Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P1175 - Adverse Events of JAK Inhibitors in IBD: An FAERS Database Study
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Mary DeMent, DO (she/her/hers)
Advocate Lutheran General
Arlington Heights, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Mary DeMent, DO, Eli Ehrenpreis, MD, FACG
Advocate Lutheran General, Park Ridge, IL
Introduction: Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKI) are small molecule drugs prescribed for myeloproliferative disorders and immune mediated inflammatory diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Tofacitinib is approved for ulcerative colitis (UC); upadacitinib for both UC and Crohn’s Disease (CD). JAKIs have an FDA-issued black box warning for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and thrombosis, which was due to the ORAL Surveillance study demonstrating higher rates of malignancy and MACE in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients prescribed tofacitinib compared to anti-TNF agents. Subsequent studies have not confirmed these findings in IBD patients. This study is the first pharmacovigilance study evaluating the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) for Adverse Drug Events (ADE) related to JAKI specifically in the IBD population.
Methods: A retrospective pharmacovigilance analysis of tofacitinib (for UC) and upadacitinib (for UC and CD) was performed. We evaluated ADEs related to the black box warning for JAKIs. We utilized the FAERS database and Open Vigil 2.1 for data extraction, using MedDRA search terms. Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) was employed for disproportionality analysis to distinguish true ADE signals from normal background noise. All available cases meeting inclusion criteria were included through March 30, 2025.
Results: We found significant signals using ROR in both JAKI in pulmonary embolism (PE): upadacitinib in UC (3.278, 95% CI 2.44-4.41), upadacitinib in CD (3.88, 95% CI 2.67-5.66), tofacitinib in UC (1.74, 95% CI 1.29-2.36). Upadacitinib had significant signals for malignancy in CD (ROR 1.61, 95% CI 1.32-1.96), non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) in UC (ROR 2.196, 95% CI 1.55-3.11), DVT in CD (ROR 3.02, 95% CI 1.60-5.70), and cerebrovascular events in UC (ROR 1.60, 95% CI 1.15-2.21). Tofacitinib was found to have statistically significant reporting in DVT (ROR 1.9; 95% CI 1.295-2.788). There were no statistically significant signals identified for MACE, serious infections, lymphoma, or lung cancer.
Discussion: Our findings suggest statistically significant disproportionality in the reporting of thrombotic events (PE and DVT), cerebrovascular events (which may be related to thrombotic risk) and malignancy (including NMSC). Notably there was no increased signaling for MACE or serious infections, contrary to the black box warning for JAKI. Prospective studies are needed to clarify the risks associated with JAKIs in the IBD population.
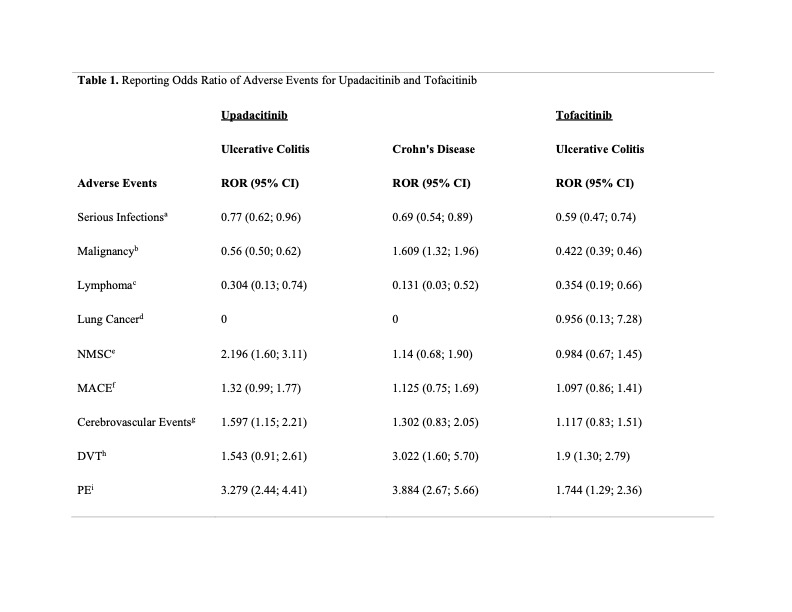
Figure: Abbreviations: ROR, reporting odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
a Serious Infections: Defined using the MedDRA SMQ_Narrow terms as infectious biliary disorders, infective pneumonia, liver infections, ocular infections, opportunistic infections, oropharyngeal infections, or sepsis; data additionally filtered by outcomes including events requiring intervention to prevent impairment or damage, initial or prolonged hospitalization, life threatening events, or death.
