Sunday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P2015 - From Indolent to Obstructive: A Rare Gastrointestinal Manifestation of Follicular Lymphoma
Sunday, October 26, 2025
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Charitha Karanam Ramapathy, MD (she/her/hers)
UAB Montgomery
Montgomery, AL
Presenting Author(s)
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy, MD1, Jeevin Singh Sandhu, DO2, Marquise Soto, MD3, Mohamad Imam, MD1
1UAB Montgomery, Montgomery, AL; 2Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 3Massachusetts General Hospital, Chelsea, MA
Introduction: Follicular lymphoma(FL) is the second most prevalent subtype of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, accounting for around 20% of all cases. It is classified as an indolent, slow-growing form of lymphoma. Most patients initially present with painless peripheral lymphadenopathy, commonly in the cervical, axillary, or inguinal regions and B symptoms. Primary extra nodal involvement by follicular lymphoma remains rare. In particular, gastrointestinal involvement with small bowel obstruction (SBO) as the first clinical manifestation of follicular lymphoma is considered exceptionally rare.
Case Description/
Methods: A 61-year-old female came to the emergency department with complaints of diffuse abdominal pain and nausea for 2 days. She denies vomiting, hematochezia, loose stools, fever, unintentional weight loss and history of abdominal surgery. She never had a colonoscopy. On physical examination, the abdomen was soft, mild diffuse tenderness with no guarding or rigidity. CT abdomen & pelvis showed enhancing mass causing partial obstruction of the distal small bowel and multiple abnormally enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes (Figure 1 & 2). Patient was started on intravenous fluids and kept NPO [nil per oral] with nasogastric tube connected to suction and as needed analgesia. Underwent exploratory laparotomy which showed obstructing circumferential mass in the distal ileum and another circumferential partially obstructing mass in the jejunum and proximal ileum requiring resection of jejunum totaling 10cm, proximal ileum totaling 15 cm, distal ileum totaling 45 cm. Pathology showed grade 3A follicular lymphoma with lymphomatous infiltration present at the small intestine resection margins. Patients diet was slowly advanced post operatively and was discharged with oncology outpatient follow up.
