Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1396 - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Is Cost-Effective for Treatment of Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction After Failed ERCP
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Noppachai Siranart, MD
Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Noppachai Siranart, MD1, Patavee Pajareya, MD2, Steven Steinway, MD3
1Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Bangkok, Krung Thep, Thailand; 3Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)- guided biliary drainage is a promising alternative after failed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in malignant distal biliary obstruction (MDBO). However, the cost-effective of this intervention compared to percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD) is not well understood. This study evaluates the cost-effectiveness of EUS-guided gallbladder drainage (EUS-GB) and EUS-guided cholecdochoduodenostomy (EUS-CBD) compared to PTBD in patients with MDBO.
Methods: A transition state Markov model was created to compare the cost-effectiveness of EUS-GB, EUS-CBD, and PTBD in a hypothetical cohort of 10,000 patients aged 65 years diagnosed with MBDO and failed ERCP. Our model set willingness-to-pay (WTP) at $100,000 per quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained and a time horizon of 2 years. A base-case analysis was utilized to evaluate the net monetary benefits (NMB) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) and to analyze the cost-effectiveness of each procedure. Deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were performed to identify the acceptability of each intervention across different WTPs and to show the influence of each model parameter on ICER and NMB after adjusting values across the plausible ranges.
Results: Both EUS-GB and EUS-CBD were cost-effective compared to PTBD. PTBD cost $14,309, EUS-GB cost $14,256 (adding 0.37 QALYS and $37,219 NMB), and EUS-CBD cost $17,305 (adding 0.55 QALYs and $52,008 NMB). Although EUS-GB showed a lower reintervention rate (43% vs 80%) with a lower cost ($11,487 vs $14,916), EUS-GB showed a lower health utility (2.04 QALYs vs 2.25 QALYs) at 24 months compared to EUS-CBD. Although PTBD had the lowest cost, it was dominated due to fewer QALYs. These findings were robust in sensitivity analyses.
Discussion: EUS-GB and EUS-CBD are more cost-effective than PTBD for MDBO after failed ERCP. EUS-GB offers similar value to EUS-CBD, potentially with lower reintervention rates. From a cost-effectiveness perspective, endoscopic management should be prioritized over PTBD for patients with MDBO who fail conventional ERCP.
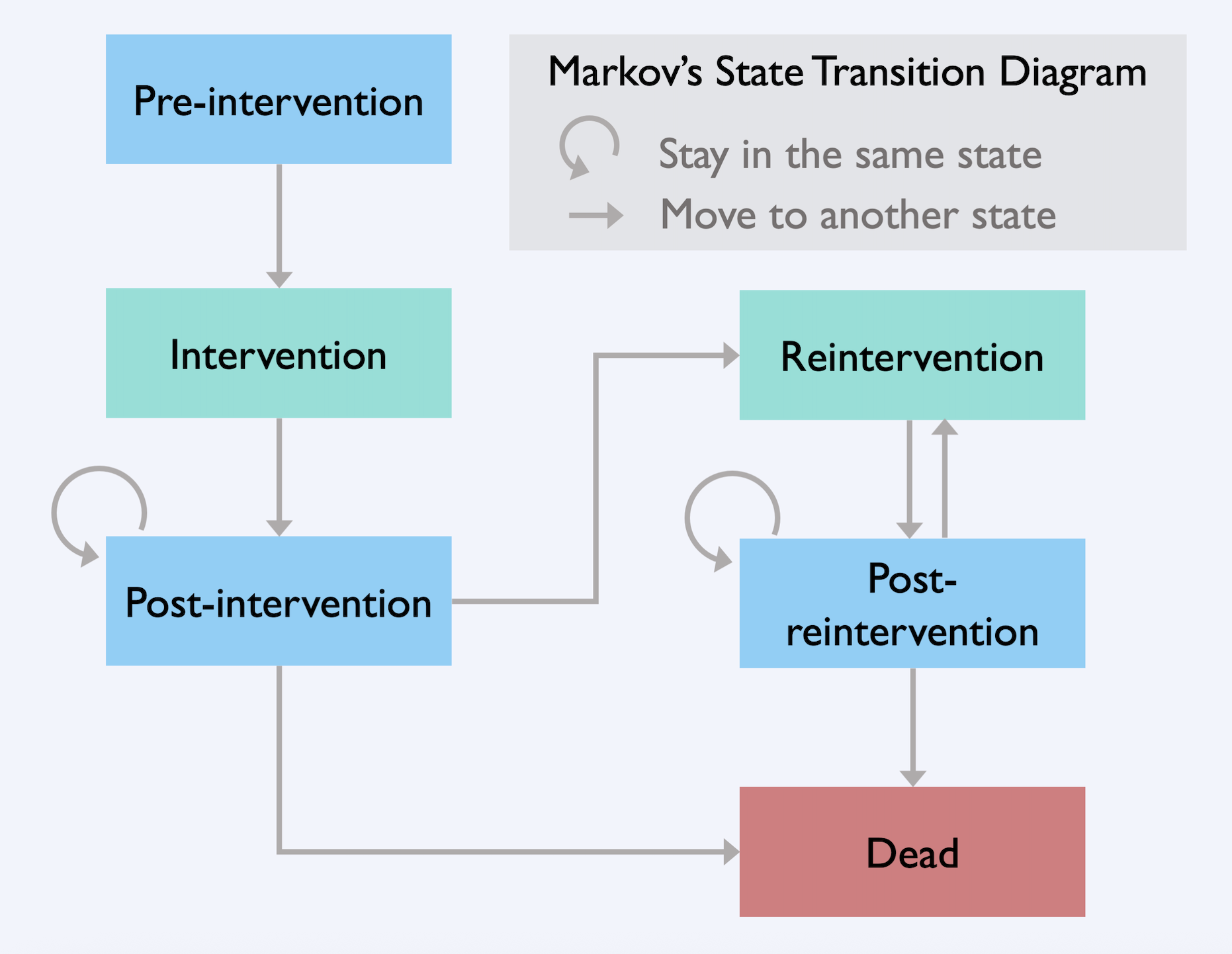
Figure: Figure 1

