Sunday Poster Session
Category: Infections and Microbiome
P1315 - Cryptogenic Liver Abscess in a Colon Cancer Patient Presenting with Persistent Fever: A Diagnostic Challenge
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
.jpg)
Deepak Kumar, MBBS, MD (he/him/his)
Northwell Health
Port Jefferson, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Deepak Kumar, MBBS, MD1, Sunny Kumar, MD2, Fnu Aakash, MD3, Aasta Kumari, MD4, Osama Abdur Rehman, MD3, Anila Mahesh, MD5, Jaspreet Singh, MD6, Kishore Kumar, MD7
1Northwell Health, Port Jefferson, NY; 2Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, PA; 3Florida State University, Cape Coral, FL; 4North Central Bronx Hospital, New York, NY; 5Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Duryea, PA; 6Northwell Health, Bay Shore, NY; 7Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Scranton, PA
Introduction: Pyogenic liver abscess is an uncommon but life-threatening condition that can present with fever, abdominal pain, and systemic inflammation. In patients with a history of gastrointestinal malignancy, hepatic lesions often raise suspicion for metastasis. Differentiating between malignant and infectious etiologies is critical for management. We present a diagnostically challenging case of liver abscess in a patient with prior colon cancer and recurrent fevers.
Case Description/
Methods: A 47-year-old woman with a history of stage III colon adenocarcinoma status post hemicolectomy (completed chemotherapy in 2022), hypertension, diabetes, iron deficiency anemia, and possible autoimmune disease presented with fever and myalgias. She had multiple prior admissions over the preceding three months for fever of unknown origin (FUO), with extensive negative infectious and oncologic evaluations. Work-up included a gallium scan (no abnormal uptake), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) abdomen (2.9 cm hepatic lesion), and ultrasound-guided aspiration of a right hepatic dome lesion yielding bloody fluid negative for malignancy and culture. Blood cultures and Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE) were also unremarkable.
She re-presented with fever to 104°F, chills, and worsening fatigue. Labs revealed leukocytosis (15K), thrombocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers and transaminitis. Computed Tomography (CT) abdomen showed interval increase in the hepatic lesion to 6.6 cm with adjacent peripancreatic stranding, raising suspicion for liver abscess or malignancy. Despite multiple antibiotics and aspirations in prior admissions, the lesion persisted. Given her current SIRS criteria and the CT findings, she was admitted and started empirically on broad-spectrum antibiotics for presumed liver abscess. She remained hemodynamically stable without abdominal tenderness.
Discussion: Liver abscess in patients with a history of gastrointestinal malignancy can be easily mistaken for metastatic disease. This case illustrates the importance of maintaining a broad differential in patients with persistent fever and hepatic lesions. Sterile or culture-negative abscesses may occur in immunocompromised or partially treated patients. Repeated imaging, aspiration, and a multidisciplinary approach including infectious disease, hepatology, and interventional radiology are crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
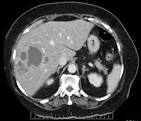
Figure: Computed Tomography (CT) abdomen showed interval increase in the hepatic lesion to 6.6 cm with adjacent peripancreatic stranding, raising suspicion for liver abscess or malignancy.
Disclosures:
Deepak Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sunny Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Aakash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aasta Kumari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Abdur Rehman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anila Mahesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jaspreet Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kishore Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deepak Kumar, MBBS, MD1, Sunny Kumar, MD2, Fnu Aakash, MD3, Aasta Kumari, MD4, Osama Abdur Rehman, MD3, Anila Mahesh, MD5, Jaspreet Singh, MD6, Kishore Kumar, MD7. P1315 - Cryptogenic Liver Abscess in a Colon Cancer Patient Presenting with Persistent Fever: A Diagnostic Challenge, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Northwell Health, Port Jefferson, NY; 2Wright Center for Graduate Medical Education, Scranton, PA; 3Florida State University, Cape Coral, FL; 4North Central Bronx Hospital, New York, NY; 5Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Duryea, PA; 6Northwell Health, Bay Shore, NY; 7Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Scranton, PA
Introduction: Pyogenic liver abscess is an uncommon but life-threatening condition that can present with fever, abdominal pain, and systemic inflammation. In patients with a history of gastrointestinal malignancy, hepatic lesions often raise suspicion for metastasis. Differentiating between malignant and infectious etiologies is critical for management. We present a diagnostically challenging case of liver abscess in a patient with prior colon cancer and recurrent fevers.
Case Description/
Methods: A 47-year-old woman with a history of stage III colon adenocarcinoma status post hemicolectomy (completed chemotherapy in 2022), hypertension, diabetes, iron deficiency anemia, and possible autoimmune disease presented with fever and myalgias. She had multiple prior admissions over the preceding three months for fever of unknown origin (FUO), with extensive negative infectious and oncologic evaluations. Work-up included a gallium scan (no abnormal uptake), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) abdomen (2.9 cm hepatic lesion), and ultrasound-guided aspiration of a right hepatic dome lesion yielding bloody fluid negative for malignancy and culture. Blood cultures and Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE) were also unremarkable.
She re-presented with fever to 104°F, chills, and worsening fatigue. Labs revealed leukocytosis (15K), thrombocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers and transaminitis. Computed Tomography (CT) abdomen showed interval increase in the hepatic lesion to 6.6 cm with adjacent peripancreatic stranding, raising suspicion for liver abscess or malignancy. Despite multiple antibiotics and aspirations in prior admissions, the lesion persisted. Given her current SIRS criteria and the CT findings, she was admitted and started empirically on broad-spectrum antibiotics for presumed liver abscess. She remained hemodynamically stable without abdominal tenderness.
Discussion: Liver abscess in patients with a history of gastrointestinal malignancy can be easily mistaken for metastatic disease. This case illustrates the importance of maintaining a broad differential in patients with persistent fever and hepatic lesions. Sterile or culture-negative abscesses may occur in immunocompromised or partially treated patients. Repeated imaging, aspiration, and a multidisciplinary approach including infectious disease, hepatology, and interventional radiology are crucial for diagnosis and treatment.

Figure: Computed Tomography (CT) abdomen showed interval increase in the hepatic lesion to 6.6 cm with adjacent peripancreatic stranding, raising suspicion for liver abscess or malignancy.
Disclosures:
Deepak Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sunny Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Aakash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aasta Kumari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Abdur Rehman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anila Mahesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jaspreet Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kishore Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deepak Kumar, MBBS, MD1, Sunny Kumar, MD2, Fnu Aakash, MD3, Aasta Kumari, MD4, Osama Abdur Rehman, MD3, Anila Mahesh, MD5, Jaspreet Singh, MD6, Kishore Kumar, MD7. P1315 - Cryptogenic Liver Abscess in a Colon Cancer Patient Presenting with Persistent Fever: A Diagnostic Challenge, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
