Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2774 - Impact of Patient and Disease Characteristics on the Effectiveness of Vonoprazan in Chinese Patients With Reflux Esophagitis: Post-Hoc Analysis of the Multicenter Prospective VIEW Study
Monday, October 27, 2025
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PDT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- FZ
Fang Zhou, MSc
Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Shanghai, China
Shanghai, Shanghai, China
Presenting Author(s)
Award: ACG Presidential Poster Award
Yinglian Xiao, MD, PhD1, XiaoBin Sun, MD, PhD2, Kailun Liang, MSc3, Fang Zhou, MSc4, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD1
1The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 2The Third People’s Hospital of Chengdu, Chengdu, China, Chengdu, Sichuan, China; 3China Medical Team, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, Shanghai, China; 4Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
Introduction: Vonoprazan, a potassium-competitive acid blocker, is approved in China as a first-line treatment for reflux esophagitis (RE). The impact of patient and disease characteristics on vonoprazan treatment outcomes is unclear. This post hoc analysis of the VIEW study evaluated its effectiveness in real-world settings in Chinese patients.
Methods: VIEW (NCT04501627) was a multicenter, single-arm, noninterventional observational study. All enrolled patients (aged ≥18 years) received standard vonoprazan treatment (20 mg) for 4 weeks (8 weeks if insufficient benefit). This post hoc analysis of patients with RE assessed changes in the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GERDQ) frequency score for heartburn and regurgitation, sleep disturbances, and additional medication use (such as TUMS, Rolaids, Maalox) from baseline to week 4, for all patients and by age group (< or ≥65 years), RE severity (mild/severe), and hiatal hernia size (< or ≥2 cm).
Results: Among the 1877 patients included in the RE safety analysis population, mean (SD) age was 49.7 (13.4) years and body mass index (SD) was 24.1 (3.5) kg/m2; 64.4% were male. The mean (SD) heartburn frequency score decreased from 1.3 (1.20) at baseline to 0.5 (0.84) at week 4 (mean change: −0.8; 95% CI: −0.90, −0.78); the regurgitation frequency score decreased from 1.4 (1.16) at baseline to 0.6 (0.91) at week 4 (mean change: −0.8; 95% CI: −0.83, −0.71); difficulty getting good night’s sleep due to heartburn/regurgitation decreased from 0.9 (1.09) at baseline to 0.3 (0.70) at week 4 (mean change: −0.6; 95% CI: −0.61, −0.50); and the frequency of taking additional medication for heartburn/regurgitation decreased from 0.5 (0.96) at baseline to 0.1 (0.54) at week 4 (mean change: −0.3; 95% CI: −0.38, −0.28) (Table 1). Improvements in symptom frequencies persisted across the subgroup categories by age, RE severity, and hiatal hernia size. Improvement in additional medication use was numerically greater in patients with mild vs severe RE, and similar in ≥65- vs < 65-year-olds. However, for all other symptoms, a trend of numerically higher improvement was observed among the elderly (vs those < 65 years) and those with severe (vs mild) RE and larger (≥2 cm) hiatal hernia size (vs < 2 cm).
Discussion: This subgroup analysis demonstrated that vonoprazan effectively provided symptom relief and improved sleep quality in patients with RE irrespective of age group, RE severity, and hiatal hernia size.