b Malignancy: Defined using the MedDRA SMQ_Broad terms as biliary tumours of unspecified malignancy, biliary neoplasms malignant and unspecified, blood premalignant disorders, breast malignant tumours, breast neoplasms malignant and unspecified, breast tumours of unspecified malignancy, gastrointestinal premalignant disorders, haematological malignant tumours, haematological tumours of unspecified malignancy, liver malignant tumours.
c Lymphoma: Defined using the MedDRA SMQ_Narrow term as malignant lymphomas.
d Lung Cancer: Defined using the MedDRA Preferred Terms as adenosquamous cell lung cancer (including recurrent and stages 0, I, II, III, and IV), lung adenocarcinoma (including recurrent and stages 0, I, II, III, and IV), lung cancer metastatic, non-small cell lung cancer (including recurrent and metastatic).
e NMSC (non-melanoma skin cancer): Defined using the MedDRA High Level Term as skin neoplasms malignant and unspecified (excl melanoma).
f MACE (Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events): Defined using MedDRA Preferred Terms as cardiac death, sudden cardiac death, acute myocardial infarction (MI), MI, myocardial ischaemia, silent MI, periprocedural MI, postprocedural MI; and High Level Terms as central nervous system haemorrhages and cerebrovascular accidents, cerebrovascular and spinal necrosis and vascular insufficiency, cerebrovascular embolism and thrombosis, cerebrovascular venous and sinus thrombosis, transient cerebrovascular events.
g Cerebrovascular Events: Defined using the MedDRA High Level Terms as central nervous system haemorrhages and cerebrovascular accidents, cerebrovascular and spinal necrosis and vascular insufficiency, cerebrovascular embolism and thrombosis, cerebrovascular venous and sinus thrombosis, transient cerebrovascular events.
h DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis): Defined using the MedDRA Preferred Terms as deep vein thrombosis.
i PE (Pulmonary Embolism): Defined using the MedDRA Preferred Terms as pulmonary embolism.
Disclosures:
Mary DeMent indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eli Ehrenpreis: E2Bio Consultants – CEO. E2Bio Life Sciences – CEO.
Mary DeMent, DO, Eli Ehrenpreis, MD, FACG. P1175 - Adverse Events of JAK Inhibitors in IBD: An FAERS Database Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Advocate Lutheran General, Park Ridge, IL
Introduction: Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKI) are small molecule drugs prescribed for myeloproliferative disorders and immune mediated inflammatory diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Tofacitinib is approved for ulcerative colitis (UC); upadacitinib for both UC and Crohn’s Disease (CD). JAKIs have an FDA-issued black box warning for serious infections, mortality, malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), and thrombosis, which was due to the ORAL Surveillance study demonstrating higher rates of malignancy and MACE in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients prescribed tofacitinib compared to anti-TNF agents. Subsequent studies have not confirmed these findings in IBD patients. This study is the first pharmacovigilance study evaluating the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) for Adverse Drug Events (ADE) related to JAKI specifically in the IBD population.
Methods: A retrospective pharmacovigilance analysis of tofacitinib (for UC) and upadacitinib (for UC and CD) was performed. We evaluated ADEs related to the black box warning for JAKIs. We utilized the FAERS database and Open Vigil 2.1 for data extraction, using MedDRA search terms. Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) was employed for disproportionality analysis to distinguish true ADE signals from normal background noise. All available cases meeting inclusion criteria were included through March 30, 2025.