Figure: Figure 2
Disclosures:
Noppachai Siranart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patavee Pajareya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steven Steinway indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noppachai Siranart, MD1, Patavee Pajareya, MD2, Steven Steinway, MD3. P1396 - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Is Cost-Effective for Treatment of Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction After Failed ERCP, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 2King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Bangkok, Krung Thep, Thailand; 3Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)- guided biliary drainage is a promising alternative after failed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in malignant distal biliary obstruction (MDBO). However, the cost-effective of this intervention compared to percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD) is not well understood. This study evaluates the cost-effectiveness of EUS-guided gallbladder drainage (EUS-GB) and EUS-guided cholecdochoduodenostomy (EUS-CBD) compared to PTBD in patients with MDBO.
Methods: A transition state Markov model was created to compare the cost-effectiveness of EUS-GB, EUS-CBD, and PTBD in a hypothetical cohort of 10,000 patients aged 65 years diagnosed with MBDO and failed ERCP. Our model set willingness-to-pay (WTP) at $100,000 per quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained and a time horizon of 2 years. A base-case analysis was utilized to evaluate the net monetary benefits (NMB) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) and to analyze the cost-effectiveness of each procedure. Deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were performed to identify the acceptability of each intervention across different WTPs and to show the influence of each model parameter on ICER and NMB after adjusting values across the plausible ranges.
Results: Both EUS-GB and EUS-CBD were cost-effective compared to PTBD. PTBD cost $14,309, EUS-GB cost $14,256 (adding 0.37 QALYS and $37,219 NMB), and EUS-CBD cost $17,305 (adding 0.55 QALYs and $52,008 NMB). Although EUS-GB showed a lower reintervention rate (43% vs 80%) with a lower cost ($11,487 vs $14,916), EUS-GB showed a lower health utility (2.04 QALYs vs 2.25 QALYs) at 24 months compared to EUS-CBD. Although PTBD had the lowest cost, it was dominated due to fewer QALYs. These findings were robust in sensitivity analyses.
Discussion: EUS-GB and EUS-CBD are more cost-effective than PTBD for MDBO after failed ERCP. EUS-GB offers similar value to EUS-CBD, potentially with lower reintervention rates. From a cost-effectiveness perspective, endoscopic management should be prioritized over PTBD for patients with MDBO who fail conventional ERCP.

Figure: Figure 1

Figure: Figure 2
Disclosures:
Noppachai Siranart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patavee Pajareya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Steven Steinway indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noppachai Siranart, MD1, Patavee Pajareya, MD2, Steven Steinway, MD3. P1396 - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biliary Drainage Is Cost-Effective for Treatment of Malignant Distal Biliary Obstruction After Failed ERCP, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