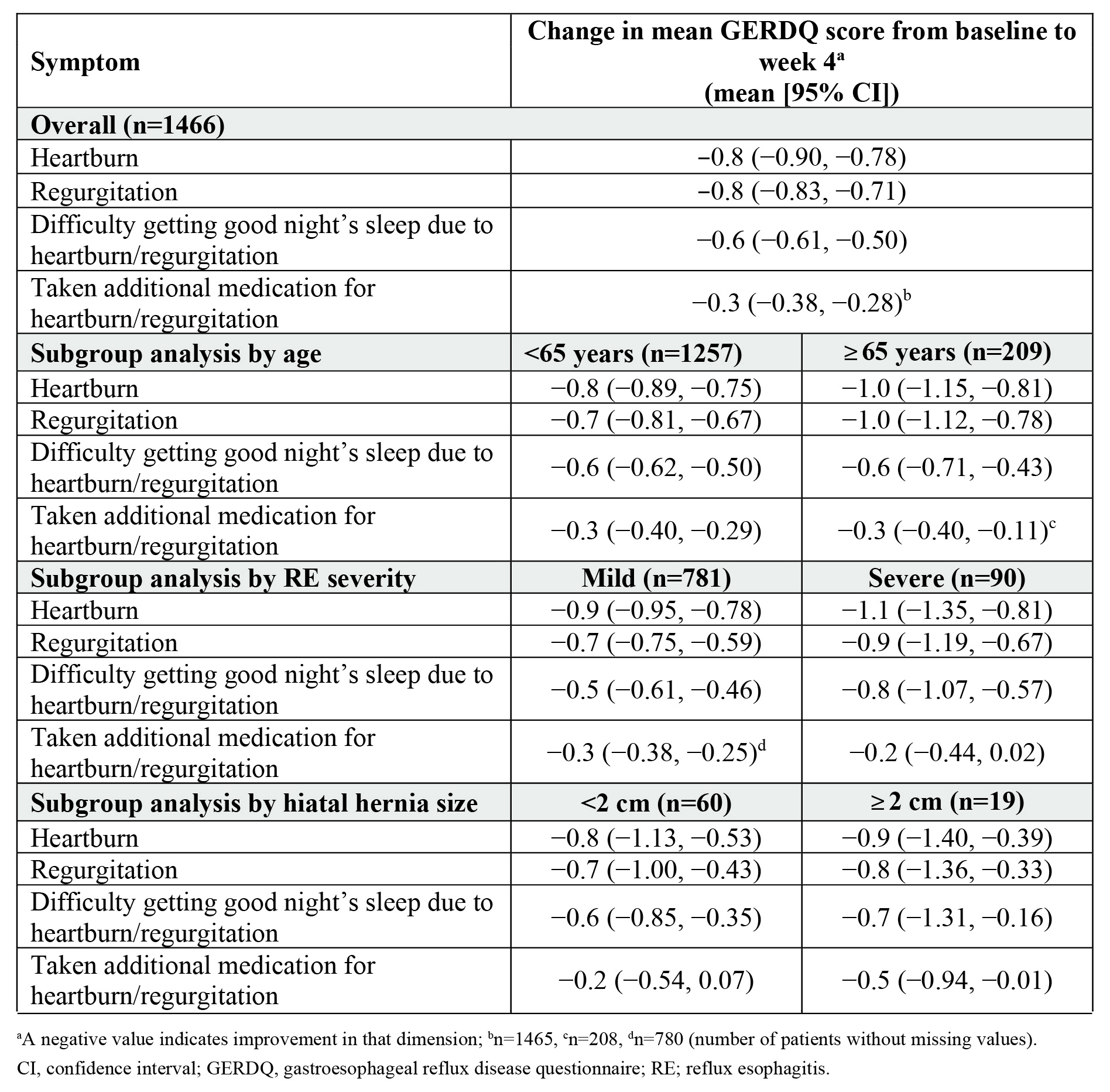
Figure: Table 1. Mean change in GERDQ scores overall and based on age, RE severity, and hiatal hernia size of patients with RE from baseline to week 4
Disclosures:
Yinglian Xiao: Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Grant/Research Support.
XiaoBin Sun: Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Grant/Research Support.
Kailun Liang: Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Employee, Stock Options.
Fang Zhou: Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Employee, Stock Options.
Minhu Chen: AstraZeneca China – Speaker honoraria. Eisai China – Speaker honoraria. Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Grant/Research Support, Royalties. Xian Janssen – Speaker honoraria.
Yinglian Xiao, MD, PhD1, XiaoBin Sun, MD, PhD2, Kailun Liang, MSc3, Fang Zhou, MSc4, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD1. P2774 - Impact of Patient and Disease Characteristics on the Effectiveness of Vonoprazan in Chinese Patients With Reflux Esophagitis: Post-Hoc Analysis of the Multicenter Prospective VIEW Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.