Discussion: SBO is usually caused by post-surgical adhesions, complicated hernia, IBD and neoplasm. When symptoms and imaging findings indicate a potential malignancy, surgical removal followed by histological examination is essential. Cases can also be diagnosed using double balloon enteroscopy (DBE), spiral enteroscopy (SE) and video capsule endoscopy (VCE). Management of FL is determined by the stage, grade and disease burden whereas the relapses are common. Radiotherapy and chemo immunotherapy are the preferred treatment modalities. Follicular lymphoma of the small bowel should be included in the differential diagnosis of small bowel obstruction, particularly in patients without a history of prior abdominal surgery.
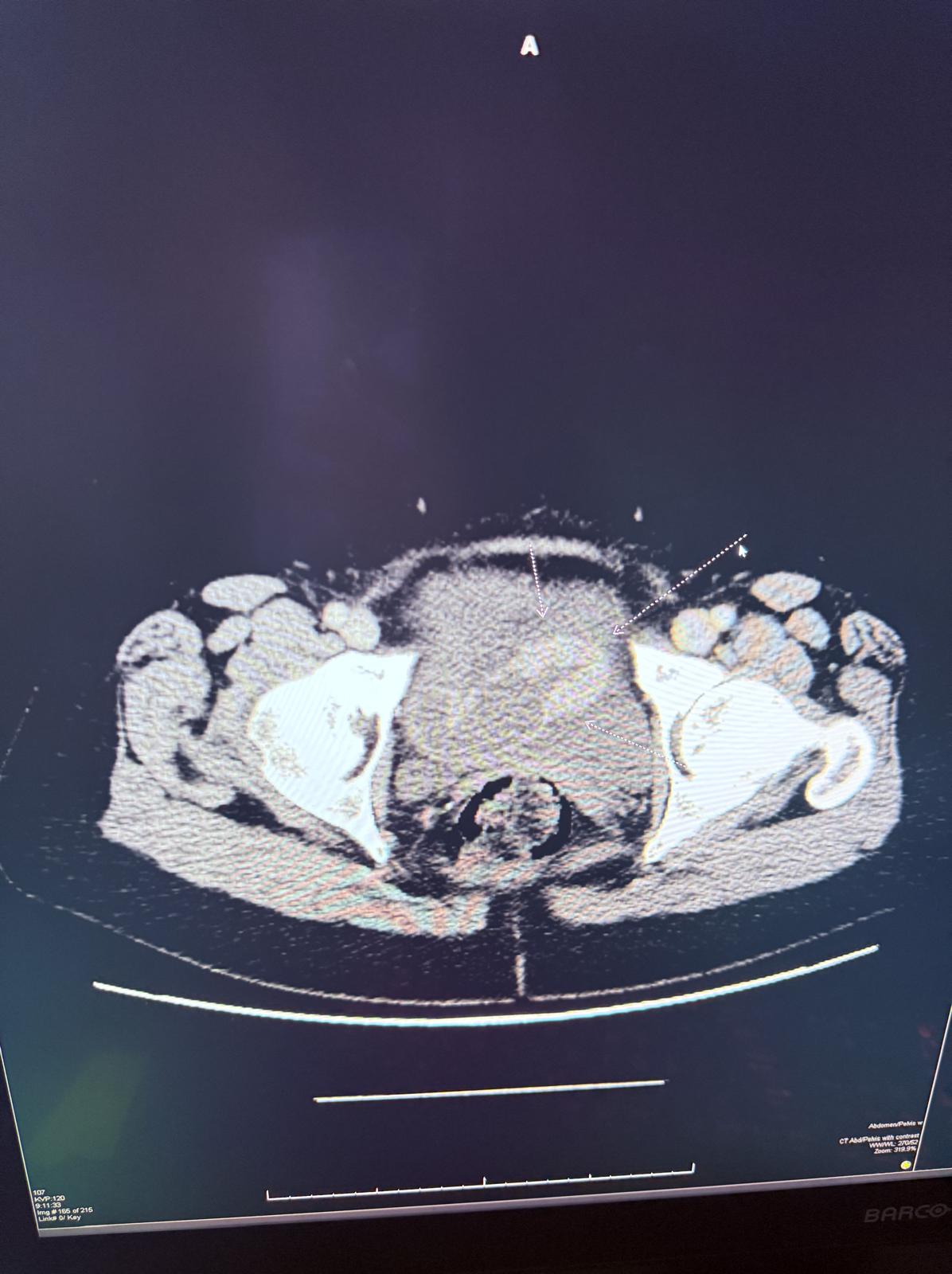
Figure: Figure 1
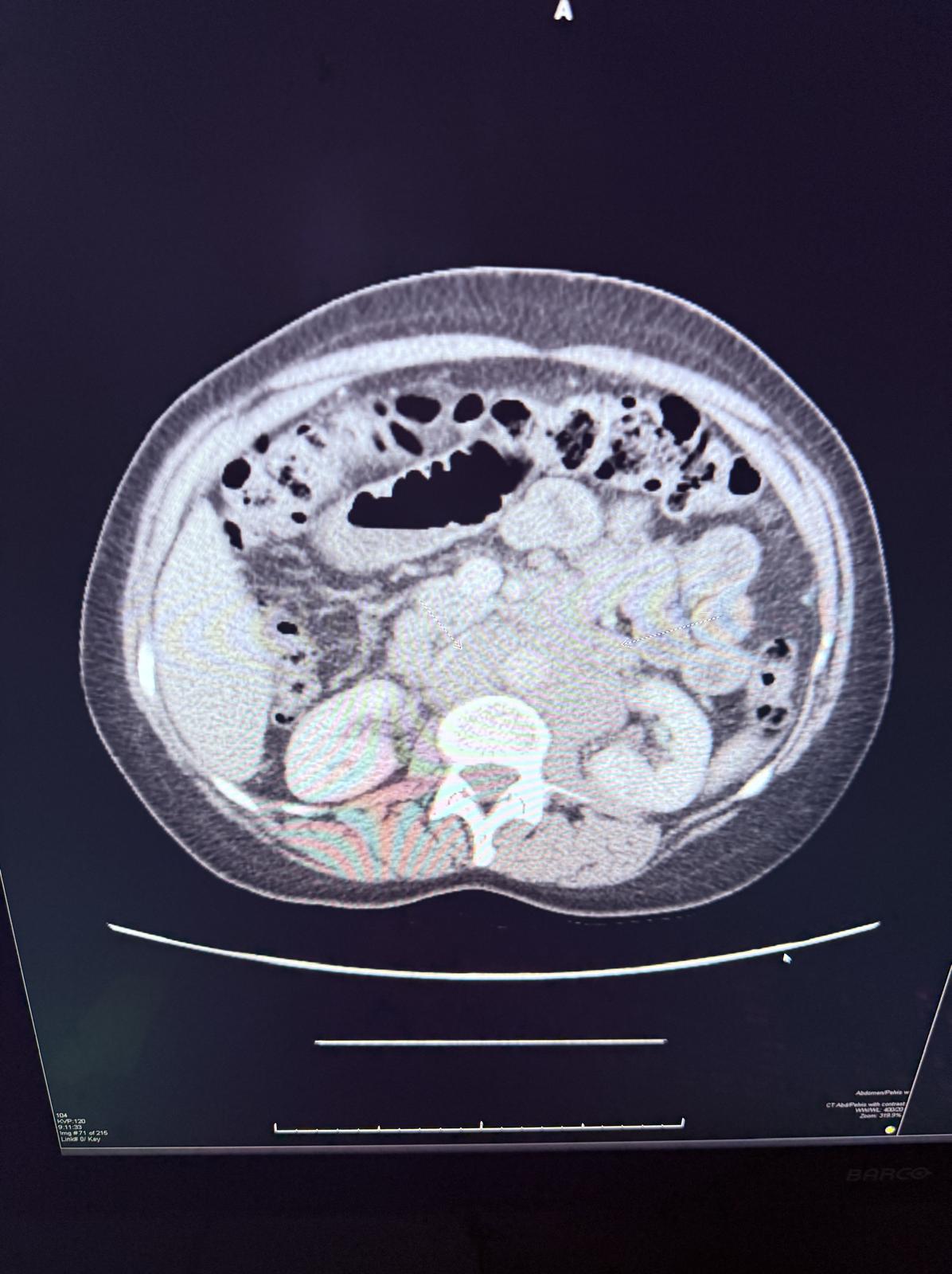
Figure: Figure 2
Disclosures:
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeevin Singh Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marquise Soto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Imam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy, MD1, Jeevin Singh Sandhu, DO2, Marquise Soto, MD3, Mohamad Imam, MD1. P2015 - From Indolent to Obstructive: A Rare Gastrointestinal Manifestation of Follicular Lymphoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UAB Montgomery, Montgomery, AL; 2Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 3Massachusetts General Hospital, Chelsea, MA
Introduction: Follicular lymphoma(FL) is the second most prevalent subtype of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, accounting for around 20% of all cases. It is classified as an indolent, slow-growing form of lymphoma. Most patients initially present with painless peripheral lymphadenopathy, commonly in the cervical, axillary, or inguinal regions and B symptoms. Primary extra nodal involvement by follicular lymphoma remains rare. In particular, gastrointestinal involvement with small bowel obstruction (SBO) as the first clinical manifestation of follicular lymphoma is considered exceptionally rare.
Case Description/