Results: We found significant signals using ROR in both JAKI in pulmonary embolism (PE): upadacitinib in UC (3.278, 95% CI 2.44-4.41), upadacitinib in CD (3.88, 95% CI 2.67-5.66), tofacitinib in UC (1.74, 95% CI 1.29-2.36). Upadacitinib had significant signals for malignancy in CD (ROR 1.61, 95% CI 1.32-1.96), non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) in UC (ROR 2.196, 95% CI 1.55-3.11), DVT in CD (ROR 3.02, 95% CI 1.60-5.70), and cerebrovascular events in UC (ROR 1.60, 95% CI 1.15-2.21). Tofacitinib was found to have statistically significant reporting in DVT (ROR 1.9; 95% CI 1.295-2.788). There were no statistically significant signals identified for MACE, serious infections, lymphoma, or lung cancer.
Discussion: Our findings suggest statistically significant disproportionality in the reporting of thrombotic events (PE and DVT), cerebrovascular events (which may be related to thrombotic risk) and malignancy (including NMSC). Notably there was no increased signaling for MACE or serious infections, contrary to the black box warning for JAKI. Prospective studies are needed to clarify the risks associated with JAKIs in the IBD population.

Figure: Abbreviations: ROR, reporting odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
a Serious Infections: Defined using the MedDRA SMQ_Narrow terms as infectious biliary disorders, infective pneumonia, liver infections, ocular infections, opportunistic infections, oropharyngeal infections, or sepsis; data additionally filtered by outcomes including events requiring intervention to prevent impairment or damage, initial or prolonged hospitalization, life threatening events, or death.
b Malignancy: Defined using the MedDRA SMQ_Broad terms as biliary tumours of unspecified malignancy, biliary neoplasms malignant and unspecified, blood premalignant disorders, breast malignant tumours, breast neoplasms malignant and unspecified, breast tumours of unspecified malignancy, gastrointestinal premalignant disorders, haematological malignant tumours, haematological tumours of unspecified malignancy, liver malignant tumours.
c Lymphoma: Defined using the MedDRA SMQ_Narrow term as malignant lymphomas.
d Lung Cancer: Defined using the MedDRA Preferred Terms as adenosquamous cell lung cancer (including recurrent and stages 0, I, II, III, and IV), lung adenocarcinoma (including recurrent and stages 0, I, II, III, and IV), lung cancer metastatic, non-small cell lung cancer (including recurrent and metastatic).
e NMSC (non-melanoma skin cancer): Defined using the MedDRA High Level Term as skin neoplasms malignant and unspecified (excl melanoma).
f MACE (Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events): Defined using MedDRA Preferred Terms as cardiac death, sudden cardiac death, acute myocardial infarction (MI), MI, myocardial ischaemia, silent MI, periprocedural MI, postprocedural MI; and High Level Terms as central nervous system haemorrhages and cerebrovascular accidents, cerebrovascular and spinal necrosis and vascular insufficiency, cerebrovascular embolism and thrombosis, cerebrovascular venous and sinus thrombosis, transient cerebrovascular events.
g Cerebrovascular Events: Defined using the MedDRA High Level Terms as central nervous system haemorrhages and cerebrovascular accidents, cerebrovascular and spinal necrosis and vascular insufficiency, cerebrovascular embolism and thrombosis, cerebrovascular venous and sinus thrombosis, transient cerebrovascular events.
h DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis): Defined using the MedDRA Preferred Terms as deep vein thrombosis.
i PE (Pulmonary Embolism): Defined using the MedDRA Preferred Terms as pulmonary embolism.
Disclosures:
Mary DeMent indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eli Ehrenpreis: E2Bio Consultants – CEO. E2Bio Life Sciences – CEO.
Mary DeMent, DO, Eli Ehrenpreis, MD, FACG. P1175 - Adverse Events of JAK Inhibitors in IBD: An FAERS Database Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
