Q3: −2) and labs (median change: −4, Q1: −7; Q3: −3) after TEN (Figure). Portal message activity also decreased in high utilizers (≥10 portal messages or ≥606 message words): number of messages (median change: −6, Q1: −19, Q3: 2) and words in messages (median change: −531, Q1: −1059, Q3: 54)) (Figure). Changes in clinical encounters and portal message activity after TEN were limited among low and moderate utilizers (Figure).
Discussion: These preliminary findings indicate that GI-related clinical encounters and patient portal message activity substantially decreased after TEN initiation among patients with high pre-TEN HCRU in each category. This suggests that TEN may reduce burden on the healthcare system and patients by reducing high HCRU, potentially leading to cost savings.

Figure: Figure: Within-Patient Change in HCRU Before and After TEN Initiation by Tertiles of Utilization Over the 365 Days Before TEN
Disclosures:
Alan Fossa: Arbor Research Collaborative for Health – Grant/Research Support.
Luisa Scott: Ardelyx, Inc. – Employee.
Asma Khapra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lavanya Viswanathan: Ardelyx, Inc. – Advisor or Review Panel Member, The above are unpaid., Speakers Bureau.
Kyle Staller: Ardelyx – Grant/Research Support. Gemelli – Consultant. Laborie – Consultant. Mahana – Consultant. Salix – Consultant. Takeda – Expert witness.
Alan Fossa, PhD1, Luisa Scott, PhD2, Asma Khapra, MD3, Lavanya Viswanathan, MD, MS, FACG4, Kyle Staller, MD, MPH5. P0787 - Reduction in Gastrointestinal Visits and Portal Messaging Following Tenapanor (IBSRELA) Initiation for Community Gastrointestinal Patients, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