Methods: A 61-year-old female came to the emergency department with complaints of diffuse abdominal pain and nausea for 2 days. She denies vomiting, hematochezia, loose stools, fever, unintentional weight loss and history of abdominal surgery. She never had a colonoscopy. On physical examination, the abdomen was soft, mild diffuse tenderness with no guarding or rigidity. CT abdomen & pelvis showed enhancing mass causing partial obstruction of the distal small bowel and multiple abnormally enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes (Figure 1 & 2). Patient was started on intravenous fluids and kept NPO [nil per oral] with nasogastric tube connected to suction and as needed analgesia. Underwent exploratory laparotomy which showed obstructing circumferential mass in the distal ileum and another circumferential partially obstructing mass in the jejunum and proximal ileum requiring resection of jejunum totaling 10cm, proximal ileum totaling 15 cm, distal ileum totaling 45 cm. Pathology showed grade 3A follicular lymphoma with lymphomatous infiltration present at the small intestine resection margins. Patients diet was slowly advanced post operatively and was discharged with oncology outpatient follow up.
Discussion: SBO is usually caused by post-surgical adhesions, complicated hernia, IBD and neoplasm. When symptoms and imaging findings indicate a potential malignancy, surgical removal followed by histological examination is essential. Cases can also be diagnosed using double balloon enteroscopy (DBE), spiral enteroscopy (SE) and video capsule endoscopy (VCE). Management of FL is determined by the stage, grade and disease burden whereas the relapses are common. Radiotherapy and chemo immunotherapy are the preferred treatment modalities. Follicular lymphoma of the small bowel should be included in the differential diagnosis of small bowel obstruction, particularly in patients without a history of prior abdominal surgery.

Figure: Figure 1

Figure: Figure 2
Disclosures:
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeevin Singh Sandhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marquise Soto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad Imam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Charitha Karanam Ramapathy, MD1, Jeevin Singh Sandhu, DO2, Marquise Soto, MD3, Mohamad Imam, MD1. P2015 - From Indolent to Obstructive: A Rare Gastrointestinal Manifestation of Follicular Lymphoma, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
