Monday Poster Session
Category: Diet, Nutrition, and Obesity
P2693 - Head-to-Head Comparison of Tirzepatide and Semaglutide: A Dose-Stratified Review of 2 Randomized Controlled Trials
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- RT
Rahul Tripathi, MD
Stony Brook Medicine
Stony Brook, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Rahul Tripathi, MD1, Nezar Zeidan, DO1, James Lee, MD2, David Stein, MD1, Lisa Fisher, MD3
1Stony Brook Medicine, Stony Brook, NY; 2Stony Brook University Hospital, Stony Brook, NY; 3Stony Brook University Hospital, Northport, NY
Introduction: Tirzepatide and semaglutide are incretin-based agents with proven weight loss efficacy in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Given their increasing relevance in gastroenterology through effects on metabolic liver disease, GERD, and bariatric management, comparative effectiveness data are needed. We performed a dose-stratified meta-analysis of two randomized controlled trials directly comparing tirzepatide and semaglutide.
Methods: We identified and extracted data from two phase 3 randomized controlled trials: SURPASS-2 (in adults with type 2 diabetes on metformin) and SURMOUNT-5 (in non-diabetic adults with obesity). Tirzepatide (5, 10, or 15 mg weekly) was compared to semaglutide (1.0 mg or 2.4 mg weekly). The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients achieving ≥10% and ≥15% total body weight loss. The secondary outcome was the incidence of adverse gastrointestinal (GI) events. Each tirzepatide dose was compared separately to semaglutide, and risk ratios (RRs) were calculated using a random-effects model.
Results: A total of 1,738 participants from two trials were included (multiple control arm comparisons). Tirzepatide significantly increased the likelihood of achieving ≥10% weight loss compared to semaglutide (RR = 1.72; 95% CI, 1.22–2.43; p < 0.001). Tirzepatide was also superior for achieving ≥15% weight loss (RR = 3.40; 95% CI, 1.75–6.62; p < 0.001). No significant difference was observed in the incidence of GI adverse events between the two agents (RR = 1.06; 95% CI, 0.85–1.31; p = 0.57).
Discussion: In this review of two high-quality randomized trials, tirzepatide was significantly more effective than semaglutide for achieving clinically meaningful weight loss, without an increased risk of GI adverse events. These findings highlight tirzepatide as a promising option in obesity management relevant to gastrointestinal care. Additional high-quality studies are required to gain a clearer understanding of their long-term effects.
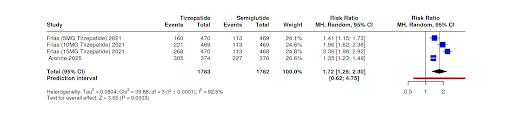
Figure: Comparison of Tirzepatide to Semaglutide in regards to 10% weight loss
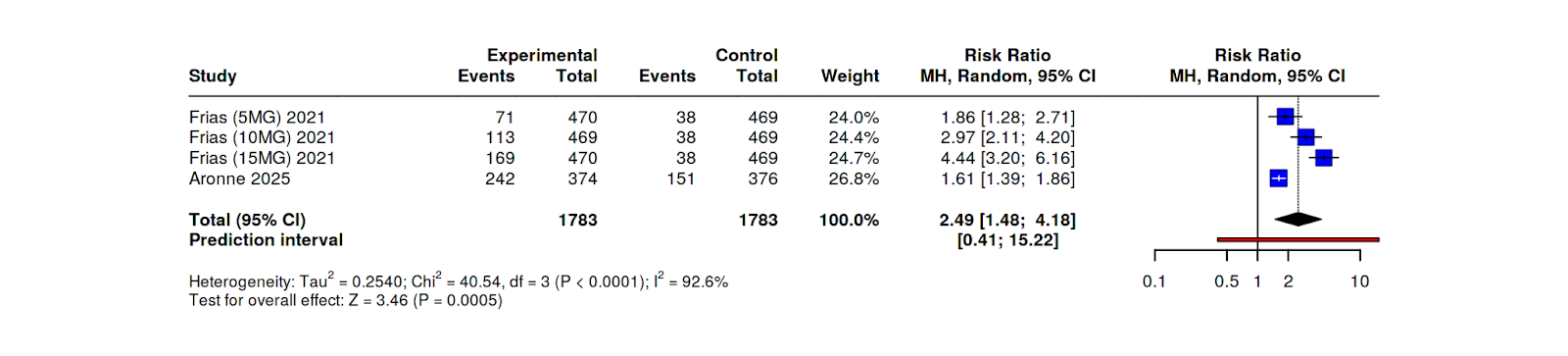
Figure: Comparison of Tirzepatide to Semaglutide in regards to 15% weight loss
Disclosures:
Rahul Tripathi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nezar Zeidan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
James Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Stein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisa Fisher indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Tripathi, MD1, Nezar Zeidan, DO1, James Lee, MD2, David Stein, MD1, Lisa Fisher, MD3. P2693 - Head-to-Head Comparison of Tirzepatide and Semaglutide: A Dose-Stratified Review of 2 Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Rahul Tripathi, MD1, Nezar Zeidan, DO1, James Lee, MD2, David Stein, MD1, Lisa Fisher, MD3
1Stony Brook Medicine, Stony Brook, NY; 2Stony Brook University Hospital, Stony Brook, NY; 3Stony Brook University Hospital, Northport, NY
Introduction: Tirzepatide and semaglutide are incretin-based agents with proven weight loss efficacy in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Given their increasing relevance in gastroenterology through effects on metabolic liver disease, GERD, and bariatric management, comparative effectiveness data are needed. We performed a dose-stratified meta-analysis of two randomized controlled trials directly comparing tirzepatide and semaglutide.
Methods: We identified and extracted data from two phase 3 randomized controlled trials: SURPASS-2 (in adults with type 2 diabetes on metformin) and SURMOUNT-5 (in non-diabetic adults with obesity). Tirzepatide (5, 10, or 15 mg weekly) was compared to semaglutide (1.0 mg or 2.4 mg weekly). The primary outcomes were the proportion of patients achieving ≥10% and ≥15% total body weight loss. The secondary outcome was the incidence of adverse gastrointestinal (GI) events. Each tirzepatide dose was compared separately to semaglutide, and risk ratios (RRs) were calculated using a random-effects model.
Results: A total of 1,738 participants from two trials were included (multiple control arm comparisons). Tirzepatide significantly increased the likelihood of achieving ≥10% weight loss compared to semaglutide (RR = 1.72; 95% CI, 1.22–2.43; p < 0.001). Tirzepatide was also superior for achieving ≥15% weight loss (RR = 3.40; 95% CI, 1.75–6.62; p < 0.001). No significant difference was observed in the incidence of GI adverse events between the two agents (RR = 1.06; 95% CI, 0.85–1.31; p = 0.57).
Discussion: In this review of two high-quality randomized trials, tirzepatide was significantly more effective than semaglutide for achieving clinically meaningful weight loss, without an increased risk of GI adverse events. These findings highlight tirzepatide as a promising option in obesity management relevant to gastrointestinal care. Additional high-quality studies are required to gain a clearer understanding of their long-term effects.

Figure: Comparison of Tirzepatide to Semaglutide in regards to 10% weight loss

Figure: Comparison of Tirzepatide to Semaglutide in regards to 15% weight loss
Disclosures:
Rahul Tripathi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nezar Zeidan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
James Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Stein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lisa Fisher indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Tripathi, MD1, Nezar Zeidan, DO1, James Lee, MD2, David Stein, MD1, Lisa Fisher, MD3. P2693 - Head-to-Head Comparison of Tirzepatide and Semaglutide: A Dose-Stratified Review of 2 Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

