Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1384 - Impact of Multidisciplinary Follow-Up on Weight Loss Outcome After Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty: A Retrospective Analysis
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- SR
Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO
Methodist Dallas Medical Center
Orlando, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO, Prashant Kedia, MD
Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX
Introduction: Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) induces weight loss by reducing gastric volume through endoscopically placed sutures. Studies suggest that patients that undergo ESG procedure who adhere to a multidisciplinary bariatric follow-up program have greater weight loss outcomes compared to those who do not. This retrospective analysis compares outcomes between patients who adhere to a follow-up regimen versus those who do not.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of ESG patients was conducted between May 2018 and May 2023. The percent total weight loss (%TWL) was evaluated at 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, and 24 months between the follow up (FU) and non-follow up (NFU) groups. Patients who adhered to the follow-up protocol had visits with their physician at 2 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months post-procedure. They also followed up with a dietician 8 times within the year post-procedure, at which time information regarding patient weight, symptoms from the procedure, and dietary/exercise habits were documented. Follow up patients received dietary and exercise counseling and were assessed for the need to revise the procedure at each visit. Statistical analysis was conducted using comparative t-test analysis.
Results: 47 patients were included, 31 in the FU arm and 16 in the NFU arm. Mean baseline weights in the FU and NFU arms were 213.3 lbs and 210.7 lbs respectively (p=0.7887). There was a statistically significant difference in %TWL at 6 (15.1% vs 8.7%, p=0.0003) and 12 months (15.6% vs 3.4%, p=0.001) between FU and NFU cohorts but not at 18 (8.3% vs 9.1%, p=0.8128) and 24 months (8.2% vs 9.7%, p=0.7331). These results are summarized in table 1.
Discussion: Our study shows that adherence to a multidisciplinary bariatric follow-up protocol following ESG significantly enhances short-term weight loss outcomes, especially 6 and 12 months. This suggests that the adherence to a post-procedure behavioral modification program is paramount to optimizing outcomes after ESG and meeting internationally published standards. The lack of significant difference at 18 and 24 months is likely due to the fact that our follow-up protocol was for one year post-procedure. Our findings highlight the importance of multidisciplinary follow-up in optimizing weight loss outcomes after ESG. Further prospective studies are needed to validate our findings.
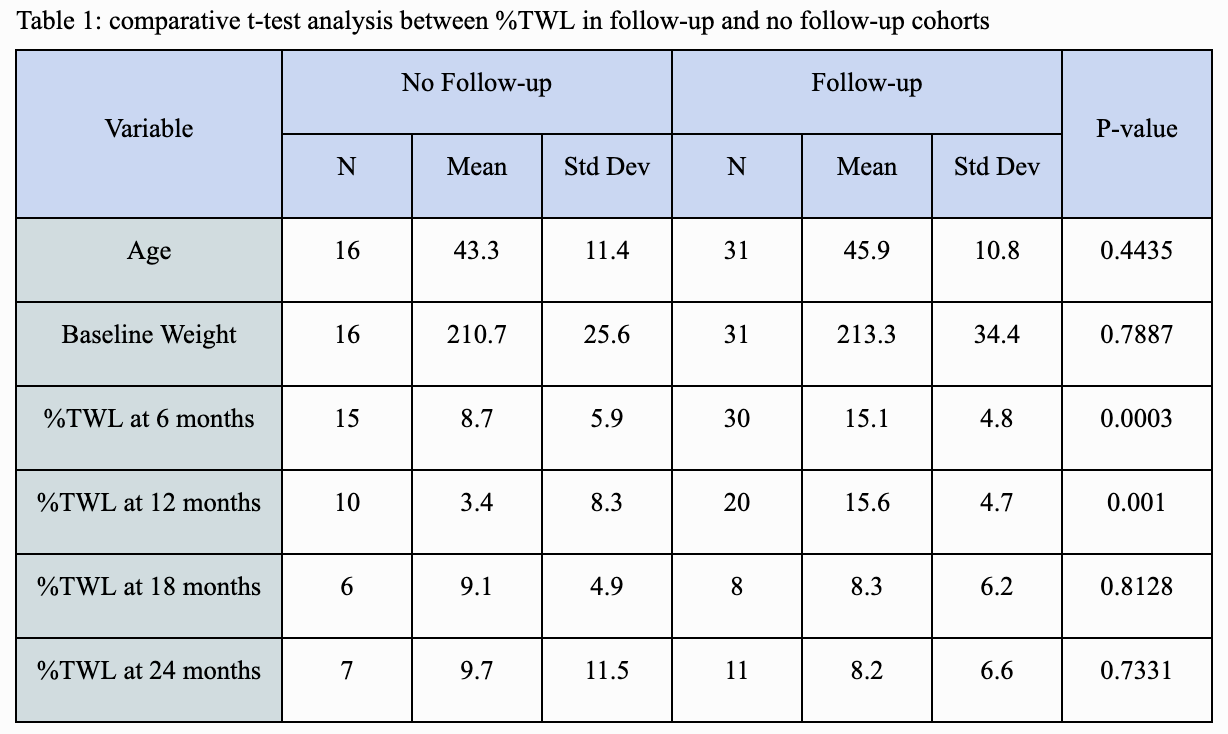
Figure: Table 1: comparative t-test analysis between %TWL in follow-up and no follow-up cohorts
Disclosures:
Syed Hamaad Rahman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prashant Kedia: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO, Prashant Kedia, MD. P1384 - Impact of Multidisciplinary Follow-Up on Weight Loss Outcome After Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty: A Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX
Introduction: Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) induces weight loss by reducing gastric volume through endoscopically placed sutures. Studies suggest that patients that undergo ESG procedure who adhere to a multidisciplinary bariatric follow-up program have greater weight loss outcomes compared to those who do not. This retrospective analysis compares outcomes between patients who adhere to a follow-up regimen versus those who do not.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of ESG patients was conducted between May 2018 and May 2023. The percent total weight loss (%TWL) was evaluated at 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, and 24 months between the follow up (FU) and non-follow up (NFU) groups. Patients who adhered to the follow-up protocol had visits with their physician at 2 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months post-procedure. They also followed up with a dietician 8 times within the year post-procedure, at which time information regarding patient weight, symptoms from the procedure, and dietary/exercise habits were documented. Follow up patients received dietary and exercise counseling and were assessed for the need to revise the procedure at each visit. Statistical analysis was conducted using comparative t-test analysis.
Results: 47 patients were included, 31 in the FU arm and 16 in the NFU arm. Mean baseline weights in the FU and NFU arms were 213.3 lbs and 210.7 lbs respectively (p=0.7887). There was a statistically significant difference in %TWL at 6 (15.1% vs 8.7%, p=0.0003) and 12 months (15.6% vs 3.4%, p=0.001) between FU and NFU cohorts but not at 18 (8.3% vs 9.1%, p=0.8128) and 24 months (8.2% vs 9.7%, p=0.7331). These results are summarized in table 1.
Discussion: Our study shows that adherence to a multidisciplinary bariatric follow-up protocol following ESG significantly enhances short-term weight loss outcomes, especially 6 and 12 months. This suggests that the adherence to a post-procedure behavioral modification program is paramount to optimizing outcomes after ESG and meeting internationally published standards. The lack of significant difference at 18 and 24 months is likely due to the fact that our follow-up protocol was for one year post-procedure. Our findings highlight the importance of multidisciplinary follow-up in optimizing weight loss outcomes after ESG. Further prospective studies are needed to validate our findings.

Figure: Table 1: comparative t-test analysis between %TWL in follow-up and no follow-up cohorts
Disclosures:
Syed Hamaad Rahman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prashant Kedia: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant.
Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO, Prashant Kedia, MD. P1384 - Impact of Multidisciplinary Follow-Up on Weight Loss Outcome After Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty: A Retrospective Analysis, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