Yinglian Xiao, MD, PhD1, XiaoBin Sun, MD, PhD2, Kailun Liang, MSc3, Fang Zhou, MSc4, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD1
1The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 2The Third People’s Hospital of Chengdu, Chengdu, China, Chengdu, Sichuan, China; 3China Medical Team, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, Shanghai, China; 4Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, Shanghai, China
Introduction: Vonoprazan, a potassium-competitive acid blocker, is approved in China as a first-line treatment for reflux esophagitis (RE). The impact of patient and disease characteristics on vonoprazan treatment outcomes is unclear. This post hoc analysis of the VIEW study evaluated its effectiveness in real-world settings in Chinese patients.
Methods: VIEW (NCT04501627) was a multicenter, single-arm, noninterventional observational study. All enrolled patients (aged ≥18 years) received standard vonoprazan treatment (20 mg) for 4 weeks (8 weeks if insufficient benefit). This post hoc analysis of patients with RE assessed changes in the gastroesophageal reflux disease questionnaire (GERDQ) frequency score for heartburn and regurgitation, sleep disturbances, and additional medication use (such as TUMS, Rolaids, Maalox) from baseline to week 4, for all patients and by age group (< or ≥65 years), RE severity (mild/severe), and hiatal hernia size (< or ≥2 cm).
Results: Among the 1877 patients included in the RE safety analysis population, mean (SD) age was 49.7 (13.4) years and body mass index (SD) was 24.1 (3.5) kg/m2; 64.4% were male. The mean (SD) heartburn frequency score decreased from 1.3 (1.20) at baseline to 0.5 (0.84) at week 4 (mean change: −0.8; 95% CI: −0.90, −0.78); the regurgitation frequency score decreased from 1.4 (1.16) at baseline to 0.6 (0.91) at week 4 (mean change: −0.8; 95% CI: −0.83, −0.71); difficulty getting good night’s sleep due to heartburn/regurgitation decreased from 0.9 (1.09) at baseline to 0.3 (0.70) at week 4 (mean change: −0.6; 95% CI: −0.61, −0.50); and the frequency of taking additional medication for heartburn/regurgitation decreased from 0.5 (0.96) at baseline to 0.1 (0.54) at week 4 (mean change: −0.3; 95% CI: −0.38, −0.28) (Table 1). Improvements in symptom frequencies persisted across the subgroup categories by age, RE severity, and hiatal hernia size. Improvement in additional medication use was numerically greater in patients with mild vs severe RE, and similar in ≥65- vs < 65-year-olds. However, for all other symptoms, a trend of numerically higher improvement was observed among the elderly (vs those < 65 years) and those with severe (vs mild) RE and larger (≥2 cm) hiatal hernia size (vs < 2 cm).
Discussion: This subgroup analysis demonstrated that vonoprazan effectively provided symptom relief and improved sleep quality in patients with RE irrespective of age group, RE severity, and hiatal hernia size.

Figure: Table 1. Mean change in GERDQ scores overall and based on age, RE severity, and hiatal hernia size of patients with RE from baseline to week 4
Disclosures:
Yinglian Xiao: Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Grant/Research Support.
XiaoBin Sun: Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Grant/Research Support.
Kailun Liang: Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Employee, Stock Options.
Fang Zhou: Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Employee, Stock Options.
Minhu Chen: AstraZeneca China – Speaker honoraria. Eisai China – Speaker honoraria. Takeda (China) International Trading Co. Ltd – Grant/Research Support, Royalties. Xian Janssen – Speaker honoraria.
Yinglian Xiao, MD, PhD1, XiaoBin Sun, MD, PhD2, Kailun Liang, MSc3, Fang Zhou, MSc4, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD1. P2774 - Impact of Patient and Disease Characteristics on the Effectiveness of Vonoprazan in Chinese Patients With Reflux Esophagitis: Post-Hoc Analysis of the Multicenter Prospective VIEW Study, ACG 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Phoenix, AZ: American College of Gastroenterology.

